(Press-News.org) A drug approved to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension may be effective at managing hypertension and end-organ damage in patients with sickle cell disease, according to a new study published in Lancet Haematology. An early phase randomized clinical trial involving 130 patients with sickle cell disease found that the drug, called riociguat, was found to be safe to use and well tolerated in these patients and significantly improved their blood pressure. Preliminary efficacy data suggested the medication might improve heart function.
An estimated 100,000 Americans have sickle cell disease, and the disease occurs in about 1 out of every 365 Black or African-American births, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. People with sickle cell disease are at high risk for vascular complications that can lead to pulmonary hypertension, stroke, and kidney failure as well as severe pain when red blood cells block blood flow through tiny blood vessels in the chest, abdomen, and joints. These complications can be worsened by hypertension.
Unfortunately, previous research found that sildenafil, an effective treatment for pulmonary hypertension, caused unacceptable side effects in patients with sickle cell disease. It found that those who took this drug experienced high levels of pain that caused increased admissions to the hospital compared to those who took a placebo treatment.
This new study was designed to test the safety of riociguat and how well it works in preventing or reducing the clinical complications for patients with sickle cell disease.
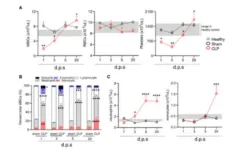
In the study, patients with sickle cell disease and mild hypertension or protein in their urine (an early sign of kidney disease) were randomly assigned to receive either riociguat or a placebo in a double-blind clinical trial. Both groups received the study drug at a starting dose of 1 milligram, which was gradually increased up to 2.5 milligram, taken three times a day for 12 weeks. The researchers found that among the participants who took riociguat, 22.7 percent experienced at least one serious adverse event related to the treatment. In comparison, in the group that received the placebo, 31.3 percent of participants had at least one serious adverse event during the study.
The differences were not statistically significant. There were no differences between the two groups in the rates of pain severity, pain interference in their daily lives, and in vascular events related to their sickle cell disease. When it comes to the effectiveness of the drug treatment, participants who took riociguat had their blood pressure drop by 8.20 mmHg, while those who took a placebo only saw a decrease of about 1.24 mmHg. The result was highly statistically significant, meaning riociguat was much more effective at lowering blood pressure compared to the placebo, with a difference of approximately 6.96 mmHg. In summary, riociguat was found to be safe and led to a significant improvement of blood pressure over the duration of the study.
“Our results are encouraging and open the door to larger clinical trials involving this class of drugs in patients with sickle cell disease who have pulmonary hypertension or kidney disease. Having a drug that’s easy to tolerate can help them better manage their blood pressure and help prevent serious complications down the road,” said study leader Mark T. Gladwin, MD, who is the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean of UMSOM, and Vice President for Medical Affairs at University of Maryland, Baltimore.
Bayer Pharmaceuticals, manufacturer of riociguat, provided funding (as well as the drug and placebo) for the study.
The study was led by the clinical and data coordinating centers at the University of Pittsburgh. Study co-authors included faculty from the University of Illinois at Chicago, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Emory University, Duke University, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and other institutions.
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 46 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs, and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished two-time winner of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1.2 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically based care for nearly 2 million patients each year. The School of Medicine has nearly $600 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total population of nearly 9,000 faculty and staff, including 2,500 students, trainees, residents, and fellows. The combined School of Medicine and Medical System ("University of Maryland Medicine") has an annual budget of over $6 billion and an economic impact of nearly $20 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity (according to the Association of American Medical Colleges profile) is an innovator in translational medicine, with 606 active patents and 52 start-up companies. In the latest U.S. News & World Report ranking of the Best Medical Schools, published in 2021, the UM School of Medicine is ranked #9 among the 92 public medical schools in the U.S., and in the top 15 percent (#27) of all 192 public and private U.S. medical schools. The School of Medicine works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu.
END
UMSOM researchers identify safety of a potential new treatment to manage complications from sickle cell disease
Treatment for lung condition could help patients with sickle cell disease control complications from hypertension and kidney damage
2024-04-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Advancing biodiversity data analysis at B-Cubed’s Hackathon
2024-04-11
B-Cubed’s Hackathon – “Hacking Biodiversity Data Cubes for Policy” – concluded successfully on 5 April in Brussels. The event marked a significant milestone in the use of data cubes for enhancing biodiversity data analysis and policy-making. Over four days, participants from diverse backgrounds collaborated to explore innovative solutions aimed at standardising and improving the accessibility of biodiversity data.
The event began with a foundational presentation on data cubes by Andrew Rodrigues ...
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy increase risk of cardiovascular death after giving birth
2024-04-11
Rutgers Health researchers have found that hypertensive disorders in pregnancy are strongly associated with fatal cardiovascular disease for up to a year after birth.
Among the hypertensive disorders that cause dangerously high blood pressure during pregnancy — chronic hypertension, gestational hypertension, preeclampsia without severe features, preeclampsia with severe features, superimposed preeclampsia and eclampsia — all but gestational diabetes were associated with a doubling in the risk of fatal cardiovascular disease compared to women with normal blood pressure.
Eclampsia, a condition whereby hypertensive ...
Blood stem cells unlock clues for helping sepsis patients fight recurring infections
2024-04-11
Severe sepsis from bacterial or viral infections can be life-threatening and even people recovering from severe sepsis may experience long-lasting effects on the immune system, making them more susceptible to recurrent infections. The causes for this sepsis-induced immune suppression are not well understood and lack an effective treatment. To better understand the cause, Katherine MacNamara and colleagues from Albany Medical College, USA, analyzed the blood stem cells of mice with prior sepsis and their results were recently published in the journal Stem Cell Reports.
During ...
Climate: Increased threat to coastlines from concurrent heatwaves and sea level rises
2024-04-11
Concurrent occurrences of heatwaves and extreme short-term sea level rises at the same coastal locations significantly increased between 1998 and 2017 when compared to the preceding twenty years, reports a study published in Communications Earth & Environment. The study also suggests that these events may be five times more likely to occur between 2025 and 2049 under a modelled high emissions scenario.
A so-called ‘concurrent heatwave and extreme sea level’ (CHWESL) event is when a heatwave and an extreme short-term sea level rise occur at the same coastal location over the same time period. Although they ...
Second primary breast cancer in young breast cancer survivors
2024-04-11
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that young breast cancer survivors without a germline pathogenic variant have a low risk of developing a second primary breast cancer in the first 10 years after diagnosis. Findings from germline genetic testing may inform treatment decision-making and follow-up care considerations in this population.
Authors: Kristen D. Brantley, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Physician empathy and chronic pain outcomes
2024-04-11
About The Study: In this study that included 1,470 adults with chronic low back pain, physician empathy was associated with better outcomes over 12 months. Greater efforts to cultivate and improve physician empathy appear warranted.
Authors: John C. Licciardone, D.O., M.S., M.B.A., of the University of North Texas Health Science Center at Fort Worth, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.6026)
Editor’s ...
Tropical coral-infecting parasites discovered in cold marine ecosystems
2024-04-11
Parasites thought only to infect tropical coral reefs have been discovered in a large variety of creatures in cold marine ecosystems along the Northeast Pacific, according to new research from University of British Columbia botanists.
The finding, published today in Current Biology, greatly expands the range of corallicolids, suggesting the parasites infect a range of organisms related to coral, like sea anemones and other cold-water marine invertebrates, around the world.
“This highlights significant blind spots in our strategies designed to sample microbial biodiversity,” says University of British Columbia biodiversity researcher Dr. Patrick Keeling, senior author on the ...
Successful murine model of dermatomyositis reveals underlying immune system involvement
2024-04-11
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have developed a murine model for a highly progressive disease called “anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis”, providing insights into underlying biological mechanisms and aiding treatment
Tokyo, Japan – Some diseases involve autoimmune reactions, when the body begins to attack its own cells and proteins. The biological mechanisms underlying these diseases are often unknown, making treatment challenging. Now, a group at TMDU has created a murine model for a disease ...
Next-gen lab chip transforms cancer detection: triple-threat cell sorting unveiled
2024-04-11
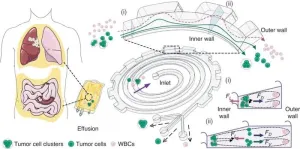
Researchers have unveiled a microfluidic device that significantly improves the separation of tumor cells and clusters from malignant effusions. This novel technology promises to advance the diagnosis and treatment monitoring of cancer by enabling the high-throughput, continuous-flow ternary separation of single tumor cells, tumor cell clusters, and white blood cells (WBCs) from clinical pleural or abdominal effusions.
Understanding the nature of malignant effusions, teeming with tumor cells and clusters, is critical in comprehending the breadth of cancer's impact. The significant role of tumor clusters, with their heightened potential ...
NCCN 2024 Annual Conference shares cancer care updates for practical, immediate use in practice
2024-04-11
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [April 11, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—hosted more than 1,700 oncology professionals during the NCCN 2024 Annual Conference on April 5-7. The yearly meeting includes opportunities for care providers to interact with world-renowned specialists on the latest evidence-based expert consensus recommendations for delivering high quality, patient-centered cancer care. Sessions focused on practical applications for improving care at every level, including clinical and administrative ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] UMSOM researchers identify safety of a potential new treatment to manage complications from sickle cell diseaseTreatment for lung condition could help patients with sickle cell disease control complications from hypertension and kidney damage