(Press-News.org) Ancient Egyptians were known for their religious beliefs and astronomical knowledge of the Sun, Moon, and planets, but up until now it has been unclear what role the Milky Way played in Egyptian religion and culture.
A new study by a University of Portsmouth astrophysicist sheds light on the relationship between the Milky Way and the Egyptian sky-goddess Nut.
Nut is goddess of the sky, who is often depicted as a star-studded woman arched over her brother, the earth god Geb. She protects the earth from being flooded by the encroaching waters of the void, and plays a key role in the solar cycle, swallowing the Sun as it sets at dusk and giving birth to it once more as it rises at dawn.
The paper draws on ancient Egyptian texts and simulations to argue that the Milky Way might have shone a spotlight, as it were, on Nut’s role as the sky. It proposes that in winter, the Milky Way highlighted Nut’s outstretched arms, while in summer, it traced her backbone across the heavens.
Associate Professor in Astrophysics, Dr Or Graur, said: “I chanced upon the sky-goddess Nut when I was writing a book on galaxies and looking into the mythology of the Milky Way. I took my daughters to a museum and they were enchanted by this image of an arched woman and kept asking to hear stories about her.
“This sparked my interest and I decided to combine both astronomy and Egyptology to do a double analysis - astronomical and cross-cultural - of the sky-goddess Nut, and whether she really could be linked to the Milky Way.”
Dr Graur drew from a rich collection of ancient sources including the Pyramid Texts, Coffin Texts, and the Book of Nut and compared them alongside sophisticated simulations of the Egyptian night sky.
He found compelling evidence that the Milky Way highlighted Nut’s divine presence.
Furthermore, Dr Graur connected Egyptian beliefs with those of other cultures, showing similarities in how different societies interpret the Milky Way.
He said: “My study also shows that Nut’s role in the transition of the deceased to the afterlife and her connection to the annual bird migration are consistent with how other cultures understand the Milky Way. For example, as a spirits' road among different peoples in North and Central America or as the Birds' Path in Finland and the Baltics.
“My research shows how combining disciplines can offer new insights into ancient beliefs, and it highlights how astronomy connects humanity across cultures, geography, and time. This paper is an exciting start to a larger project to catalogue and study the multicultural mythology of the Milky Way.”
The paper is published in the Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage and has been highlighted in Scientific American.
END
The hidden role of the Milky Way in ancient Egyptian mythology
2024-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Major strides forward: MizzouForward makes new $5 million investment in student success initiatives
2024-04-10
In 2021, the University of Missouri launched MizzouForward, the boldest investment in the university’s 185-year history. The goals of the 10-year, $1.5 billion initiative include:
Enriching students’ educational experiences
Hiring 150 new faculty to Mizzou
Boosting research productivity
Strengthening the state’s economy
Upgrading infrastructure on Mizzou’s campus
One of the earliest investments in MizzouForward involved dedicating more than $4 million to fund 53 student success initiatives, including ...
Size of salty snack influences eating behavior that determines amount consumed
2024-04-10
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The size of an individual snack piece not only influences how fast a person eats it, but also how much of it they eat, according to a new study led by researchers at Penn State. With nearly a quarter of daily calorie intake in the United States coming from snacks, these findings may have implications for helping people better understand how eating behavior impacts calorie and sodium intake.
The team of food scientists investigated how the size of pretzels influences eating behavior — overall intake, eating rate, bite size and snacking duration — and found that people eat larger pretzels ...
Using CO2 and biomass, FAMU-FSU researchers find path to more environmentally friendly recyclable plastics
2024-04-10
Modern life relies on plastic. This lightweight, adaptable product is a cornerstone of packaging, medical equipment, the aerospace and automotive industries and more. But plastic waste remains a problem as it degrades in landfills and pollutes oceans.
FAMU-FSU College of Engineering researchers have created a potential alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastic that is made from carbon dioxide (CO2) and lignin, a component of wood that is a low-cost byproduct of paper manufacturing and biofuel production. Their research was published in Advanced Functional Materials.
“Our study takes the harmful greenhouse gas CO2 ...
Geraniol attenuates oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in mouse aging model
2024-04-10
“Our data demonstrated, for the first time, the antioxidant activity of geraniol and its function to attenuate brain hippocampus injury induced in vivo by D-galactose.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 10, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 6, entitled, “Geraniol attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation-mediated cognitive impairment in D galactose-induced mouse aging model.”
D-galactose (D-gal) administration was proven to induce cognitive impairment and aging in rodents’ models. Geraniol ...
Experiencing racial discrimination impacts the mental health of teens in the U.S. justice system
2024-04-10
DALLAS (SMU) – A new study by SMU psychologists shows interpersonal racial discrimination and other forms of violence can impact the mental health of adolescents in the justice system.
The research advocates for a more holistic approach to mental health intervention, emphasizing the importance of considering adolescents' experiences of interpersonal racial discrimination alongside other more recognized forms of violence. By acknowledging and addressing these intersecting factors, stakeholders can better tailor support systems to meet ...
New 3D-printing method makes printing objects more affordable and eco-friendly
2024-04-10
University of Florida engineers have developed a method for 3D printing called vapor-induced phase-separation 3D printing, or VIPS-3DP, to create single-material as well as multi-material objects. The discovery has the potential to advance the world of additive manufacturing.
Yong Huang, Ph. D., a professor in UF’s department of mechanical and aerospace engineering, said the printing process he and colleagues developed allows manufacturers to create custom-made objects economically and sustainably. The novel approach was reported Tuesday in the journal Nature Communications.
“It is more economical and much simpler than current ...
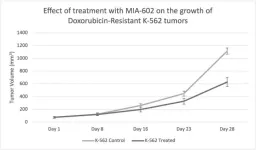
Exploring the role of MIA-602 in overcoming Doxorubicin-resistance in acute myeloid leukemia
2024-04-10
“Our results reveal that MIA-602 may be a useful treatment for Doxorubicin-resistant AML [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- April 10, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on April 8, 2024, entitled, “Exploring the role of GHRH antagonist MIA-602 in overcoming Doxorubicin-resistance in acute myeloid leukemia.”
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is characterized by the rapid proliferation of mutagenic hematopoietic progenitors in the bone marrow. Conventional therapies include chemotherapy and bone marrow stem cell transplantation; however, they are often associated with poor prognosis. Notably, growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) ...
More than half a million global stroke deaths may be tied to climate change
2024-04-10
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, APRIL 10, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A changing climate may be linked to growing death and disability from stroke in regions around the world, according to a study published in the April 10, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Researchers found over three decades that non-optimal temperatures, those above or below temperatures associated with the lowest death rates, were increasingly linked to death and disability due to stroke. The study does not prove that climate change causes ...
Nearly half of B2B startups choose not to market themselves, researchers find
2024-04-10
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Marketing is one of the most effective ways for an early-stage business-to-business (B2B) startup firm to grow, yet nearly half of such firms that would benefit from it choose not to do any marketing, according to the findings of a paper co-authored by a Smeal College of Business professor and published in the journal Industrial Marketing Management.
The researchers focused on systematic marketing — where a firm has an ongoing process of collecting and using customer data to improve its offerings, communications and distribution programs. They specifically examined which startup firms conduct systematic marketing, what causes them to do so and what ...
U.S. Department of Energy’s INCITE program seeks proposals for 2025 to advance science and engineering at U.S. leadership computing facilities
2024-04-10
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Innovative and Novel Computational Impact on Theory and Experiment (INCITE) program is now accepting proposals for high-impact, computationally intensive research projects in a broad array of science, engineering and computer science domains. Proposals must be submitted between April 10 and June 14.
The INCITE program aims to accelerate scientific discoveries and technological innovations by awarding researchers with substantial allocations of supercomputer time and supporting resources at the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility (ALCF) and the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF). The ALCF and OLCF are DOE Office ...