To date, most network security architectures have used perimeter-based defense to isolate internal networks from external networks. Firewalls, virtual private networks (VPN), and demilitarized zone (DMZ) networks prevent external attacks by creating a network security perimeter. This can effectively prevent external attacks, but it is difficult to prevent internal attacks because once an intruder breaches the security perimeter, further illegal actions will not be hindered. In addition, with the rapid development of digital technologies such as 5G, the internet of things and cloud computing, the number of network users and devices and their security concerns are growing exponentially, as the perimeter of the network is becoming increasingly blurred. This makes it more difficult to protect organizational resources, especially as more data access points, information inputs and outputs are created. Therefore, preventing internal attacks requires a security architecture that does not trust any network.
Zero trust architecture (ZTA) is a new concept of network security architecture based on the principle of least privilege, which aims to solve the above problems by restricting the behavior of subjects inside the network. Based on the core idea of “never trust, always verify”, ZTA follows a resource-based security policy: no users, devices, or applications (services) can access the data without authentication and authorization. However, while ZTA provides more robust cyber protection measures, it still faces significant implementation challenges. The implementation of ZTA requires multiple security tools (e.g., firewalls) and policies to work together, and traditional stand-alone security detection approaches may not be applicable. In addition, the large amount of data collected and produced by these security tools can be used for risk analysis, prediction, and evaluation within the framework. Thus, to maximize the security protection performance of ZTA, the components of existing frameworks need to be automated and orchestrated. In this context, artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms are considered as one of the most suitable technologies to automate and orchestrate ZTA.
AI technologies are considered as enablers for the security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) solutions designed to automate and integrate different security tasks and processes in response to incidents. SOAR is also one of the functions to be considered in the execution of ZTA, which provides a reference for AI to perform automation and orchestration across components.
Security teams consider ZTA as an enabler to uphold security in their organization′s networks. In particular, ZTA needs to develop capabilities that orchestrate and learn continuously to secure an environment based on hyper-granular access privileges. ZTA automation and orchestration can relieve security personnel from manually assigning and reassigning access credentials throughout the organization′s network. Moreover, permission changes over ZTA should be orchestrated in minutes, eliminating the friction and annoyance of security procedures for employees and devices. The paper published in Machine Intelligence Research by the team of Prof. Gang Li focuses on the potential of AI algorithms in the automation and orchestration for ZTA components.
The main purpose of ZTA is to enhance security. Although enterprises or organizations propose different strategies to understand and implement ZTA depending on their application environments, they are all based on the following three principles: 1) Access control should be resource-centric and context-aware. 2) All users and devices must be authenticated and authorized based on dynamic policies before accessing the resources, following the least privilege policy. 3) Improve security by continuously monitoring the integrity and security of owned or associated assets.
Although a large number of studies on ZTA have been published, there are a few literature reviews on ZTA. Researchers classify the existing review works based on the following five categories: Q1: Details of ZTA principles. Q2: Comparison of security technologies based on perimeter and non-perimeter. Q3: Categorization and revision of ZTA components. Q4: Challenges of ZTA migration, automation, and orchestration. Q5: Future research directions of ZTA.
Existing surveys provide a careful review and analysis of different ZTA theoretical frameworks and application scenarios. However, none of them elaborates on the potential benefits of the automation and orchestration of ZTA using AI techniques. In the wide range of ZTA application scenarios, where ZTA needs to process and analyze huge amounts of data from different sources, researchers have shown increasing interest in AI-driven automation and orchestration, which can provide assistance to ZTA in data classification, authentication and access control. Therefore, researchers’ focus in this survey is to fill the gap by developing a systematic review of AI-focused approaches important for ZTA automation technologies from a technical perspective in conjunction with existing surveys.
The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows: 1) Researchers comprehensively review and compare existing perimetrized-based and deperimetrized-based trust architectures. 2) Researchers provide an in-depth analysis of existing AI technologies for ZTA automation and orchestration. 3) Researchers discuss the challenges of implementing AI-based solutions in ZTA automation and future developments.
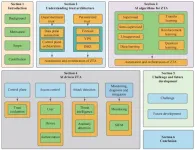
Section 2 provides a fine-grained categorization of the logical components, data sources of ZTA, and discuss the ZTA automation workflow. Researchers also compare the difference between perimetrized and deperimetrized architecture from seven aspects: principle, privilege, boundary, authentication, authorization, access control and security.
In light of the increasing demand for AI technologies in zero-trust, researchers focus on, but are not limited to AI technologies that can be applied to the automation and orchestration of ZTA. There is a figure in Section 3 which shows the categories of ZTA components which can use AI algorithms. Researchers divide ZTA components into four parts: control plane, identity verification, attack detection automation and automated resources monitoring.
ZTA automation and orchestration can be considered as the process of reducing frequent mediation by security personnel via automating the detection and prevention of cyber threats. In Section 4, researchers review the AI approaches for ZTA components to ZTA automation and orchestration. There are two Tables in this part that surveyed the recent AI-based approaches to trust evaluation, authentication, attack detection and system monitoring, respectively.
Section 5 describes limitations and challenges, and points to future research development. Researchers propose challenges from three aspects: harmonization policy, legacy system, and data inconsistency. And they provide suggestions on future development from the angle of human expertise, data quality, secure access service edge (SASE) and fast communication.
This survey provides an insightful analysis of the recent literature on ZTA, revealing gaps in addressing AI in ZTA component automation and orchestration. In addition, this survey has identified trust evaluation, authentication, attack detection, and monitoring as the fundamental classifications that constitute the operation of ZTA component automation. To address the challenges associated with these classifications, an overview of AI-based solutions is provided.
See the article:
Automation and Orchestration of Zero Trust Architecture: Potential Solutions and Challenges
http://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-023-1456-2
END