(Press-News.org) Bentham Science Publishers is now a signatory organization of United2Act's consensus statement on paper mills.
We are committed to upholding the highest standards of research integrity in academic and scientific publishing. Part of the effort to uphold integrity in scientific publishing includes preventing publication from fraudulent 'paper mills' which negatively impact the credibility of research. We fully support the COPE position statement on this critical issue.
The intrusion of fraudulent papers into the publication record not only undermines public trust in research but also poses significant risks to public health and the sanctity of the scientific process. The role of paper mills in generating false or manipulated data and articles is a matter of grave concern for the entire academic community.
By signing the United2Act consensus statement on action against paper mills, we join hands with COPE and other publishers in a unified stance against this threat. We recognize the urgency of this situation and commit to actively engaging in the collective effort to combat these unethical practices. Our participation in this initiative also aligns with our ongoing endeavors to foster transparency, responsibility, and ethical standards in research publishing.
We believe that through collaborative and concerted action we can safeguard the integrity of scholarly publishing and ensure the veracity of academic research. Bentham Science Publishers looks forward to being involved in the conversation guided by Unidted2Act, and encourages collective action that makes research reliable.
END
Bentham Science joins United2Act
2024-04-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When thoughts flow in one direction
2024-04-18
Contrary to previous assumptions, nerve cells in the human neocortex are wired differently than in mice. Those are the findings of a new study conducted by Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and published in the journal Science.* The study found that human neurons communicate in one direction, while in mice, signals tend to flow in loops. This increases the efficiency and capacity of the human brain to process information. These discoveries could further the development of artificial neural networks.
The neocortex, a critical structure for human intelligence, is less than five millimeters thick. There, in the outermost layer of the brain, 20 billion neurons process ...
Scientists identify airway cells that sense aspirated water and acid reflux
2024-04-18
Scientists Identify Airway Cells That Sense Aspirated Water and Acid Reflux
The new work by UCSF researchers could lead to interventions to prevent pneumonia or treat certain types of chronic cough.
When a mouthful of water goes down the wrong pipe – heading toward a healthy person’s lungs instead of their gut – they start coughing uncontrollably. That’s because their upper airway senses the water and quickly signals the brain. The same coughing reflex is set off in people with acid reflux, when acid from the stomach reaches the throat.
Now, UC San Francisco scientists have identified the rare type of cell responsible ...
China’s major cities show considerable subsidence from human activities
2024-04-18
The land under nearly half of China’s major cities is undergoing moderate to severe subsidence, affecting roughly one-third of the nation’s urban population, according to a systematic national-scale satellite assessment. The findings suggest that within the next century, 22 to 26% of China’s coastal land will have a relative elevation lower than sea level, putting hundreds of millions of people at elevated risk of flooding due to sea-level rise. Over the last several decades, China has experienced one of the most rapid and extensive urban expansions in human history. This massive wave of urbanization may be threatened ...
Drugs of abuse alter neuronal signaling to reprioritize use over innate needs
2024-04-18
Drugs of abuse, like cocaine and opioids, alter neuronal signaling in the nucleus accumbens (NAc), hijacking a key brain reward system involved with the fulfillment of innate needs for survival, according to a new study in mice. The findings provide mechanistic insights into the intensification of drug-seeking behaviors in substance use disorders. Persistent drug use is accompanied by a profound reprioritization of motivations, skewing decision-making behaviors toward a myopic focus on drug use over other innate needs, like eating or drinking water, often ...
Mess is best: disordered structure of battery-like devices improves performance
2024-04-18
The energy density of supercapacitors – battery-like devices that can charge in seconds or a few minutes – can be improved by increasing the ‘messiness’ of their internal structure.
Researchers led by the University of Cambridge used experimental and computer modelling techniques to study the porous carbon electrodes used in supercapacitors. They found that electrodes with a more disordered chemical structure stored far more energy than electrodes with a highly ordered structure.
Supercapacitors are a key technology for the energy transition and could be useful for certain forms of public transport, as well as for ...
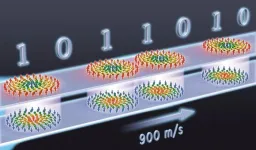
Skyrmions move at record speeds: a step towards the computing of the future
2024-04-18
An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be moved by electrical currents, attaining record speeds up to 900 m/s.
Anticipated as future bits in computer memory, these nanobubbles offer enhanced avenues for information processing in electronic devices. Their tiny size3 provides great computing and information storage capacity, as well as low energy consumption.
Until now, these nanobubbles moved no faster than 100 m/s, which is too slow for computing applications. ...
A third of China’s urban population at risk of city sinking, new satellite data shows
2024-04-18
Land subsidence is overlooked as a hazard in cities, according to scientists from the University of East Anglia (UEA) and Virginia Tech.
Writing in the journal Science, Prof Robert Nicholls of the Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research at UEA and Prof Manoochehr Shirzaei of Virginia Tech and United Nations University for Water, Environment and Health, Ontario, highlight the importance of a new research paper analysing satellite data that accurately and consistently maps land movement across China.
While they say in their comment article that consistently measuring subsidence is a great achievement, they argue it is only the start of finding solutions. Predicting ...
International experts issue renewed call for Global Plastics Treaty to be grounded in robust science
2024-04-18
With negotiations around the Global Plastics Treaty set to resume next week, an international group of scientists has renewed calls for the ambitions and commitments of the Treaty to be driven by robust scientific evidence that is free from conflicts of interest.
Government officials from across the world, and around 4,000 observers representing different aspects in society will gather in Ottawa, Canada, from April 23 to 29 for the fourth session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-4).
It will be the fourth of an expected five sessions convened to negotiate an international and legally binding global treaty after the mandate ...
Novel material supercharges innovation in electrostatic energy storage
2024-04-18
By Shawn Ballard
Electrostatic capacitors play a crucial role in modern electronics. They enable ultrafast charging and discharging, providing energy storage and power for devices ranging from smartphones, laptops and routers to medical devices, automotive electronics and industrial equipment. However, the ferroelectric materials used in capacitors have significant energy loss due to their material properties, making it difficult to provide high energy storage capability.
Sang-Hoon Bae, assistant professor of mechanical engineering and materials science in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in ...
A common pathway in the brain that enables addictive drugs to hijack natural reward processing has been identified by Mount Sinai
2024-04-18
Mount Sinai researchers, in collaboration with scientists at The Rockefeller University, have uncovered a mechanism in the brain that allows cocaine and morphine to take over natural reward processing systems. Published online in Science on April 18, these findings shed new light on the neural underpinnings of drug addiction and could offer new mechanistic insights to inform basic research, clinical practice, and potential therapeutic solutions.
“While this field has been explored for decades, our study is ...