(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – Large language model GPT-4 matched the performance of radiologists in detecting errors in radiology reports, according to research published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Errors in radiology reports may occur due to resident-to-attending discrepancies, speech recognition inaccuracies and high workload. Large language models, such as GPT-4, have the potential to enhance the report generation process.
“Our research offers a novel examination of the potential of OpenAI’s GPT-4,” said study lead author Roman J. Gertz, M.D., resident in the Department of Radiology at University Hospital of Cologne, in Cologne, Germany. “Prior studies have demonstrated potential applications of GPT-4 across various stages of the patient journey in radiology: for instance, selecting the correct imaging exam and protocol based on a patient’s medical history, transforming free-text radiology reports into structured reports or automatically generating the impression section of a report.”
However, this is the first study to distinctively compare GPT-4 and human performance in error detection in radiology reports, assessing its capabilities against radiologists of varied experience levels in terms of accuracy, speed and cost-effectiveness, Dr. Gertz noted.
Dr. Gertz and colleagues set out to assess GPT-4’s effectiveness in identifying common errors in radiology reports, focusing on performance, time and cost-efficiency.
For the study, 200 radiology reports (X-rays and CT/MRI imaging) were gathered between June 2023 and December 2023 at a single institution. The researchers intentionally inserted 150 errors from five error categories (omission, insertion, spelling, side confusion and “other”) into 100 of the reports. Six radiologists (two senior radiologists, two attending physicians and two residents) and GPT-4 were tasked with detecting these errors.
Researchers found that GPT-4 had a detection rate of 82.7% (124 of 150). The error detection rates were 89.3% for senior radiologists (134 out of 150) and 80.0% for attending radiologists and radiology residents (120 out of 150), on average.
In the overall analysis, GPT-4 detected less errors compared with the best performing senior radiologist (82.7% vs 94.7%). However, there was no evidence of a difference in the percentage of average performance in error detection rate between GPT-4 and all the other radiologists.
GPT-4 required less processing time per radiology report than even the fastest human reader, and the use of GPT-4 resulted in lower mean correction cost per report than the most cost-efficient radiologist.
“This efficiency in detecting errors may hint at a future where AI can help optimize the workflow within radiology departments, ensuring that reports are both accurate and promptly available,” Dr. Gertz said, “thus enhancing the radiology department’s capacity to deliver timely and reliable diagnostics.”
Dr. Gertz notes that the study’s findings are significant for their potential to improve patient care by enhancing the accuracy of radiology reports through GPT-4 assisted proofreading. Demonstrating that GPT-4 can match the error detection performance of radiologists—while significantly reducing the time and cost associated with report correction—this research shows the potential benefits of integrating AI into radiology departments.
“The study addresses critical health care challenges such as the increasing demand for radiology services and the pressure to reduce operational costs,” he said. “Ultimately, our research provides a concrete example of how AI, specifically through applications like GPT-4, can revolutionize health care by boosting efficiency, minimizing errors and ensuring broader access to reliable, affordable diagnostic services—fundamental steps toward improving patient care outcomes.”
###
“Potential of GPT-4 for Detecting Errors in Radiology Reports: Implications for Reporting Accuracy.” Collaborating with Dr. Gertz were Thomas Dratsch, M.D., Alexander Christian Bunck, M.D., Simon Lennartz, M.D., Andra-Iza Iuga, M.D., Martin Gunnar Hellmich, Ph.D., Thorsten Persigehl, M.D., Lenhard Pennig, M.D., Carsten Herbert Gietzen, M.D., Philipp Fervers, M.D., David Maintz, M.D., Robert Hahnfeldt, M.D., and Jonathan Kottlors, M.D.
Radiology is edited by Linda Moy, M.D., New York University, New York, N.Y., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on radiology reports, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
SAN ANTONIO — August 16, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute helps the automotive industry transition to smart, sustainable mobility, developing hybrid, electric and hydrogen solutions and applying artificial intelligence for safe, eco-friendly driving. SwRI engineers will be in Detroit April 16-18 to share their expertise at the 2024 SAE International WCX™ World Congress Experience.
WCX invites mechanical, electrical and software engineers working in mobility from around the world to share new knowledge and advancements.
“The automotive and transportation sectors are going through tremendous change and challenges as they navigate ...
A component of the human intestinal flora that has been little studied to date is the focus of a new study. Plasmids are small extrachromosomal genetic elements that frequently occur in bacterial cells and can influence microbial lifestyles – yet their diversity in natural habitats is poorly understood. An international team led by Prof. Dr. A. Murat Eren from the Helmholtz Institute for Functional Marine Biodiversity at the University of Oldenburg (HIFMB) reports in the science journal Cell, a mysterious plasmid, is one of the most numerous genetic elements in the human gut that could potentially serve as a powerful biomarker for identifying ...
Shipowners around the world are in a very difficult position, because they are having to order new ships now that will run on fuel and technologies that are not yet fully developed.
A new study suggests that ammonia could be a smart and energy-efficient fuel in the race to achieve net zero in shipping. Researchers at the Department of Industrial Economics and Technology Management (IØT) and the Department of Marine Technology (IMT) at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) ...
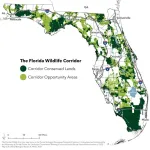
From rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns to intense weather events such as hurricanes, Florida is experiencing significant climate-related challenges in tandem with skyrocketing insurance rates. As the state’s population continues to surge by 1,000 new residents a day, it is projected to lose 3.5 million acres of land to development by 2070, threatening Florida’s future ability to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem services.
A first-of-its-kind study highlights how Florida can buffer itself against both climate change ...
In their ongoing quest to develop a range of methods for managing plasma so it can be used to generate electricity in a process known as fusion, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have shown how two old methods can be combined to provide greater flexibility.
While the two methods – known as electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) and applying resonant magnetic perturbations (RMP) – have long been studied, this is the first time researchers have simulated how they can be used together to ...
Each summer, a hypoxic dead zone forms in the Gulf of Mexico, making some marine habitats unlivable. The dead zone is caused by nutrients—primarily from agricultural fertilizers—flowing into the Gulf from the Mississippi River. Restoring wetlands at field margins has been proposed to intercept some of the runoff, as wetland plants and soils are capable of absorbing nutrients like a living sponge. But estimates of nutrient removal by restored wetlands have varied widely. Shan Zuidema and colleagues took a whole-system approach to modeling the potential for wetlands to ameliorate the flow of nitrate to the ...
A high-profile study made headlines in 2023 stating that the scientific and innovation system is producing less and less completely new knowledge. Researchers at the University of Basel are now refuting this claim, at least for patents: It is based on a measurement error.
The discovery of mRNA in the 1960s was groundbreaking. Suddenly there were completely new findings that ushered in new developments. This kind of discovery is described as “disruptive”. In contrast, research findings are “consolidating” when they build upon existing knowledge. They are also important, as the example of the ...
The fall armyworm is a destructive corn pest, which recently arrived in Africa and Asia from the Americas and began causing major yield losses and increased use of insecticides, which pose environmental and human health risks. Entomopathogenic nematodes are soil-dwelling roundworms that can parasitize and kill fall armyworms with no risks to people or the environment, but application can be tricky because the nematodes are susceptible to desiccation and UV radiation from sunlight. Patrick Fallet and colleagues report success using an innocuous biodegradable ...
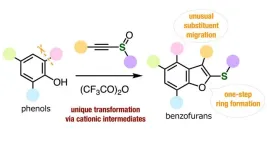
In the field of organic chemistry, scientists are always looking out for new types of reactions to unlock synthesis routes for challenging compounds. Most of the progress that we have witnessed in pharmaceutics and agrochemicals over the past few decades can be traced back to the discovery of novel practical reaction pathways. Such pathways often involve the selective replacement of a functional group with another, the formation of aromatic rings, or the strategic cleaving of parts of a molecule. But what about the rearrangement of existing functional groups within a molecule?
Also known as ‘substituent ...
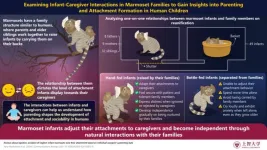
The connection that infants form with their parents or caregivers is crucial for their cognitive, social, and emotional development. These attachments vary in quality, depending on how caregivers respond to the infant's needs. When caregivers are attentive, infants are likely to develop secure attachments. However, if caregivers neglect their needs, infants may develop insecurity, leading to challenges in emotional development and difficulty in forming healthy relationships later in life.
To understand how parenting influences attachment formation and child development, researchers led by Associate Professor Atsuko ...