(Press-News.org) The full power of next-generation quantum computing could soon be harnessed by millions of individuals and companies, thanks to a breakthrough by scientists at Oxford University Physics guaranteeing security and privacy. This advance promises to unlock the transformative potential of cloud-based quantum computing and is detailed in a new study published in the influential U.S. scientific journal Physical Review Letters.
Quantum computing is developing rapidly, paving the way for new applications which could transform services in many areas like healthcare and financial services. It works in a fundamentally different way to conventional computing and is potentially far more powerful. However, it currently requires controlled conditions to remain stable and there are concerns around data authenticity and the effectiveness of current security and encryption systems.
Several leading providers of cloud-based services, like Google, Amazon, and IBM, already separately offer some elements of quantum computing. Safeguarding the privacy and security of customer data is a vital precursor to scaling up and expending its use, and for the development of new applications as the technology advances. The new study by researchers at Oxford University Physics addresses these challenges.
“We have shown for the first time that quantum computing in the cloud can be accessed in a scalable, practical way which will also give people complete security and privacy of data, plus the ability to verify its authenticity,” said Professor David Lucas, who co-heads the Oxford University Physics research team and is lead scientist at the UK Quantum Computing and Simulation Hub, led from Oxford University Physics.
In the new study, the researchers use an approach dubbed “blind quantum computing”, which connects two totally separate quantum computing entities – potentially an individual at home or in an office accessing a cloud server – in a completely secure way. Importantly, their new methods could be scaled up to large quantum computations.
“Using blind quantum computing, clients can access remote quantum computers to process confidential data with secret algorithms and even verify the results are correct, without revealing any useful information. Realising this concept is a big step forward in both quantum computing and keeping our information safe online’’ said study lead Dr Peter Drmota, of Oxford University Physics.
The researchers created a system comprising a fibre network link between a quantum computing server and a simple device detecting photons, or particles of light, at an independent computer remotely accessing its cloud services. This allows so-called blind quantum computing over a network. Every computation incurs a correction which must be applied to all that follow and needs real-time information to comply with the algorithm. The researchers used a unique combination of quantum memory and photons to achieve this.
“Never in history have the issues surrounding privacy of data and code been more urgently debated than in the present era of cloud computing and artificial intelligence,” said Professor David Lucas. “As quantum computers become more capable, people will seek to use them with complete security and privacy over networks, and our new results mark a step change in capability in this respect.”
The results could ultimately lead to commercial development of devices to plug into laptops, to safeguard data when people are using quantum cloud computing services.
Researchers exploring quantum computing and technologies at Oxford University Physics have access to the state-of-the-art Beecroft laboratory facility, specially constructed to create stable and secure conditions including eliminating vibration.
Funding for the research came from the UK Quantum Computing and Simulation (QCS) Hub, with scientists from the UK National Quantum Computing Centre, the Paris-Sorbonne University, the University of Edinburgh, and the University of Maryland, collaborating on the work.
Read further detail on the study here:
The study ‘Verifiable blind quantum computing with trapped ions and single photons’ has been published in Physical Review Letters: http://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.150604
Images, animation and media pack here are available at: https://www.physics.ox.ac.uk/about-us/media/latest-media-release or via tessa.curtis@physics.ox.ac.uk
Images and video are for editorial use only and must be credited. These must NOT be sold on to third parties. A video summary is available at https://youtu.be/PBZLrmk1c4s
Further information and media interviews/ enquiries:
PR & Media Contact: Tessa Curtis, Department of Physics
E: tessa.curtis@physics.ox.ac.uk
M: +44 7767 654122
NOTES TO EDITORS
About Oxford University Physics
Oxford University Physics is one of the largest physics departments in the world, top-ranked in the UK and among the lead research universities globally in all key areas of physics. Its mission is to apply the transformative power of physics to the foremost scientific problems and educate the next generation of physicists as well as to promote innovation and public engagement with physics.
Oxford University Physics leads ground-breaking scientific research across a wide spectrum of challenges: from quantum computing, quantum materials and quantum matter to space missions and observation; from climate science to the development of next-generation technologies for renewable energy; and from designing experiments to understand the nature of existence to revolutionising medicine and healthcare through biophysics.
Oxford University Physics has spun out 18 companies since launching the University’s first commercial venture in 1959 and works with enterprise across most areas of its leading scientific research.
About Oxford University
Oxford University has been placed number 1 in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings for the eighth year running, and number 3 in the QS World Rankings 2024. At the heart of this success are the twin-pillars of our ground-breaking research and innovation and our distinctive educational offer.
Oxford is world-famous for research and teaching excellence and home to some of the most talented people from across the globe. Our work helps the lives of millions, solving real-world problems through a huge network of partnerships and collaborations. The breadth and interdisciplinary nature of our research alongside our personalised approach to teaching sparks imaginative and inventive insights and solutions.
Through its research commercialisation arm, Oxford University Innovation, Oxford is the highest university patent filer in the UK and is ranked first in the UK for university spinouts, having created more than 300 new companies since 1988. Over a third of these companies have been created in the past five years. The university is a catalyst for prosperity in Oxfordshire and the United Kingdom, contributing £15.7 billion to the UK economy in 2018/19, and supports more than 28,000 full time jobs.
About the Quantum Computing and Simulation (QCS) Hub
The Quantum Computing & Simulation Hub (QCS) is a collaboration of 17 universities, supported by a wide range of commercial and governmental organisations, with the University of Oxford as its lead partner. It is one of four quantum technologies hubs in the UK National Quantum Technologies Programme, a £1 billion dynamic collaboration between industry, academia and government.
END
Breakthrough promises secure quantum computing at home
2024-04-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Discovery brings all-solid-state sodium batteries closer to practical use
2024-04-11
The pursuit of greener energy also requires efficient rechargeable batteries to store that energy. While lithium-ion batteries are currently the most widely used, all-solid-state sodium batteries are attracting attention as sodium is far more plentiful than lithium. This should make sodium batteries less expensive, and solid-state batteries are thought to be safer, but processing issues mean mass production has been difficult.
Osaka Metropolitan University Associate Professor Atsushi Sakuda and Professor Akitoshi Hayashi, both of the Graduate School of Engineering, led a research team in developing ...
Case study of 4-year-old with down syndrome and sleep apnea suggests hypoglossal nerve stimulation can be effective treatment at young ages
2024-04-11
While Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) affects about five percent of the general pediatric population, 80 percent of children with Down syndrome experience OSA. Continual OSA results in poor health, including disruptions to cognitive development and functioning, leading physician-researchers from Mass General Brigham to investigate better methods to treat these patients as early as possible to maximize their health outcomes.
In a new case study published April 11 in Pediatrics, they report on a 4-year-old boy with Down syndrome and OSA who underwent a procedure to implant a hypoglossal nerve stimulation device, and experienced improvements thereafter. ...
Transmission risk of multidrug-resistant bacteria appears highest in hospital sinks
2024-04-11
Arlington, Va. — April 11, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) reports the infection prevention steps taken to control a months-long multispecies outbreak of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales that occurred in a pediatric ward at the Toho University Omori Medical Center in Tokyo in 2017. This study highlights the particular vulnerability for contamination through sinks and other water sources; indeed, even replacing all sinks in the ward did not stop this outbreak.
Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPE) are a major public health threat ...
Colorless, odorless gas likely linked to alarming rise in non-smoking lung cancer
2024-04-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Although lung cancer is traditionally thought of as a “smoker’s disease,” a surprising 15-20% of newly diagnosed lung cancers occur in people who have never smoked, many of whom are in their 40s or 50s.
Doctors say this concerning rise in non-smoking lung cancer cases is likely linked to long-term, high exposures of radon gas. This colorless, odorless gas is emitted from the breakdown of radioactive material naturally occurring underground that then seeps through building foundations. The gas can linger and ...
How is green and sustainable agriculture evolving in youngest province of China?
2024-04-11
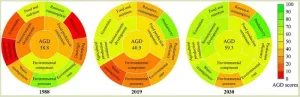
With the increasing environmental and resource problems associated with agriculture, the promotion of sustainable agricultural development has been recommended in many areas of China and also beyond its borders. As a contribution to achieving sustainable development goals, the Chinese government first proposed green development in 2015 and implemented the agriculture green development (AGD) program in 2017 to address a range of issues related to the future development of agriculture in China and the well-being ...
Automation and orchestration of zero trust architecture: Potential solutions and challenges
2024-04-11
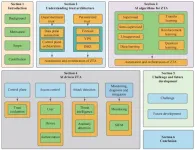
To date, most network security architectures have used perimeter-based defense to isolate internal networks from external networks. Firewalls, virtual private networks (VPN), and demilitarized zone (DMZ) networks prevent external attacks by creating a network security perimeter. This can effectively prevent external attacks, but it is difficult to prevent internal attacks because once an intruder breaches the security perimeter, further illegal actions will not be hindered. In addition, with the rapid development of digital technologies such as 5G, the ...
The RUBY reporter for visual selection in soybean genome editing
2024-04-11
This study is led by Professor Wensheng Hou (Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China). The authors engineered a novel expression vector designed to facilitate gene editing and enable visual confirmation of successful modifications. To achieve this, the authors used RUBY reporter which harnessed the ability to convert tyrosine into a vivid red betalain pigment. This breakthrough allowed to visually confirm gene expression in soybean plants without the need for specialized equipment.
By utilizing this innovative color-based screening system, the authors could quickly assess whether genetic modifications ...
Pacific cities much older than previously thought
2024-04-11
New evidence of one of the first cities in the Pacific shows they were established much earlier than previously thought, according to new research from The Australian National University (ANU).
The study used aerial laser scanning to map archaeological sites on the island of Tongatapu in Tonga.
Lead author, PhD scholar Phillip Parton, said the new timeline also indicates that urbanisation in the Pacific was an indigenous innovation that developed before Western influence.
“Earth structures were being constructed in Tongatapu around AD 300. This is 700 years earlier than previously thought,” ...
Scientists create octopus survival guide to minimize impacts of fishing
2024-04-11
Octopuses have been around for hundreds of millions of years, but did you know that most only live for a few years, dying soon after mating or laying eggs?
Until now that hasn’t been a problem, but octopus catches have doubled in recent decades as the world strives to meet the nutritional demands of a rising global population.
How do we ensure octopus fisheries remain sustainable, protecting the longevity of this ancient animal while guaranteeing the world doesn’t go hungry?
An accurate, reliable, cost effective and easy-to-use method to determine an octopus’s ...
Esketamine injection just after childbirth reduces depression in new mothers
2024-04-11
A single low dose injection of esketamine given immediately after childbirth reduces major depressive episodes in individuals with depressive symptoms during pregnancy (prenatal depression), finds a clinical trial published by The BMJ today.
The results suggest that low dose esketamine should be considered in new mothers with prenatal depressive symptoms.
Depression is common during pregnancy and shortly after giving birth and can have several adverse effects on new mothers and their infants.
Esketamine ...