(Press-News.org) The microorganisms in the intestines of many overweight people produce alcohol to an increased extent, as Max Nieuwdorp, professor of Internal Medicine at Amsterdam UMC discovered a few years ago. Breaking down that excessive alcohol leads to fatty liver, which in turn increases the risk of serious diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Nieuwdorp has now received an ERC Advanced grant of 2.5 million euros for a major study into the underlying causes of excessive alcohol production. Ultimately, he hopes to find a way to prevent excess alcohol produced in the intestines, and thus the related diseases.
In 2022, Nieuwdorp and his team published a study in Nature Medicine on alcohol production in the intestines of overweight patients. "Our findings showed that the turnover of sugars in the intestines of these patients releases far too much alcohol, equivalent to almost half a litre of whisky of alcohol. This is because the composition of the microbiome in their small and large intestines is disrupted. It seems that a change in acidity plays a role in this," Nieuwdorp explains.
Liver has to work hard
For patients, large quantities of alcohol in the intestines can have major consequences. "The liver, as with alcohol from liquor, has to work hard to breakdown the alcohol, and that is done by storing it as fat. This causes people to develop a fatty liver disease that can eventually become inflamed and lead to serious conditions such as cirrhosis of the liver and cardiovascular disease," says Nieuwdorp.
Almost 1 in 5 adults in the Netherlands are overweight and more than 80% of them have fatty liver. Nieuwdorp suspects that the high quantities of sugar in our modern diet can lead to increased alcohol production in the intestines. With the European money from the ERC Advanced grant, he will investigate this further, for example by analysing the medical data and eating patterns of participants in the long-term HELIUS study.
Bacteria in the gut
Nieuwdorp hopes that the discovery of the increased alcohol production due to the disrupted microbiome in the intestines will create a new path in the search for a way to treat fatty liver disease and liver inflammation. For example, he wants to see if it is possible to control alcohol production in the intestines by equipping bacteria in the intestine with properties that allow them to breakdown more alcohol. "But whether and how that actually works is still unknown. That's what we're going to investigate in this FATGAP-project," Nieuwdorp adds.
ERC Advanced grant
The ERC Advanced grants offer European researchers the opportunity to pursue ambitious, curiosity-driven projects that can lead to important scientific breakthroughs. They are awarded to established, leading researchers with a proven trackrecord of significant research achievements over the past decade.
END
Studying alcohol production in the intestines of overweight patients
ERC Advanced Grant worth 2.5 million euros to search for a way to prevent excess alcohol production in the intestines
2024-04-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Robotically assisted lung transplants are on the horizon
2024-04-11
Embargoed until 8:30 am Thursday, 11 April, 2024 Central European Summer Time (GMT +2)
11 April, 2024, Prague, Czech Republic—While debating the pros and cons of robotically assisted lung transplantation, Albert Jauregui, MD, PhD told attendees at the Annual Meeting and Scientific Sessions of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT), today in Prague that the time for robotic surgery is now.
Although robots are commonly used to assist in surgery, robotically assisted surgery is not routinely used for lung transplants. Approximately 4,600 ...
Breakthrough promises secure quantum computing at home
2024-04-11
The full power of next-generation quantum computing could soon be harnessed by millions of individuals and companies, thanks to a breakthrough by scientists at Oxford University Physics guaranteeing security and privacy. This advance promises to unlock the transformative potential of cloud-based quantum computing and is detailed in a new study published in the influential U.S. scientific journal Physical Review Letters.
Quantum computing is developing rapidly, paving the way for new applications which could transform services in many ...
Discovery brings all-solid-state sodium batteries closer to practical use
2024-04-11
The pursuit of greener energy also requires efficient rechargeable batteries to store that energy. While lithium-ion batteries are currently the most widely used, all-solid-state sodium batteries are attracting attention as sodium is far more plentiful than lithium. This should make sodium batteries less expensive, and solid-state batteries are thought to be safer, but processing issues mean mass production has been difficult.
Osaka Metropolitan University Associate Professor Atsushi Sakuda and Professor Akitoshi Hayashi, both of the Graduate School of Engineering, led a research team in developing ...
Case study of 4-year-old with down syndrome and sleep apnea suggests hypoglossal nerve stimulation can be effective treatment at young ages
2024-04-11
While Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) affects about five percent of the general pediatric population, 80 percent of children with Down syndrome experience OSA. Continual OSA results in poor health, including disruptions to cognitive development and functioning, leading physician-researchers from Mass General Brigham to investigate better methods to treat these patients as early as possible to maximize their health outcomes.
In a new case study published April 11 in Pediatrics, they report on a 4-year-old boy with Down syndrome and OSA who underwent a procedure to implant a hypoglossal nerve stimulation device, and experienced improvements thereafter. ...
Transmission risk of multidrug-resistant bacteria appears highest in hospital sinks
2024-04-11
Arlington, Va. — April 11, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) reports the infection prevention steps taken to control a months-long multispecies outbreak of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales that occurred in a pediatric ward at the Toho University Omori Medical Center in Tokyo in 2017. This study highlights the particular vulnerability for contamination through sinks and other water sources; indeed, even replacing all sinks in the ward did not stop this outbreak.
Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPE) are a major public health threat ...
Colorless, odorless gas likely linked to alarming rise in non-smoking lung cancer
2024-04-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Although lung cancer is traditionally thought of as a “smoker’s disease,” a surprising 15-20% of newly diagnosed lung cancers occur in people who have never smoked, many of whom are in their 40s or 50s.
Doctors say this concerning rise in non-smoking lung cancer cases is likely linked to long-term, high exposures of radon gas. This colorless, odorless gas is emitted from the breakdown of radioactive material naturally occurring underground that then seeps through building foundations. The gas can linger and ...
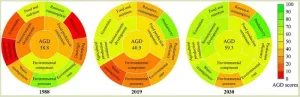
How is green and sustainable agriculture evolving in youngest province of China?
2024-04-11
With the increasing environmental and resource problems associated with agriculture, the promotion of sustainable agricultural development has been recommended in many areas of China and also beyond its borders. As a contribution to achieving sustainable development goals, the Chinese government first proposed green development in 2015 and implemented the agriculture green development (AGD) program in 2017 to address a range of issues related to the future development of agriculture in China and the well-being ...
Automation and orchestration of zero trust architecture: Potential solutions and challenges
2024-04-11
To date, most network security architectures have used perimeter-based defense to isolate internal networks from external networks. Firewalls, virtual private networks (VPN), and demilitarized zone (DMZ) networks prevent external attacks by creating a network security perimeter. This can effectively prevent external attacks, but it is difficult to prevent internal attacks because once an intruder breaches the security perimeter, further illegal actions will not be hindered. In addition, with the rapid development of digital technologies such as 5G, the ...
The RUBY reporter for visual selection in soybean genome editing
2024-04-11
This study is led by Professor Wensheng Hou (Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China). The authors engineered a novel expression vector designed to facilitate gene editing and enable visual confirmation of successful modifications. To achieve this, the authors used RUBY reporter which harnessed the ability to convert tyrosine into a vivid red betalain pigment. This breakthrough allowed to visually confirm gene expression in soybean plants without the need for specialized equipment.
By utilizing this innovative color-based screening system, the authors could quickly assess whether genetic modifications ...
Pacific cities much older than previously thought
2024-04-11
New evidence of one of the first cities in the Pacific shows they were established much earlier than previously thought, according to new research from The Australian National University (ANU).
The study used aerial laser scanning to map archaeological sites on the island of Tongatapu in Tonga.
Lead author, PhD scholar Phillip Parton, said the new timeline also indicates that urbanisation in the Pacific was an indigenous innovation that developed before Western influence.
“Earth structures were being constructed in Tongatapu around AD 300. This is 700 years earlier than previously thought,” ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How can you rescue a “kidnapped” robot? A new AI system helps the robot regain its sense of location in dynamic, ever-changing environments
Brainwaves of mothers and children synchronize when playing together – even in an acquired language
A holiday to better recovery
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
Combining AI with OCT shows potential for detecting lipid-rich plaques in coronary arteries
SeaCast revolutionizes Mediterranean Sea forecasting with AI-powered speed and accuracy
JMIR Publications’ JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology invites submissions on Bridging Data, AI, and Innovation to Transform Health
Honey bees navigate more precisely than previously thought
Air pollution may directly contribute to Alzheimer’s disease
Study finds early imaging after pediatric UTIs may do more harm than good
UC San Diego Health joins national research for maternal-fetal care
New biomarker predicts chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
Treatment algorithms featured in Brain Trauma Foundation’s update of guidelines for care of patients with penetrating traumatic brain injury
Over 40% of musicians experience tinnitus; hearing loss and hyperacusis also significantly elevated
Artificial intelligence predicts colorectal cancer risk in ulcerative colitis patients
[Press-News.org] Studying alcohol production in the intestines of overweight patientsERC Advanced Grant worth 2.5 million euros to search for a way to prevent excess alcohol production in the intestines