(Press-News.org) DALLAS, April 23, 2024 — Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, estimated to affect about 12.1 million U.S. adults by 2030.[1] The abnormal firing of electrical impulses causes part of the heart to quiver, or fibrillate, often leading to complications and up to a fivefold increased risk of stroke. To help ensure all patients with AFib receive the most appropriate care, the American Heart Association is launching a new effort to educate and engage pharmacists, an important but underrepresented voice in AFib care.
This new effort, being conducted through June 2025, is the latest phase of the Association’s Four Fs of Atrial Fibrillation initiative, supported by Bristol Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance. The Four Fs are patient health concerns impeding guideline-directed anticoagulant therapy, including:
fear of falling,
fear of bleeding,
forgetfulness, or cognitive dysfunction and
frailty.
Pharmacists are often not consulted in the decision-making conversations for Afib patients during the patient care journey. During this next phase of the initiative, the Association will convene pharmacists in a roundtable event to identify gaps and opportunities related to AFib in this field. The Association then will share resources and insights nationally across thousands of hospitals and outpatient clinics.
“Pharmacists are an integral part of the multidisciplinary team to optimize care for individuals with atrial fibrillation,” said Cody Parsons, APh, PharmD, BCCCP, manager of clinical operations for Stanford Health Care's cardiovascular health service line. “The insight of pharmacists in evaluating the medical complexity and use of multiple medications is essential in facilitating safe and effective anticoagulation and ultimately preventing life-altering medical consequences of AFib.”
AFib is often only detectable during physical examination, although some affected people may experience fatigue, rapid and irregular heartbeat or other discomfort. The use of anticoagulant therapy to reduce stroke risk is supported by science, but many patients remain untreated or undertreated.
This is the latest in ongoing efforts by the American Heart Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health and this year celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service, to advance health and hope for everyone, everywhere.
Additional Resources:
Spanish News Release (To be added when available)
Atrial Fibrillation | American Heart Association
Anticoagulant Therapy Toolkit | American Heart Association
Get With The Guidelines® - AFIB | American Heart Association
###
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public’s health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for a century. During 2024 - our Centennial year - we celebrate our rich 100-year history and accomplishments. As we forge ahead into our second century of bold discovery and impact our vision is to advance health and hope for everyone, everywhere. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, X or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
END
Engaging pharmacists to improve atrial fibrillation care
New phase of American Heart Association initiative will share science-based insights and health resources with pharmacists, an underrepresented voice in AFib treatment
2024-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
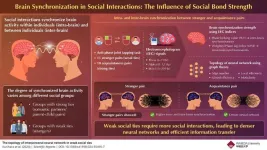
Exploring brain synchronization patterns during social interactions
2024-04-23
We experience the world and connect with others through social interactions. Engaging in activities, such as conversations, cooperative tasks, and intimate relationships, deeply affect brain activity leading to coordinated neural activity within an individual's brain (intra-brain synchronization) and between the brains of multiple individuals (inter-brain synchronization).
Researchers study brain synchronizations to understand the neural processes behind social behaviors. This knowledge can help diagnose and treat conditions like social anxiety and communication-related disorders. However, investigations on brain synchronization ...
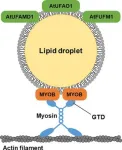
Unveiling the molecular functions of lipid droplet proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves
2024-04-23
Lipids are biomolecules essential for the proper functioning of the living cell, ranging from comprising cell membranes to forming integral components of cell signaling pathways. Plant cells possess cell subcellular structures or organelles called lipid droplets (LDs) in the leaves and seeds, which store excess lipids (fats).
Recent studies have shown that LDs also localize unique plant proteins that perform essential molecular functions. For example, seed LDs localize plant proteins called oleosins, which help seeds weather freezing temperatures and germinate properly. With an expanding body of proof ...
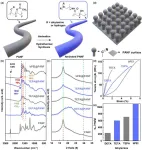
Perfecting the view on a crystal’s imperfection
2024-04-23
NEW YORK, April 23, 2024 — Single-photon emitters (SPEs) are akin to microscopic lightbulbs that emit only one photon (a quantum of light) at a time. These tiny structures hold immense importance for the development of quantum technology, particularly in applications such as secure communications and high-resolution imaging. However, many materials that contain SPEs are impractical for use in mass manufacturing due to their high cost and the difficulty of integrating them into complex devices.
In 2015, scientists discovered SPEs within a material called hexagonal boron nitride (hBN). Since then, hBN has gained widespread attention and ...
Fossil frogs share their skincare secrets
2024-04-23
Palaeontologists at University College Cork (UCC), Ireland, have solved a hundred-year-old mystery of how some fossil frogs preserve their fleshy parts – it’s all down to their skin.
Palaeontologists Daniel Falk and Prof. Maria McNamara, together with scientists from Ireland, Germany and the UK, studied 45-million-year-old fossil frogs from the Geiseltal site in central Germany. Remarkably, the fossils show full body outlines of the soft tissues. The team discovered that the excellent condition of the fossil frogs is due to preservation of ancient skin remnants.
The team studied the fossils with high-precision ...
Existing drugs studied in patients with rare immune diseases
2024-04-23
Existing drugs studied in patients with rare immune diseases
This month the first study within the DRIMID consortium (DRIMID stands for Drug Rediscovery for Rare Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases) has started. This study will investigate the efficacy and safety of the drug filgotinib (approved for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis) in three rare immune diseases (Behçet's disease, idiopathic inflammatory myositis, IgG4-related disease). DRIMID aims to investigate whether this drug - despite the absence of formal ...
Loma Linda University study reveals alarming rates of pediatric injuries from mechanical bull riding
2024-04-23
A new study conducted by researchers at Loma Linda University Children’s Health has shed light on the alarming rates of pediatric injuries resulting from mechanical bull riding. The study, titled "Mechanical Bull Injuries in Pediatric Patients: A Call for Safety Regulations," highlights the urgent need for enhanced safety measures and regulations.
The findings were published in the journal Children's Health Care and revealed that mechanical bull riding poses a significant risk to children, with traumatic brain injuries being the most common outcome.
“Mechanical bulls, even when ...
Excessive pregnancy weight gain and substantial postpartum weight retention common in military health care beneficiaries
2024-04-23
ROCKVILLE, Md.— Compared to their civilian counterparts, excessive pregnancy weight gain is more frequent among military health care beneficiaries, in particular active duty personnel, and is associated with costly maternal/neonatal complications. Women in this sample with excessive pregnancy weight gain were also three times more likely to have substantial postpartum weight retention, according to a new study published in the journal Obesity, The Obesity Society’s (TOS) flagship journal.
Substantial weight retention ...
Odor-causing bacteria in armpits targeted using bacteriophage-derived lysin
2024-04-23
Body odor from the armpits comes from bacteria metabolizing sweat produced by the apocrine glands. These bacteria are native to our skin, but the odors produced differ among people. Generally, people use deodorants on their armpits, but perhaps there is a way to get rid of the bacteria.
To find out, a research team led by Osaka Metropolitan University Professor Satoshi Uematsu and Associate Professor Kosuke Fujimoto at the Graduate School of Medicine collected body fluid samples from the armpits of 20 men that were deemed healthy. In advance, a subjective olfactory panel classified ...
Women’s heart disease is underdiagnosed, but new machine learning models can help solve this problem
2024-04-23
When it comes to matters of the heart, cardiovascular disease in women is underdiagnosed compared to men. A popular scoring system used to estimate how likely a person is to develop a cardiovascular disease within the next 10 years is the Framingham Risk Score. It is based on factors including age, sex, cholesterol levels, and blood pressure.
Researchers in the US and the Netherlands have now used a large dataset to build more accurate cardiovascular risk models than the Framingham Risk Score. They also quantified the underdiagnosis of women compared to men. The results were published in Frontiers ...
Extracting high-purity gold from electrical and electronic waste
2024-04-23
Korea relies on imports for most of its metal resources, and in recent years, due to resource depletion and rising raw material prices, 'circular resources' that recycle waste metal resources have emerged. In response, SK hynix has established a mid- to long-term plan to increase the percentage of copper, gold, etc. recovered and reused from waste generated in the semiconductor manufacturing process to more than 30% by 2030, and Samsung Electronics is running a collection program for used mobile phones in cooperation with E-circulation Governance, a non-profit corporation. The global circular economy market is expected ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Engaging pharmacists to improve atrial fibrillation careNew phase of American Heart Association initiative will share science-based insights and health resources with pharmacists, an underrepresented voice in AFib treatment