(Press-News.org) Analysis of mooring observations and hydrographic data suggest the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation deep water limb in the North Atlantic has weakened. Two decades of continual observations provide a greater understanding of the Earth’s climate regulating system.
A new study published in the journal Nature Geoscience led by scientists at University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, found that human-induced environmental changes around Antarctica are contributing to sea level rise in the North Atlantic.
The research team analyzed two decades of deep sea oceanographic data collected by observational mooring programs to show that a critical piece of Earth’s global system of ocean currents in the North Atlantic has weakened by about 12 percent over the past two decades.
“Although these regions are tens of thousands of miles away from each other and abyssal areas are a few miles below the ocean surface, our results reinforce the notion that even the most remote areas of the world's oceans are not untouched by human activity,” said the study’s lead author Tiago Biló, an assistant scientist at the Rosenstiel School’s NOAA Cooperative Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Studies.
As part of the NOAA-funded project DeepT (Innovative analysis of deep and abyssal temperatures from bottom-moored instrument), the scientists analyzed data from several observational programs to study changes over time in a cold, dense, and deep water mass located at depths greater than 4,000 meters (2.5 miles) below the ocean surface that flow from the Southern Ocean northward and eventually upwells to shallower depths in other parts of the global ocean such as the North Atlantic.
This shrinking deep-ocean branch — that scientists call the abyssal limb – is part of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a three-dimensional system of ocean currents that act as a “conveyer belt” to distribute heat, nutrients, and carbon dioxide across the world’s oceans.
This near-bottom branch is comprised of Antarctic bottom water, which forms from the cooling of seawater in the Southern Ocean around Antarctica during winter months. Among the different formation mechanisms of this bottom water, perhaps the most important is the so-called brine rejection, a process that occurs when salty water freezes. As sea ice forms, it releases salt into the surrounding water, increasing its density. This dense water sinks to the ocean floor, creating a cold, dense water layer that spreads northward to fill all three ocean basins – the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. During the 21st century, the researchers observed that the flow of this Antarctic layer across 16°N latitude in the Atlantic had slowed down, reducing the inflow of cold waters to higher latitudes, and leading to warming of waters in the deep ocean.
“The areas affected by this warming spans thousands of miles in the north-south and east-west directions between 4,000- and 6,000-meters of depth,” said William Johns, a co-author and professor of ocean sciences at the Rosenstiel School. “As a result, there is a significant increase in the abyssal ocean heat content, contributing to local sea level rise due to the thermal expansion of the water.”
“Our observational analysis matches what the numerical models have predicted—human activity could potentially impose circulation changes on the entire ocean,” said Biló. “This analysis was only possible because of the decades of collective planning and efforts by multiple oceanographic institutions worldwide.”
The study, titled “Weakening of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation Abyssal Limb in the North Atlantic,” was published in the April 19 issue of the journal Nature Geoscience. The study’s authors include: Tiago Biló, William Johns from the Rosenstiel School; Renellys Perez and Shenfu Dong from NOAA’s Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, and Torsten Kanzow from the Alfred-Wegener-Institute Helmholtz Center for Polar and Marine Research in Germany.
The research was supported by NOAA’s Global Ocean Monitoring and Observing program (100007298); NOAA’s Climate Program Office, Climate Observations and Monitoring, and Climate Variability and Predictability programs (NOFO NOAA-OAR-CPO-2021-2006389), U.S. National Science Foundation (grants OCE-1332978 and OCE-1926008), the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program (grant 821001 (SO-CHIC), and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft German Research Foundation project number 274762653), with additional NOAA Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory support.
About the University of Miami
The University of Miami is a private research university and academic health system with a distinct geographic capacity to connect institutions, individuals, and ideas across the hemisphere and around the world. The University’s vibrant and diverse academic community comprises 12 schools and colleges serving more than 17,000 undergraduate and graduate students in more than 180 majors and programs. Located within one of the most dynamic and multicultural cities in the world, the University is building new bridges across geographic, cultural, and intellectual borders, bringing a passion for scholarly excellence, a spirit of innovation, a respect for including and elevating diverse voices, and a commitment to tackling the challenges facing our world. Founded in the 1940’s, the Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science has grown into one of the world’s premier marine and atmospheric research institutions. Offering dynamic interdisciplinary academics, the Rosenstiel School is dedicated to helping communities to better understand the planet, participating in the establishment of environmental policies, and aiding in the improvement of society and quality of life. www.earth.miami.edu.
END
Warming of Antarctic deep-sea waters contribute to sea level rise in North Atlantic, study finds
2024-04-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study opens new avenue for immunotherapy drug development
2024-04-19
HOUSTON ― In a new study published today in Nature Biomedical Engineering, researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have designed a new method for developing immunotherapy drugs using engineered peptides to elicit a natural immune response inside the body.
In preclinical models of locally advanced and metastatic breast cancer, this method improved tumor control and prolonged survival, both as a monotherapy and in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
“Amino acids are the building blocks of life and, when a few of them are linked together, they create a peptide. ...
Baby sharks prefer being closer to shore, show scientists
2024-04-19
Remember #BabyShark? And no, this was not the very catchy song for kids that took the internet by storm. Earlier this year, social media was abuzz with stunning footage of a newborn great white shark, captured by a flying drone.
Now, marine scientists have shown for the first time that juvenile great white sharks select warm and shallow waters to aggregate within one kilometer from the shore. These results, published in Frontiers in Marine Science, are important for conservation of great white sharks – especially as ocean temperatures increase due ...
UBC research helps migrating salmon survive mortality hot-spot
2024-04-19
When Kevin Ryan and the other hardworking volunteers at Mossom Creek Hatchery in Port Moody, B.C. release young coho smolts into the ocean, they’re never quite certain how many will return as adults.
Mossom releases between 5,000 and 10,000 coho smolts each year, and is one of the few hatcheries to release coho directly into the ocean, rather than into a river. Until now, no research had looked at the success of direct ocean releases of coho.
UBC researchers used acoustic telemetry to tag and track coho on their journey. The results were revealing: ...
Technical Trials for Easing the (Cosmological) Tension
2024-04-19
Thanks to the dizzying growth of cosmic observations and measurement tools and some new advancements (primarily the “discovery” of what we call dark matter and dark energy) all against the backdrop of General Relativity, the early 2000s were a time when nothing seemed capable of challenging the advancement of our knowledge about the cosmos, its origins, and its future evolution.
Even though we were aware there was still much to uncover, the apparent agreement between our observations, calculations, and theoretical framework was indicating that our knowledge of the universe was set to grow significantly and without ...
Mapping plant functional diversity from space: HKU ecologists revolutionize ecosystem monitoring with novel field-satellite integration
2024-04-19
An international team of researchers, led by Professor Jin WU from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong Kong (HKU), has made a promising advancement in mapping plant functional traits from space using time-series satellite data. The study, published in Remote Sensing of Environment, showcases the innovative combination of the Sentinel-2 satellite mission and its dynamic time-series capabilities. This innovative approach not only unlocks a deeper understanding of essential foliar traits, providing crucial insights ...
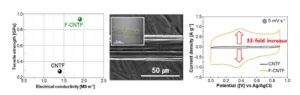
Lightweight and flexible yet strong? Versatile fibers with dramatically improved energy storage capacity
2024-04-19
The latest wearable devices, such as Samsung's Galaxy Ring and Apple's Vision Pro, are taking healthcare a step further and even enabling people to work virtually. Given the characteristics of wearable devices that require them to be small and lightweight, there is an inevitable limitation on battery capacity, still presenting a technical barrier to incorporating a variety of functions. In order for wearable devices to fully realize the imagined life, it is necessary to develop a lighter and more fromlessenergy storage method.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that a joint research team led by Dr. Hyeonsu Jeong ...
3 ways to improve diabetes care through telehealth
2024-04-19
Grocery stores, airports and beaches aren’t great places to have telehealth visits with your endocrinologist. But home can be one of the best locations, giving a doctor helpful insights into a patient’s home environment, which can positively impact their care.
This is just one finding shared in a new study published this week in The Journal of Clinical Diabetes.
Researchers interviewed clinicians and staff who provide diabetes care through telehealth across four University of California academic medical ...
A flexible and efficient DC power converter for sustainable-energy microgrids
2024-04-19
A new DC-DC power converter is superior to previous designs and paves the way for more efficient, reliable and sustainable energy storage and conversion solutions. The Kobe University development can efficiently interface with a wide range of energy sources while enhancing system stability and simplicity at an unprecedented efficiency.
Electric power comes in two kinds, AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current). Famously, the question over which kind should be used for national power grids, the “Current War” of the late 19th century, got settled in favor of AC and most power plants today produce ...
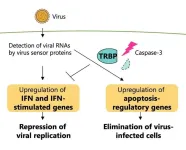
Key protein regulates immune response to viruses in mammal cells
2024-04-19
Researchers have revealed the regulatory mechanism of a specific protein that plays a key role in balancing the immune response triggered by viral infections in mammal cells. These findings could help drive the development of antiviral therapies and nucleic acid medicines to treat genetic disorders.
For cells to protect themselves from viral infections, a series of immune responses typically occur, including programmed cell death called apoptosis and interferon signaling. While apoptosis is a normal process, which occurs with or without the presence ...
Development of organic semiconductors featuring ultrafast electrons
2024-04-19
Professors Kimoon Kim and Ji Hoon Shim along with Dr. Yeonsang Lee from the Department of Chemistry at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and Professor Jun Sung Kim from POSTECH’s Department of Physics and the Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems at the Institute for Basic Science created conducting two-dimensional polymers exhibiting electron mobility comparable to graphene. Their research has been featured in the online edition of Chem, an international chemistry journal.
Graphene, called a ...