Three advances in pavement technology — for safer, more sustainable roadways
2024-04-15
(Press-News.org) While April showers bring May flowers, these months also kick off road construction season — when cracks and potholes that developed over the winter get fixed. But recent advances could make future roadways safer and repairs more sustainable, thanks to smart pothole monitoring, snail shells and graphene. The new approaches can be found in three papers recently published in ACS journals. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
A smart pothole monitoring system for cars. By harnessing the vibrations that shake a vehicle as it drives over uneven pavement, researchers have created a system that could monitor and report a road’s health in real time. A demonstration of the technology is published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. In the experiments, a vehicle equipped with the pavement monitoring system identified a pothole and a speed bump while driving around 6 miles per hour and displayed the information on a screen inside the car, which could direct road-fixing efforts faster.
Cooling concrete with snail shells. Researchers developed a powder from snail shells infused with carbon dioxide that can reduce the amount of heat that concrete pavement and roofs absorb from sunlight, as described in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering. The resulting material was mixed with Portland cement, water and a plasticizer, creating a highly reflective concrete. An outdoor test of the new concrete demonstrated its cooling ability, maintaining a surface temperature up to 10 degrees Fahrenheit lower than standard concrete.
Lighter, stronger concrete without sand. A proof-of-concept study in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces details how a coal-derived product called coke could replace sand in concrete mixtures. Researchers converted the coke into a fine, graphene powder using an advanced heating process. The new graphene additive along with cement and water formed a concrete that, when cured, was both lighter and stronger than a version made with sand. The team says the new concrete’s properties are suitable for many types of construction.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-15
Alyssa Ryan, an assistant professor of civil and architectural engineering and mechanics, in the University of Arizona College of Engineering, is leading a national study to identify disparities in traffic safety for all transportation users, including drivers, bicyclists and walkers.
"Transportation engineering is very focused on people and impacting society and how people interact with the world," said Ryan. "If you don't have transportation, you can't do anything."
With a $467,000 ...
2024-04-15
Chicago (April 15, 2024) – New research published on Monday, April 15 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) identifies how gentrified parts of a city have notably more urban wildlife than ungentrified parts of the same city, further limiting marginalized communities’ opportunity to connect with nature. The study, led by Lincoln Park Zoo’s Urban Wildlife Institute, analyzed data from 23 cities across the continental U.S., collected by partners of the Urban Wildlife Information Network ...
2024-04-15
Scientists at UC Riverside have demonstrated a new, RNA-based vaccine strategy that is effective against any strain of a virus and can be used safely even by babies or the immunocompromised.
Every year, researchers try to predict the four influenza strains that are most likely to be prevalent during the upcoming flu season. And every year, people line up to get their updated vaccine, hoping the researchers formulated the shot correctly.
The same is true of COVID vaccines, which have been reformulated to target sub-variants of the most prevalent strains ...
2024-04-15
A drug used to treat children with epilepsy prevents brain tumor formation and growth in two mouse models of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. NF1 is a genetic condition that causes tumors to grow on nerves throughout the body, including the optic nerves, which connect the eyes to the brain.
The findings lay the groundwork for a clinical trial to assess whether the drug, lamotrigine, can prevent or delay brain tumors in children with NF1. The study is online in the journal Neuro-Oncology.
“Based on these data, the Neurofibromatosis Clinical Trials Consortium is considering launching a first-of-its-kind ...
2024-04-15
The idea that the Universe is expanding dates from almost a century ago. It was first put forward by Belgian cosmologist Georges Lemaître (1894-1966) in 1927 and confirmed observationally by American astronomer Edwin Hubble (1889-1953) two years later. Hubble observed that the redshift in the electromagnetic spectrum of the light received from celestial objects was directly proportional to their distance from Earth, which meant that bodies farther away from Earth were moving away faster and the universe must be expanding.
A surprising new ingredient was added to the model in 1998 when observations of ...
2024-04-15
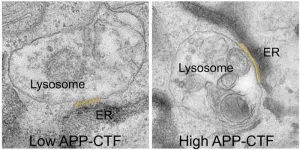
Leuven (Belgium), 16 April 2024 – Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains one of the most challenging and prevalent neurodegenerative disorders, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. In a new study published in Developmental Cell, researchers from the lab of Wim Annaert (VIB-KU Leuven) have identified a novel mechanism potentially connected to the early stages of AD. They demonstrated that a fragment of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), called APP-CTF, disrupts communication between cellular compartments crucial for calcium storage and waste disposal, which ...
2024-04-15
Nations battling for Olympic success in a global sporting ‘arms race’ has led to elite coaches migrating to Western countries as they bid to escape antiquated and restrictive coaching regimes in their home countries, reveals a new study funded by the International Olympic Committee’s Olympic Studies Centre.
National teams pursuing Olympic gold medals are increasingly recruiting foreign elite coaches from the leading countries, as they try to close the gap between themselves and the top medal-winners in particular ...
2024-04-15
Leveraging gamers and video game technology can dramatically boost scientific research according to a new study published today in Nature Biotechnology.
4.5 million gamers around the world have advanced medical science by helping to reconstruct microbial evolutionary histories using a minigame included inside the critically and commercially successful video game, Borderlands 3. Their playing has led to a significantly refined estimate of the relationships of microbes in the human gut. The results of this collaboration will both substantially advance our knowledge of the microbiome ...
2024-04-15
Manufacturing nations in the Global North are stockpiling energy and emission problems by outsourcing energy-intensive industrial processes to countries in the Global South, a new study reveals.
Global North countries use their advantages in capital and technology to grab a large amount of energy through outsourcing - creating a ‘false decoupling’ of energy consumption from economic growth.
But backward production technologies in the Global South tend to result in more energy consumption per unit of output – leading to greater carbon emissions ...
2024-04-15
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Mayo Clinic researchers recently invented a new class of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms called hypothesis-driven AI that are a significant departure from traditional AI models which learn solely from data.
In a review published in Cancers, the researchers note that this emerging class of AI offers an innovative way to use massive datasets to help discover the complex causes of diseases such as cancer and improve treatment strategies.
"This fosters a new era in designing targeted and informed AI algorithms to solve scientific questions, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Three advances in pavement technology — for safer, more sustainable roadways