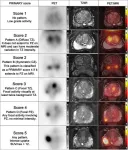
(Press-News.org) Reston, VA—PET/MRI can improve diagnostic accuracy for prostate cancer patients and help avoid unnecessary biopsies, according to new research published in the April issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. By applying the PRIMARY scoring system to PET/MRI results, researchers found that more than 80 percent of unnecessary biopsies could be avoided at the expense of missing one in eight clinically significant prostate cancer cases.
The Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) is a five-point scale used to evaluate suspected prostate cancer on MR images. PI-RADS category 3, which presents an unclear suggestion of clinically significant prostate cancer, remains a diagnostic challenge. Although biopsy is recommended under the current guidelines, less than 20 percent of PI-RADS 3 lesions contain clinically significant prostate cancer.
“PI-RADS 3 lesions present a dilemma to both urologists and patients because immediate biopsy could be unnecessary; however, a monitoring strategy could lead to some missed diagnoses of clinically significant prostate cancer,” stated Hongqian Guo, MD, a urologist at Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital at the Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School in Nanjing, China. “Hence, specifically ruling out clinically significant prostate cancer among PI-RADS 3 lesions has significant clinical implications.”
In this study, 56 men with PI-RADS 3 lesions underwent 68Ga-PSMA PET/MRI. The five-level PRIMARY system, which is based on a combination of 68Ga-PSMA pattern, localization, and intensity information, was used to report prostate 68Ga-PSMA PET/MRI findings. After imaging, all patients underwent prostate systematic biopsy in combination with targeted biopsy to determine clinically significant prostate cancer.
Among the 56 patients, clinically significant prostate cancer was detected in eight patients (14.3 percent) by biopsy. When a PRIMARY score of at least four was used to make a biopsy decision in men with PI-RADS 3 lesions, 40 of 48 (83.3 percent) participants could have avoided unnecessary biopsies, at the expense of missing 1 in 8 (12.5 percent) of clinically significant prostate cancer cases.
“By demonstrating the additive value of 68Ga-PSMA PET/MRI in classifying PI-RADS 3 lesions, this study provides new insight into the clinical indication for 68Ga-PSMA PET/MRI,” noted Guo. “In the future, PI-RADS 3 patients could be referred for 68Ga-PSMA PET/MRI before prostate biopsy.”
This study was published online in March 2024.
The authors of “The Value of 68Ga-PSMA PET/MRI for Classifying Patients with PI-RADS 3 Lesions on Multiparametric MRI: A Prospective Single-Center Study” include Jingyan Shi, Mengxia Chen, Qing Zhang, Jing Liang, Qun Lu, Xuefeng Qiu and Hongqian Guo, Department of Urology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China; Danyan Li and Jiaming Lu, Department of Radiology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China; Yao Fu and Shan Peng, Department of Pathology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China; and Shuyue Ai and Feng Wang, Department of Nuclear Medicine, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
Visit the JNM website for the latest research, and follow our new Twitter and Facebook pages @JournalofNucMed or follow us on LinkedIn.
###
Please visit the SNMMI Media Center for more information about molecular imaging and precision imaging. To schedule an interview with the researchers, please contact Rebecca Maxey at (703) 652-6772 or rmaxey@snmmi.org.
About JNM and the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (JNM) is the world’s leading nuclear medicine, molecular imaging and theranostics journal, accessed more than 16 million times each year by practitioners around the globe, providing them with the information they need to advance this rapidly expanding field. Current and past issues of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine can be found online at http://jnm.snmjournals.org.
JNM is published by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI), an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to advancing nuclear medicine and molecular imaging—precision medicine that allows diagnosis and treatment to be tailored to individual patients in order to achieve the best possible outcomes. For more information, visit www.snmmi.org.
END
The concept of “One Health” – which emphasizes the relationship between human, animal, plant and environmental health – has been gaining ground in scientific discussions in recent years. Brazilian and North American researchers developing research using this approach presented their work on Tuesday (April 9th), in Chicago (United States), during FAPESP Week Illinois.
One of the panelists was Eduardo Esteban Bustamante, a professor at the University of Illinois in Chicago. He talked about behavioral interventions that have been tested to promote physical activity and healthy eating – practices that, according to the researcher, ...
AMHERST, Mass. – A team of computer scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst working on two different problems—how to quickly detect damaged buildings in crisis zones and how to accurately estimate the size of bird flocks—recently announced an AI framework that can do both. The framework, called DISCount, blends the speed and massive data-crunching power of artificial intelligence with the reliability of human analysis to quickly deliver reliable estimates that can quickly pinpoint and count specific features from very large collections ...
PRESS RELEASE
Chicago, IL and Philadelphia, PA, USA, April 11, 2024: The Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) and The GOG Foundation, Inc. (GOG-F) Launch BRIDGES 2.0 Research Initiative with support from the Foundation for Women’s Cancer (FWC). After a successful inaugural year, the SGO and the GOG-F join forces to collaborate, and proudly announce the launch of an expanded two-year clinical trial education program supported by the FWC. This important career and clinical trial development initiative aims to cultivate the next generation of investigators in gynecologic oncology and will focus on clinical and translational research ...
It’s challenging to sustain a pregnancy when food is short, or conditions are otherwise tough. That’s why many mammalian embryos can postpone their growth to get through periods of environmental stress and then re-enter development when conditions improve. This stalling of development is known as embryonic diapause, and understanding the mechanisms behind it might help improve infertility treatments, such as embryo freezing. Now, researchers at the Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Shanghai, China, have discovered how nutrient depletion is sensed by embryos growing in hungry mouse mums to induce diapause. ...
LA JOLLA, CA—Most disease-causing bacteria are known for their speed: In mere minutes, they can double their population, quickly making a person sick. But just as dangerous as this rapid growth can be a bacterium’s resting state, which helps the pathogen evade antibiotics and contributes to severe chronic infections in the lungs and blood, within wounds, and on the surfaces of medical devices.
Now, Scripps Research scientists have discovered how long chains of molecules called polyphosphates (polyP) are needed for bacteria to slow down movements within cells and let them enter this resting ...
SAN ANTONIO, April 10, 2024 – The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) has appointed Anthony Francis, a renowned leader in translating research to market opportunity, as associate vice president for innovation and development in the Office of the Vice President for Research.
He joins the institution from the University of California San Francisco, where he was executive director of the Office of Technology Management and Advancement. Francis is credited with transforming ...
Researchers from the International Blast Injury Research Network at the University of Southampton conducted a survey to understand how the mental health of displaced Ukrainians has been affected by the ongoing war. Their findings, published in PLOS Global Public Health, describe high levels of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and generalized anxiety among both refugees and people displaced within Ukraine.
Since the Russian invasion of Ukraine began in February 2022, at least 13 million people have been displaced from their homes. Both exposure ...
Image-based artificial intelligence spots parasitic worm infections in children's stool samples, particularly light intensity infections that may be missed by manual microscopy.
#####
Article URL: http://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0012041
Article Title: Diagnosis of soil-transmitted helminth infections with digital mobile microscopy and artificial intelligence in a resource-limited setting
Author Countries: Finland, Kenya, Sweden
Funding: This research was financially supported by The Erling-Persson Foundation (grant number 2021 0110) JL, Vetenskapsrådet (grant number 2021-04811) JL, Finska Läkaresällskapet ...
What if changes in a person’s stress levels could be detected while they sleep using wearable devices? A new study by University of Vermont researchers published today in PLOS Digital Health is the first to find changes in perceived stress levels reflected in sleep data—an important step towards identifying biomarkers that may help flag individuals in need of support.
Given how critical sleep is to physical and mental health, the research team suspected signals might exist in sleep data, says Laura Bloomfield, a research assistant professor of mathematics and statistics and lead author of the study. “Changes in stress are visible.”
When parsing baseline sleep ...
When astronomers looked at a stellar pair at the heart of a stunning cloud of gas and dust, they were in for a surprise. Star pairs are typically very similar, like twins, but in HD 148937, one star appears younger and, unlike the other, is magnetic. New data from the European Southern Observatory (ESO) suggest there were originally three stars in the system, until two of them clashed and merged. This violent event created the surrounding cloud and forever altered the system’s fate.
“When doing background reading, ...