(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The size of an individual snack piece not only influences how fast a person eats it, but also how much of it they eat, according to a new study led by researchers at Penn State. With nearly a quarter of daily calorie intake in the United States coming from snacks, these findings may have implications for helping people better understand how eating behavior impacts calorie and sodium intake.
The team of food scientists investigated how the size of pretzels influences eating behavior — overall intake, eating rate, bite size and snacking duration — and found that people eat larger pretzels quicker with larger bites. They also found that while people ate smaller pretzels slower and with smaller bites, and ate less overall, they still had higher intake of sodium. Their results are available online now and will be published in the June issue of Appetite.
Seventy-five adults participated in the study, eating snacks three different times in the Sensory Evaluation Center. The oversized snack was about 2.5 servings of one of three sizes of pretzel — small, medium or large. To calculate eating rate and bite size, the researchers video recorded each snacking session, noting how many minutes each participant spent snacking and the number of bites. They also measured how much each participant ate in both weight and calories.
When participants were given the same amount of food, how much they ate — in both snack weight and calories — depended on unit size, with study participants consuming 31% and 22% more of the large pretzels compared to the small and medium sized pretzels, respectively. Size of the pretzel also influenced eating rate and bite size, with the largest pretzel size yielding the fastest eating rate and largest mean bite size.
The researchers also reported that, after accounting for eating behavior, the pretzel size alone did not significantly affect how much a person ate, suggesting the eating behavior the different pretzel sizes prompted was driving total intake. Their results suggest larger pretzel size induces a person to eat more quickly and take bigger bites.
Together, these findings indicate that unit size influences intake by affecting eating behavior and they show that food characteristics such as unit size can be leveraged to moderate snack intake, explained corresponding author John Hayes, professor of food science and director of the Penn State Sensory Evaluation Center.
“The study suggests that food structure — texture, size and shape — can be used to modulate eating behavior and food intake,” he said. “Food geometry, specifically unit size, is of particular utility for snack foods. We're interested in how the material properties of foods can be harnessed to help people eat less without impacting their enjoyment.”
The relationship between pretzel size and sodium intake was obvious but previously overlooked, noted Madeline Harper, a graduate student in food science and lead author on the study. She explained that eating more smaller pretzels likely results in higher sodium consumption. The smaller size has more surface area for the same weight, so the researchers hypothesize that more total salt on the surface means that a snacker would consume more sodium eating them.
“So, we're suggesting that if you're trying to watch your calorie intake or are trying to reduce the amount that you're eating in a snack, then maybe a smaller pretzel would meet your needs better, because of the inherent way the size of the pretzel affects your eating rate,” she said. “But if you're more worried about hypertension or the amount of sodium you're consuming, the larger pretzel might be better for you, because you'll consume less sodium in that treatment, even though you might consume more grams of pretzel.”
Paige Cunningham, postdoctoral scholar in the Department of Food Science and the Department of Nutritional Sciences at Penn State, and Ciaran Forde, professor and chair in Sensory Science and Eating Behaviour Group in the Division of Nutrition, at Wageningen University, contributed to the research.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture supported this research.
END
Size of salty snack influences eating behavior that determines amount consumed
Study suggests pretzel size affects intake by governing how quickly a person eats and how big their bites are
2024-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using CO2 and biomass, FAMU-FSU researchers find path to more environmentally friendly recyclable plastics
2024-04-10
Modern life relies on plastic. This lightweight, adaptable product is a cornerstone of packaging, medical equipment, the aerospace and automotive industries and more. But plastic waste remains a problem as it degrades in landfills and pollutes oceans.
FAMU-FSU College of Engineering researchers have created a potential alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastic that is made from carbon dioxide (CO2) and lignin, a component of wood that is a low-cost byproduct of paper manufacturing and biofuel production. Their research was published in Advanced Functional Materials.
“Our study takes the harmful greenhouse gas CO2 ...
Geraniol attenuates oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in mouse aging model
2024-04-10
“Our data demonstrated, for the first time, the antioxidant activity of geraniol and its function to attenuate brain hippocampus injury induced in vivo by D-galactose.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 10, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 6, entitled, “Geraniol attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation-mediated cognitive impairment in D galactose-induced mouse aging model.”
D-galactose (D-gal) administration was proven to induce cognitive impairment and aging in rodents’ models. Geraniol ...
Experiencing racial discrimination impacts the mental health of teens in the U.S. justice system
2024-04-10
DALLAS (SMU) – A new study by SMU psychologists shows interpersonal racial discrimination and other forms of violence can impact the mental health of adolescents in the justice system.
The research advocates for a more holistic approach to mental health intervention, emphasizing the importance of considering adolescents' experiences of interpersonal racial discrimination alongside other more recognized forms of violence. By acknowledging and addressing these intersecting factors, stakeholders can better tailor support systems to meet ...
New 3D-printing method makes printing objects more affordable and eco-friendly
2024-04-10
University of Florida engineers have developed a method for 3D printing called vapor-induced phase-separation 3D printing, or VIPS-3DP, to create single-material as well as multi-material objects. The discovery has the potential to advance the world of additive manufacturing.
Yong Huang, Ph. D., a professor in UF’s department of mechanical and aerospace engineering, said the printing process he and colleagues developed allows manufacturers to create custom-made objects economically and sustainably. The novel approach was reported Tuesday in the journal Nature Communications.
“It is more economical and much simpler than current ...
Exploring the role of MIA-602 in overcoming Doxorubicin-resistance in acute myeloid leukemia
2024-04-10
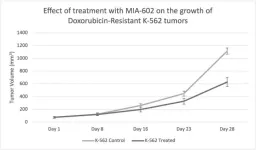
“Our results reveal that MIA-602 may be a useful treatment for Doxorubicin-resistant AML [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- April 10, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on April 8, 2024, entitled, “Exploring the role of GHRH antagonist MIA-602 in overcoming Doxorubicin-resistance in acute myeloid leukemia.”
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is characterized by the rapid proliferation of mutagenic hematopoietic progenitors in the bone marrow. Conventional therapies include chemotherapy and bone marrow stem cell transplantation; however, they are often associated with poor prognosis. Notably, growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) ...
More than half a million global stroke deaths may be tied to climate change
2024-04-10
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, APRIL 10, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A changing climate may be linked to growing death and disability from stroke in regions around the world, according to a study published in the April 10, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Researchers found over three decades that non-optimal temperatures, those above or below temperatures associated with the lowest death rates, were increasingly linked to death and disability due to stroke. The study does not prove that climate change causes ...
Nearly half of B2B startups choose not to market themselves, researchers find
2024-04-10
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Marketing is one of the most effective ways for an early-stage business-to-business (B2B) startup firm to grow, yet nearly half of such firms that would benefit from it choose not to do any marketing, according to the findings of a paper co-authored by a Smeal College of Business professor and published in the journal Industrial Marketing Management.
The researchers focused on systematic marketing — where a firm has an ongoing process of collecting and using customer data to improve its offerings, communications and distribution programs. They specifically examined which startup firms conduct systematic marketing, what causes them to do so and what ...
U.S. Department of Energy’s INCITE program seeks proposals for 2025 to advance science and engineering at U.S. leadership computing facilities
2024-04-10
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Innovative and Novel Computational Impact on Theory and Experiment (INCITE) program is now accepting proposals for high-impact, computationally intensive research projects in a broad array of science, engineering and computer science domains. Proposals must be submitted between April 10 and June 14.
The INCITE program aims to accelerate scientific discoveries and technological innovations by awarding researchers with substantial allocations of supercomputer time and supporting resources at the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility (ALCF) and the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF). The ALCF and OLCF are DOE Office ...
Organizations need to beware whispering death from “institutional parasites”, study finds
2024-04-10
Organisations that fail to identify or swiftly expel “institutional parasites” risk long-term damage, academics from leading British and Finnish business schools have warned.
In a paper published in the respected Academy of Management Review, they argue that the increasingly complex and opaque nature of many organisations provides fertile ground for institutional parasites – such as suppliers or other key external partners and employees.
Dr Jukka Rintamäki from Finland’s Aalto University School of Business, Dr Simon Parker from Nottingham University Business School and Professor Andre Spicer, Professor ...
New book helps citizen scientists navigate complexities of infectious disease outbreaks
2024-04-10
WASHINGTON (April 10, 2024) — Citizen scientists have long contributed to the collection and observation of natural events - from weather watchers to wildlife trackers – with thousands of organized community projects spanning decades. Beginning in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic gave rise to an explosion of novice infectious disease detectives adding to the collection of science-enthusiasts.
To give these new disease detectives more tools for their craft, a new book written by two Georgetown University global health researchers, “Outbreak ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
[Press-News.org] Size of salty snack influences eating behavior that determines amount consumedStudy suggests pretzel size affects intake by governing how quickly a person eats and how big their bites are