(Press-News.org) - Euvichol-S, developed jointly by EuBiologics and IVI, improves productivity by approximately 40% over Euvichol-Plus®
- Production and supply of Euvichol-S expected to help address cholera vaccine shortages
April 15, 2024, SEOUL, Republic of Korea – EuBiologics and the International Vaccine Institute (IVI) announced that Euvichol-S, an improved oral cholera vaccine (OCV) developed jointly by EuBiologics and IVI, has achieved World Health Organization prequalification (PQ). Euvichol-S is a new OCV that has improved productivity by about 40 percent over the existing Euvichol-Plus® by modifying the formulation and manufacturing method of the original vaccine material.
In May last year, EuBiologics submitted a PQ application to WHO with technical support from IVI after a field inspection of its GMP facilities by the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety on behalf of WHO. The new vaccine received an export license from KMFDS in December before winning the WHO seal of approval in about 10 months after application.
EuBiologics will now be able to produce and supply three oral cholera vaccines, including Euvichol® (in glass vials) and Euvichol-Plus®. There is a significant global shortage of vaccine for cholera prevention as reported recently by The New York Times, and the expected supply of Euvichol-S to UN agencies is expected to ease this supply shortage.
Euvichol-S was developed through technological collaboration between EuBiologics and Dr. Julia Lynch's team at IVI, and its efficacy was demonstrated in a Phase 3 comparative clinical trial in Nepal last year. The development of the vaccine was funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, and the vaccine will be produced and distributed by EuBiologics. After the scale-up process, Euvichol-S will be mass produced in GMP facilities at the company’s Chuncheon Plant 1 and Plant 2 in the Republic of Korea beginning in the second quarter.
Dr. Julia Lynch, Director of IVI’s Cholera Program, said, "The addition of Euvichol-S to global health market will contribute to easing the shortage of OCV supply amid a dire global cholera situation. IVI will continue efforts to enhance the availability of OCV worldwide and develop new and improved vaccines that are equally safe, effective, and affordable."
###
About the International Vaccine Institute (IVI)
The International Vaccine Institute (IVI) is a non-profit international organization established in 1997 at the initiative of the United Nations Development Programme with a mission to discover, develop, and deliver safe, effective, and affordable vaccines for global health.
IVI’s current portfolio includes vaccines at all stages of pre-clinical and clinical development for infectious diseases that disproportionately affect low- and middle-income countries, such as cholera, typhoid, chikungunya, shigella, salmonella, schistosomiasis, hepatitis E, HPV, COVID-19, and more. IVI developed the world’s first low-cost oral cholera vaccine, pre-qualified by the World Health Organization (WHO), and developed a new-generation typhoid conjugate vaccine that also achieved WHO prequalification in early 2024.
IVI is headquartered in Seoul, Republic of Korea with a Europe Regional Office in Sweden, an Africa Regional Office in Rwanda, a Country Office in Austria, and a Country and Project Office in Kenya. IVI additionally co-founded the Hong Kong Jockey Club Global Health Institute in Hong Kong and hosts Collaborating Centers in Ghana, Ethiopia, and Madagascar. 39 countries and the WHO are members of IVI, and the governments of the Republic of Korea, Sweden, India, Finland, and Thailand provide state funding. For more information, please visit https://www.ivi.int.
END
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Large language model GPT-4 matched the performance of radiologists in detecting errors in radiology reports, according to research published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Errors in radiology reports may occur due to resident-to-attending discrepancies, speech recognition inaccuracies and high workload. Large language models, such as GPT-4, have the potential to enhance the report generation process.
“Our research offers a novel examination of the potential of OpenAI’s GPT-4,” said study lead author Roman J. Gertz, M.D., resident in the Department ...
SAN ANTONIO — August 16, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute helps the automotive industry transition to smart, sustainable mobility, developing hybrid, electric and hydrogen solutions and applying artificial intelligence for safe, eco-friendly driving. SwRI engineers will be in Detroit April 16-18 to share their expertise at the 2024 SAE International WCX™ World Congress Experience.
WCX invites mechanical, electrical and software engineers working in mobility from around the world to share new knowledge and advancements.
“The automotive and transportation sectors are going through tremendous change and challenges as they navigate ...
A component of the human intestinal flora that has been little studied to date is the focus of a new study. Plasmids are small extrachromosomal genetic elements that frequently occur in bacterial cells and can influence microbial lifestyles – yet their diversity in natural habitats is poorly understood. An international team led by Prof. Dr. A. Murat Eren from the Helmholtz Institute for Functional Marine Biodiversity at the University of Oldenburg (HIFMB) reports in the science journal Cell, a mysterious plasmid, is one of the most numerous genetic elements in the human gut that could potentially serve as a powerful biomarker for identifying ...
Shipowners around the world are in a very difficult position, because they are having to order new ships now that will run on fuel and technologies that are not yet fully developed.
A new study suggests that ammonia could be a smart and energy-efficient fuel in the race to achieve net zero in shipping. Researchers at the Department of Industrial Economics and Technology Management (IØT) and the Department of Marine Technology (IMT) at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) ...
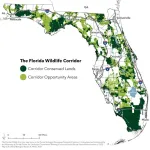
From rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns to intense weather events such as hurricanes, Florida is experiencing significant climate-related challenges in tandem with skyrocketing insurance rates. As the state’s population continues to surge by 1,000 new residents a day, it is projected to lose 3.5 million acres of land to development by 2070, threatening Florida’s future ability to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem services.
A first-of-its-kind study highlights how Florida can buffer itself against both climate change ...
In their ongoing quest to develop a range of methods for managing plasma so it can be used to generate electricity in a process known as fusion, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have shown how two old methods can be combined to provide greater flexibility.
While the two methods – known as electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) and applying resonant magnetic perturbations (RMP) – have long been studied, this is the first time researchers have simulated how they can be used together to ...
Each summer, a hypoxic dead zone forms in the Gulf of Mexico, making some marine habitats unlivable. The dead zone is caused by nutrients—primarily from agricultural fertilizers—flowing into the Gulf from the Mississippi River. Restoring wetlands at field margins has been proposed to intercept some of the runoff, as wetland plants and soils are capable of absorbing nutrients like a living sponge. But estimates of nutrient removal by restored wetlands have varied widely. Shan Zuidema and colleagues took a whole-system approach to modeling the potential for wetlands to ameliorate the flow of nitrate to the ...
A high-profile study made headlines in 2023 stating that the scientific and innovation system is producing less and less completely new knowledge. Researchers at the University of Basel are now refuting this claim, at least for patents: It is based on a measurement error.
The discovery of mRNA in the 1960s was groundbreaking. Suddenly there were completely new findings that ushered in new developments. This kind of discovery is described as “disruptive”. In contrast, research findings are “consolidating” when they build upon existing knowledge. They are also important, as the example of the ...
The fall armyworm is a destructive corn pest, which recently arrived in Africa and Asia from the Americas and began causing major yield losses and increased use of insecticides, which pose environmental and human health risks. Entomopathogenic nematodes are soil-dwelling roundworms that can parasitize and kill fall armyworms with no risks to people or the environment, but application can be tricky because the nematodes are susceptible to desiccation and UV radiation from sunlight. Patrick Fallet and colleagues report success using an innocuous biodegradable ...
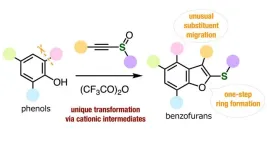
In the field of organic chemistry, scientists are always looking out for new types of reactions to unlock synthesis routes for challenging compounds. Most of the progress that we have witnessed in pharmaceutics and agrochemicals over the past few decades can be traced back to the discovery of novel practical reaction pathways. Such pathways often involve the selective replacement of a functional group with another, the formation of aromatic rings, or the strategic cleaving of parts of a molecule. But what about the rearrangement of existing functional groups within a molecule?
Also known as ‘substituent ...