(Press-News.org) NORMAN, OKLA. – Hanping Ding, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the School of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering at the University of Oklahoma, has been awarded a $3.1 million grant from the Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies Office in the Department of Energy through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to further research in clean hydrogen production. The funding is part of a $750 million effort in President Biden’s Investing in American agenda. The money from the Department of Energy will go to 52 projects across 24 states to position the United States as a global leader in the clean hydrogen industry.
The combined outcomes of the 52 projects should allow the U.S. to produce enough technology per year to power 15% of medium- and heavy-duty trucks sold each year, produce an extra 1.3 million tons of clean hydrogen annually, and support more than 1,500 new jobs.
Ding’s three-year project will address the technical challenges of proton-conducting solid oxide electrolysis cell stacks, a type of technology that splits water into hydrogen and oxygen gases using electricity. By enabling this process, the stacks allow for the efficient conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy, producing hydrogen as a clean and renewable fuel source. Hydrogen produced through this method can result in zero greenhouse gas emissions. The goal of Ding’s project is to develop the technology to be suitable for real-world use.
“This project will advance the technology maturity of [the technology] and, from a bigger picture, promote the green hydrogen applications of the state of Oklahoma,” Ding said.
Finding a way to store and convert energy is necessary to make renewable and sustainable energy more feasible. Clean hydrogen is a way for industries to reduce emissions while continuing to provide services needed for modern life. Ding’s Advanced Materials and Clean Energy Laboratory researches technological improvements to reach net-zero emissions. The lab specializes in materials research, development and prototype system demonstration for fuel cells, hydrogen production and electrochemical processing.
Under this grant, OU will collaborate with researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Kansas State University and Chemtronergy LLC to deliver this advanced electrolysis technology. The Idaho National Laboratory and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory also support the research.
Ding’s project is well aligned with the goals of the Oklahoma Hydrogen Roadmap from the Hydrogen Production, Transportation and Infrastructure Task Force report, which includes a near-term goal of hydrogen storage and innovative technologies and long-term goals of low carbon hydrogen and equipment manufacturing.
About the project: The project, “Development of Readily Manufactured and Interface Engineered Proton-Conducting Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells with High Efficiency and Durability,” is funded through the Department of Energy grant DE-FOA-0002922.
About the University of Oklahoma: Founded in 1890, the University of Oklahoma is a public research university in Norman, Oklahoma. As the state’s flagship university, OU serves the educational, cultural, economic and health care needs of the state, region and nation. OU was named the state’s highest-ranking university in U.S. News & World Report’s most recent Best Colleges list. For more information, visit www.ou.edu
END
University of Oklahoma engineer receives $3.1M grant for clean hydrogen technologies
The project is part of $750M in funding through President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law granted to reduce the cost of clean hydrogen.
2024-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Prestigious European grant for research into biodegradable plastics
2024-04-12
Professor dr. Linda Amaral-Zettler, Research Leader at NIOZ Royal Netherlands Institute of Sea Research and the Chair in Marine Microbiology at the University of Amsterdam has been awarded a prestigious Advanced ERC-grant by the European Commission today. Amaral-Zettler receives almost 3,5 million euros for her research into biodegradation in the marine environment. “Biodegradable sounds really nice”, she admits. “But before we repeat the mistakes we’ve made with fossil-fuel-based plastics back in the last millenium, we really want to understand how these materials interact with marine life and how long they last in the environment.” “Biodegradable ...
New study finds potential targets at chromosome ends for degenerative disease prevention
2024-04-11
We depend on our cells being able to divide and multiply, whether it’s to replace sunburnt skin or replenish our blood supply and recover from injury. Chromosomes, which carry all of our genetic instructions, must be copied in a complete way during cell division. Telomeres, which cap the ends of chromosomes, play a critical role in this cell-renewal process—with a direct bearing on health and disease.
The enzyme telomerase plays a key role in maintaining the length of telomeres as chromosomes replicate during ...
Scientists discover first nitrogen-fixing organelle
2024-04-11
Modern biology textbooks assert that only bacteria can take nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert it into a form that is usable for life. Plants that fix nitrogen, such as legumes, do so by harboring symbiotic bacteria in root nodules. But a recent discovery upends that rule.
In two recent papers, an international team of scientists describe the first known nitrogen-fixing organelle within a eukaryotic cell. The organelle is the fourth example in history of primary endosymbiosis — the process by which a prokaryotic cell is engulfed by a eukaryotic cell and evolves beyond symbiosis into an organelle.
“It’s very rare that organelles ...
PET/MRI accurately classifies prostate cancer patients, offers potential to avoid unnecessary biopsies
2024-04-11
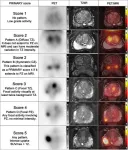
Reston, VA—PET/MRI can improve diagnostic accuracy for prostate cancer patients and help avoid unnecessary biopsies, according to new research published in the April issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. By applying the PRIMARY scoring system to PET/MRI results, researchers found that more than 80 percent of unnecessary biopsies could be avoided at the expense of missing one in eight clinically significant prostate cancer cases.
The Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) is a five-point ...
Researchers test new behavioral health interventions
2024-04-11
The concept of “One Health” – which emphasizes the relationship between human, animal, plant and environmental health – has been gaining ground in scientific discussions in recent years. Brazilian and North American researchers developing research using this approach presented their work on Tuesday (April 9th), in Chicago (United States), during FAPESP Week Illinois.
One of the panelists was Eduardo Esteban Bustamante, a professor at the University of Illinois in Chicago. He talked about behavioral interventions that have been tested to promote physical activity and healthy eating – practices that, according to the researcher, ...
New computer vision tool wins prize for social impact
2024-04-11
AMHERST, Mass. – A team of computer scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst working on two different problems—how to quickly detect damaged buildings in crisis zones and how to accurately estimate the size of bird flocks—recently announced an AI framework that can do both. The framework, called DISCount, blends the speed and massive data-crunching power of artificial intelligence with the reliability of human analysis to quickly deliver reliable estimates that can quickly pinpoint and count specific features from very large collections ...
The Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) and The GOG Foundation, Inc. (GOG-F) launch BRIDGES 2.0 Research Initiative with support from the Foundation for Women’s Cancer (FWC).
2024-04-11
PRESS RELEASE
Chicago, IL and Philadelphia, PA, USA, April 11, 2024: The Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) and The GOG Foundation, Inc. (GOG-F) Launch BRIDGES 2.0 Research Initiative with support from the Foundation for Women’s Cancer (FWC). After a successful inaugural year, the SGO and the GOG-F join forces to collaborate, and proudly announce the launch of an expanded two-year clinical trial education program supported by the FWC. This important career and clinical trial development initiative aims to cultivate the next generation of investigators in gynecologic oncology and will focus on clinical and translational research ...
Embryos in hungry mouse mums postpone development
2024-04-11
It’s challenging to sustain a pregnancy when food is short, or conditions are otherwise tough. That’s why many mammalian embryos can postpone their growth to get through periods of environmental stress and then re-enter development when conditions improve. This stalling of development is known as embryonic diapause, and understanding the mechanisms behind it might help improve infertility treatments, such as embryo freezing. Now, researchers at the Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Shanghai, China, have discovered how nutrient depletion is sensed by embryos growing in hungry mouse mums to induce diapause. ...
Scripps Research study reveals new approach for combatting “resting” bacteria
2024-04-11
LA JOLLA, CA—Most disease-causing bacteria are known for their speed: In mere minutes, they can double their population, quickly making a person sick. But just as dangerous as this rapid growth can be a bacterium’s resting state, which helps the pathogen evade antibiotics and contributes to severe chronic infections in the lungs and blood, within wounds, and on the surfaces of medical devices.
Now, Scripps Research scientists have discovered how long chains of molecules called polyphosphates (polyP) are needed for bacteria to slow down movements within cells and let them enter this resting ...
UT Health San Antonio appoints Anthony Francis as associate vice president for innovation and development
2024-04-11
SAN ANTONIO, April 10, 2024 – The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) has appointed Anthony Francis, a renowned leader in translating research to market opportunity, as associate vice president for innovation and development in the Office of the Vice President for Research.
He joins the institution from the University of California San Francisco, where he was executive director of the Office of Technology Management and Advancement. Francis is credited with transforming ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] University of Oklahoma engineer receives $3.1M grant for clean hydrogen technologiesThe project is part of $750M in funding through President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law granted to reduce the cost of clean hydrogen.