(Press-News.org) “Where is my life going?” “Who do I want to be?”
As future-thinkers, adolescents spend significant time contemplating these types of questions about their life goals. A new study from the University of Houston shows that as people grow from teenagers to young adults, they tend to change the importance they place on certain life goals, but one thing is certain: The existence of high prestige and education goals, as well as their positive development, can drive success.
“Adolescents who endorsed higher levels of prestige and education goals tended to have higher educational attainment, income, occupational creativity, occupational prestige and job complexity after 12 years,” reports Rodica Damian, associate professor of psychology in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. The paper’s first author, Andreea Sutu, is a former graduate student of Damian’s. Also on the team are former UH assistant professor Kevin Hoff and Sif Einarsdóttir of the University of Iceland.
No prior studies have investigated associations between life goal development and educational or occupational outcomes.
Damian and colleagues found that goals fluctuate – some dreams and goals of youth fall away while some, related to family (like being close to your relatives), relationships (like having good friendships or a romantic partner) and community (like being involved in your neighborhood or helping others) stay strong. These goals might become even more significant as people get older.
“Life goals are expected to change over time and these changes are expected to have consequences for future life outcomes, including occupational outcomes,” said Damian. “By understanding how changes in life goals relate to educational and occupational outcomes (above and beyond adolescent levels), we show how changes within individuals may also predict desired educational and occupational attainment.”
The study examined how life goals developed with age and how adolescent levels of goals, and their development through young adulthood, related to educational attainment and occupational outcomes in young adulthood. The study used two nationally representative samples of Icelandic youth followed longitudinally across 12 years from late adolescence to young adulthood.
“For educational attainment, the strongest effects were found for education goals. Both initial levels and slopes of education goals were positively associated with educational attainment in both samples,” said Damian. “This indicates that adolescents with higher education goals, and those who showed a more positive change pattern in education goals, had higher educational attainment in young adulthood.”
Education and prestige goals emerged as the most consistent predictors of later income and that changes in these goals across time were the most consistent predictors of later occupational prestige and complexity.
“Our work highlights the importance of better understanding sources of goal development in adolescence and young adulthood. Overall, our focus on life goal development, educational attainment and occupational outcomes informs theoretical and practical understanding about the importance of life goals for real-world outcomes,” said Damian.
END
Life goals and their changes drive success
New study from University of Houston indicates if you can dream it, you can be it
2024-04-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Newmetasurface innovation unlocks precision control in wireless signals
2024-04-22
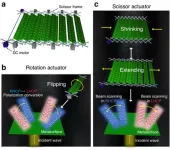
Researchers have unveiled a technology that propels the field of wireless communication forward. This cutting-edge design, termed a reconfigurable transmissive metasurface, utilizes a synergistic blend of scissor and rotation actuators to independently manage beam scanning and polarization conversion. This introduces an innovative approach to boosting signal strength and efficiency within wireless networks.
Reconfigurable metasurfaces are transforming wireless communication by adjusting electromagnetic (EM) wave characteristics such as amplitude, phase, and polarization. These planar arrays enhance wave control, boosting functionalities ...
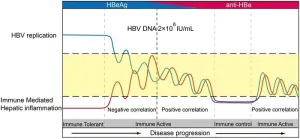
The relationship between viral replication and the severity of hepatic necroinflammatory damage changed before HBeAg loss in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection
2024-04-22
Background and Aims
Disease progression of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is driven by the interactions between viral replication and the host immune response against the infection. This study aimed to clarify the relationship between HBV replication and hepatic inflammation during disease progression.
Methods
Two cross-sectional, one validation cohort, and meta-analyses were used to explore the relationship between HBV replication and liver inflammation. Spearman analysis, multiple linear regression, and logistic regression were used to explore the relationship between variables.
Results
In ...
Sleeter to receive funding for website project
2024-04-22
Nathan Sleeter, Research Assistant Professor, History and Art History, Roy Rosenzweig Center for History and New Media (RRCHNM), is set to receive funding for: “American Indian Science and Engineering Society (AISES) at 50 website.”
RRCHNM researchers will develop a website that will tell the story of AISES’s first 50 years, its founding mission, its growth, and the individuals who have been part of its work supporting American Indians in STEM. Sleeter will serve as project director.
The researchers will also conduct and record oral history ...
Alem conducting PRNT analysis of samples from Athari Biosciences
2024-04-22
Farhang Alem, Interim Director of the Biomedical Research Laboratory, Institute for Biohealth Innovation, received funding for: “PRNT Analysis of Samples from Athari BioSciences.”
Researchers with the Biomedical Research Laboratory will perform Plaque Reduction Neutralization Tests (PRNTs) on Athari patient serum samples with parameters defined by Athari. They will also produce and deliver a report containing all patient serum sample titer results for SARS-CoV-2.
PRNT analysis is a serological test that utilizes the ability of a specific antibody to neutralize a virus, and in turn, prevent the virus ...
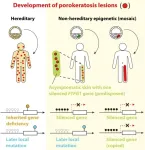
Mosaics of predisposition cause skin disease
2024-04-22
Clarifying the cause of a skin disease led to the discovery of a new disease-causing gene, a new category of diseases, and new perspectives for both counseling and therapy. The Kobe University discovery is the first time that epigenetic silencing, the “switching off” of an otherwise intact gene, has been recognized as the cause for a skin disease.
Porokeratosis is a skin disease that leads to the development of annular or circular, red and itchy lesions. In some individuals, these develop all over the body, in some localized in lines, and in some only in one or very few spots. Kobe University dermatologist KUBO Akiharu previously ...
Preoperative GLP-1 receptor agonist use and risk of postoperative respiratory complications
2024-04-22
About The Study: Preoperative use of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in patients undergoing emergency surgery was not associated with a higher risk of postoperative respiratory complications compared with patients not using GLP-1 RAs. The results of this study suggest that liberalizing withholding guidelines for GLP-1 RAs preoperatively should be considered.
Authors: Anjali A. Dixit, M.D., M.P.H., of the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California, ...
International scientific collaboration produces a comprehensive atlas of human skeletal muscle aging
2024-04-22
In a world with rapidly aging societies, there’s a need for a detailed understanding of the cause and progression of diseases associated with aging. Skeletal muscle is the key motor system in the human body and plays a pivotal role in body metabolic regulation. With increased age, particularly in individuals over 80 years old, skeletal muscles suffer from sarcopenia, a progressive loss of muscle mass and function. Sarcopenia not only increases the individual’s disability but also plays a role in the rapid decline of general functions in the elderly, making them frailer. The underlying ...
Developmental milestone attainment in children before and during the pandemic
2024-04-22
About The Study: Modest decreases in developmental screening scores suggest reason for cautious optimism about the development of a generation of U.S. children exposed to the COVID-19 pandemic in this study including 50,000 children. Continued attention to developmental surveillance is critical since the long-term population- and individual-level implications of these changes are unclear.
Authors: Sara B. Johnson, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Antihypertensive medication and fracture risk in older VHA nursing home residents
2024-04-22
About The Study: The findings of this study indicated that initiation of antihypertensive medication was associated with elevated risks of fractures and falls among older long-term care nursing home residents in the Veterans Health Administration. These risks were numerically higher among residents with dementia, higher baseline blood pressures values, and no recent antihypertensive medication use. Caution and additional monitoring are advised when initiating antihypertensive medication in this vulnerable population.
Authors: Chintan V. Dave, Pharm.D., Ph.D., of Rutgers University in New Brunswick, ...
Social programs save millions of lives, especially in times of crisis
2024-04-22
Primary health care, conditional cash transfers and social pensions have prevented 1.4 million deaths of all ages in Brazil over the past two decades, according to a study coordinated by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by “la Caixa” Foundation. If expanded, these programmes could avert an additional 1.3 million deaths and 6.6 million hospitalisations by 2030.
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated poverty and social inequalities worldwide, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). In addition, the economic consequences of the ongoing war in Ukraine and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Life goals and their changes drive successNew study from University of Houston indicates if you can dream it, you can be it