(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this study that included 1,470 adults with chronic low back pain, physician empathy was associated with better outcomes over 12 months. Greater efforts to cultivate and improve physician empathy appear warranted.
Authors: John C. Licciardone, D.O., M.S., M.B.A., of the University of North Texas Health Science Center at Fort Worth, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.6026)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.6026?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=041124
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Physician empathy and chronic pain outcomes
JAMA Network Open
2024-04-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tropical coral-infecting parasites discovered in cold marine ecosystems
2024-04-11
Parasites thought only to infect tropical coral reefs have been discovered in a large variety of creatures in cold marine ecosystems along the Northeast Pacific, according to new research from University of British Columbia botanists.
The finding, published today in Current Biology, greatly expands the range of corallicolids, suggesting the parasites infect a range of organisms related to coral, like sea anemones and other cold-water marine invertebrates, around the world.
“This highlights significant blind spots in our strategies designed to sample microbial biodiversity,” says University of British Columbia biodiversity researcher Dr. Patrick Keeling, senior author on the ...
Successful murine model of dermatomyositis reveals underlying immune system involvement
2024-04-11
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have developed a murine model for a highly progressive disease called “anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis”, providing insights into underlying biological mechanisms and aiding treatment
Tokyo, Japan – Some diseases involve autoimmune reactions, when the body begins to attack its own cells and proteins. The biological mechanisms underlying these diseases are often unknown, making treatment challenging. Now, a group at TMDU has created a murine model for a disease ...
Next-gen lab chip transforms cancer detection: triple-threat cell sorting unveiled
2024-04-11
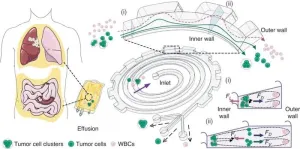
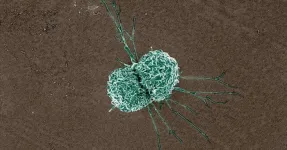
Researchers have unveiled a microfluidic device that significantly improves the separation of tumor cells and clusters from malignant effusions. This novel technology promises to advance the diagnosis and treatment monitoring of cancer by enabling the high-throughput, continuous-flow ternary separation of single tumor cells, tumor cell clusters, and white blood cells (WBCs) from clinical pleural or abdominal effusions.
Understanding the nature of malignant effusions, teeming with tumor cells and clusters, is critical in comprehending the breadth of cancer's impact. The significant role of tumor clusters, with their heightened potential ...
NCCN 2024 Annual Conference shares cancer care updates for practical, immediate use in practice
2024-04-11
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [April 11, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—hosted more than 1,700 oncology professionals during the NCCN 2024 Annual Conference on April 5-7. The yearly meeting includes opportunities for care providers to interact with world-renowned specialists on the latest evidence-based expert consensus recommendations for delivering high quality, patient-centered cancer care. Sessions focused on practical applications for improving care at every level, including clinical and administrative ...
Genetic underpinnings of environmental stress identified in model plant
2024-04-11
Plants can be temperamental. Even weeds along the side of highways or pushing their way up in the cracks of concrete sidewalks can get stressed out by dehydration, cold, excess salt and more. Researchers at Hiroshima University have identified 14 genes that thale cress — a plant commonly used in genetic investigations since its genome is well documented — express more when responding to five specific stressors, as well as eight genes that the plant suppresses.
They published their results on March 22 in Frontiers in Plant Science.
“Abiotic stresses — as opposed to biotic stresses like pests or disease — such as drought, salinity and cold negatively ...
This outdated diabetes drug still has something to offer
2024-04-11
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are a class of drug that can be used to treat type 2 diabetes by reversing insulin resistance, one of the main hallmarks of the disease. While TZDs were extremely popular in the 1990’s and early 2000’s, they have fallen out of use among physicians in recent decades because they were discovered to cause unwanted side effects, including weight gain and excess fluid accumulation in body tissues.
Now, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine are ...
Developing best practices for human-AI collaboration in engineering design
2024-04-11
As artificial intelligence is inevitably woven into the workplace, teams of humans will increasingly collaborate with robots on complex design problems, such as those in the auto, aviation, and space industries.
“Right now, design is mainly done by humans, and it’s based on their expertise and intuitive decision-making, which is learned over time,” says A. Emrah Bayrak, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering and mechanics in Lehigh University’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science. “Usually, ...
Novel CT exam reduces need for invasive artery treatment
2024-04-11
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new study showed that a non-invasive imaging test can help identify patients with coronary artery blockage or narrowing who need a revascularization procedure. The findings were published as a Special Report in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Doctors use coronary CT angiography (CTA) to diagnose narrowed or blocked arteries in the heart. A CTA exam receives a score from mild (0-1) to moderate (2-3) to severe (4-5). Patients ...
ERC Advanced Grant: 2.5 million euros for Tobias Brixner
2024-04-11
Many people are familiar with the principle of electronic excitation from their physics lessons: electrons in atoms or molecules absorb energy, typically from light, and rise to a higher energy level. This can have various consequences – in photovoltaic technology, the phenomenon ensures that electricity can be generated from sunlight.
Measuring electronic excitation according to scientific standards and investigating how excited electrons influence each other is a real challenge: “Electronic excitation and the subsequent processes take place extremely quickly, many things happen simultaneously“, explains Tobias Brixner, Chair of Physical Chemistry ...
Proud seafarers have strong doubts about the safety of autonomous ships
2024-04-11
The maritime profession is among the world’s oldest professions, and today’s shipping is based on long and proud traditions. Professional pride and commitment are often deeply ingrained in seafarers, and for many, the job is more of a way of life. New technologies will bring about major changes in the work of bridge officers, who have the ultimate responsibility on board Norwegian vessels.
Strong doubts about safety
“Bridge officers rely on automated systems that are already found on board, such as advanced autopilot systems. However, there is strong scepticism, almost mistrust, that increased automation and autonomous ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
[Press-News.org] Physician empathy and chronic pain outcomesJAMA Network Open