(Press-News.org) Korea relies on imports for most of its metal resources, and in recent years, due to resource depletion and rising raw material prices, 'circular resources' that recycle waste metal resources have emerged. In response, SK hynix has established a mid- to long-term plan to increase the percentage of copper, gold, etc. recovered and reused from waste generated in the semiconductor manufacturing process to more than 30% by 2030, and Samsung Electronics is running a collection program for used mobile phones in cooperation with E-circulation Governance, a non-profit corporation. The global circular economy market is expected to more than double in size from approximately $338 billion in 2022 to approximately $712 billion in 2026.
In this context, a team led by Dr. Jae-Woo Choi of the Water Resource Cycle Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that they have developed a technology that can selectively recover high-purity gold from electrical and electronic waste containing various metals using textile materials.
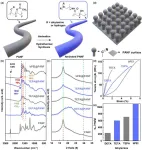
Adsorbents for metal recovery are generally granular in shape to increase adsorption efficiency based on high specific surface area, but they are difficult to control underwater, resulting in low recovery rates and even secondary environmental pollution. On the other hand, fiber-like materials are easy to control underwater and can be made into various shapes through the weaving process, so they have high potential for industrial application. However, due to their thin thickness and low strength, they are easily broken when gold recovery is applied to the support.
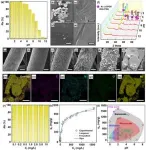
KIST researchers have chemically immobilized alkaline molecules on the surface of polyacrylonitrile (PANF) fibers to improve both molecular gold recovery performance and structural stability. The amine-containing polymer fiber has a dramatically larger surface area, which can improve the adsorption performance of gold ions (Au) in waste by up to 2.5 times (from 576 mg/g to 1,462 mg/g) compared to the team's previously developed granular gold adsorption material.
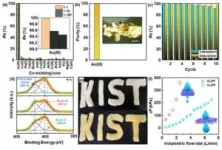
The developed fibrous adsorbent not only showed a gold recovery efficiency of more than 99.9% in solutions obtained by leaching real CPUs, but also achieved a gold recovery efficiency close to 100% in a wide range of pH 1-4, which includes most waste liquids. It is particularly noteworthy that only gold ions can be recovered with a high purity of over 99.9%, even in the presence of 14 other metal ions coexisting in the solution. Furthermore, the gold recovery rate was maintained at 91% even after 10 uses, demonstrating excellent reusability.
"By enabling efficient and eco-friendly metal resource recovery, the fiber-type adsorbent developed by KIST can reduce Korea's dependence on resource imports and prepare for the risk of rising raw material prices," said Dr. Jae-Woo Choi. "We plan to expand the scope of future research to selectively recover various target metals in addition to gold, said Dr. Youngkyun Jung."
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
The research, which was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Jong-ho Lee) through the Leading Materials Innovation Project (2020M3H4A3106366) and the KIST Air Environment Complex Response Research Project (2E33081), was published in the international journal Chemical Engineering Journal.
END
Extracting high-purity gold from electrical and electronic waste
A fibrous adsorbent selectively recovers high-purity gold from waste. Dramatically reduces the cost and time of the recovery process and enables material to be mass-produced and repeatedly recycled
2024-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tropical fish are invading Australian ocean water
2024-04-23
A University of Adelaide study of shallow-water fish communities on rocky reefs in south-eastern Australia has found climate change is helping tropical fish species invade temperate Australian waters.
“The fish are travelling into these Australian ecosystems as larvae caught in the Eastern Australian Current, which is strengthening due to the warming climate,” said the University of Adelaide’s Professor Ivan Nagelkerken, Chief Investigator of the study.
“These larvae would not normally survive in the cooler Australian ...
No bull: How creating less-gassy cows could help fight climate change
2024-04-23
A Curtin University study has revealed breeding less-flatulent cows and restoring agricultural land could significantly reduce rising methane emission levels, which play a considerable role in climate change.
The food system, including grazing animals such as cows, generates major sources of methane mainly due to cattle digestion, manure decomposition and land use for grazing.
To look for solutions, researchers from the Curtin University Sustainability Policy Institute analysed 27 academic publications and identified dozens of potential strategies to reduce methane emissions from Australia’s beef and dairy sectors.
Study ...
ECU researchers call for enhanced research into common post-stroke condition
2024-04-23
Lateropulsion, a clinical condition which results in the body leaning to one side, affects about half of all stroke survivors.
Edith Cowan University (ECU) PhD graduate Dr Jessica Nolan said while the problem is common, lateropulsion is still severely under recognised and under assessed around the world.
“A person with lateropulsion uses the limbs on their stronger side, to push themselves over toward their weaker side. Often those with lateropulsion resist correction back towards their stronger ...
SharpeRatio@k: novel metric for evaluation of risk-return tradeoff in off-policy evaluation
2024-04-23
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a machine learning technique that trains software by mimicking the trial-and-error learning process of humans. It has demonstrated considerable success in many areas that involve sequential decision-making. However, training RL models with real-world online tests is often undesirable as it can be risky, time-consuming and, importantly, unethical. Thus, using offline datasets that are naturally collected through past operations is becoming increasingly popular for training and evaluating RL and bandit ...
$1.8M NIH grant will help researchers follow a virus on its path to the nucleus
2024-04-23
Researchers at the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson were awarded a $1.8 million grant by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, a division of the National Institutes of Health, to learn how human papillomavirus makes its way to a cell’s nucleus.
Human papillomavirus, or HPV, which can cause warts and certain cancers, has been with us since the dawn of humanity and causes about 5% of cancers worldwide. It also is an important source of information about human biology, according to Samuel K. Campos, PhD, an associate professor of immunobiology at the University of Arizona College of Medicine ...
Follow-up 50 years on finds landmark steroid study remains safe
2024-04-23
A new study has found there are no adverse long-term cardiovascular health consequences for the now-adult children of mothers who were given corticosteroids because they were at risk of early birth in a landmark trial conducted in Auckland, New Zealand, 50 years ago.
The Auckland Steroid Study by obstetrician Professor Graham ‘Mont’ Liggins and paediatrician colleague Dr Ross Howie from 1969 to 1974 in Green Lane Hospital, Auckland, found that two corticosteroid injections given to pregnant women at risk of early (preterm) birth halved the incidence of respiratory distress in the babies and significantly reduced neonatal deaths.
Co-author of the new study, Dr ...
Active military service may heighten women’s risk of having low birthweight babies
2024-04-23
Active military service may heighten a woman’s risk of having a low birthweight baby, suggests a review of the available scientific evidence published online in the journal BMJ Military Health.
The findings highlight the need for more research specifically focused on women in the armed forces, and their reproductive health in particular, conclude the study authors.
Worldwide, increasing numbers of women are on active service in their country’s armed forces. The UK Armed Forces, for example, has set a target of 30% female representation by 2030. And more and more countries are deploying women in combat ...
Significant global variation in national COVID-19 treatment guidelines
2024-04-23
National clinical guidelines for the treatment of COVID-19 vary significantly around the world, with under-resourced countries the most likely to diverge from gold standard (World Health Organization; WHO) treatment recommendations, finds a comparative analysis published in the open access journal BMJ Global Health.
And nearly every national guideline recommends at least one treatment proven not to work, the analysis shows.
Significant variations in national COVID-19 treatment recommendations have been suspected since the advent of the pandemic, but these haven’t been ...
Cost increasingly important motive for quitting smoking for 1 in 4 adults in England
2024-04-23
Health concerns are still the primary motive for more than half of those who say they want to stop smoking in England, but cost is now a key factor for more than 1 in 4, finds an analysis of national survey responses, published in the open access journal BMJ Public Health.
Given this shift in thinking, making much more of the potential savings to be had might encourage more people to stub out for good, suggest the researchers.
Health concerns are generally the primary motive for people trying to stop smoking, with social and ...
Is there an association between HPV vaccination and anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis?
2024-04-22
Anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate (Anti-NMDA) receptor encephalitis is an acute
autoimmune disorder that develops both neurological symptoms and psychiatric
symptoms, including hallucination, cognitive disturbance, epilepsy, movement
disorder, and impaired consciousness. This disease may be misdiagnosed at the early
stage as a psychosis disease because of primary psychiatric symptoms. The
misdiagnosis may delay appropriate therapeutic intervention. Most patients with
anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis respond to immunotherapy [1, 2].
The pathology of this disease is ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
[Press-News.org] Extracting high-purity gold from electrical and electronic wasteA fibrous adsorbent selectively recovers high-purity gold from waste. Dramatically reduces the cost and time of the recovery process and enables material to be mass-produced and repeatedly recycled