RAMP1 protects hepatocytes against ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting the ERK/YAP pathway
2024-04-23
(Press-News.org) Background and Aims
Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI) is a prevalent complication of liver transplantation, partial hepatectomy, and severe infection, necessitating the development of more effective clinical strategies. Receptor activity–modifying protein 1 (RAMP1), a member of the G protein–coupled receptor adapter family, has been implicated in numerous physiological and pathological processes. The study aimed to investigate the pathogenesis of RAMP1 in HIRI.
Methods
We established a 70% liver ischemia-reperfusion model in RAMP1 knockout (KO) and wild-type mice. Liver and blood samples were collected after 0, 6, and 24 h of hypoxia/reperfusion. Liver histological and serological analyses were performed to evaluate liver damage. We also conducted in-vitro and in-vivo experiments to explore the molecular mechanism underlying RAMP1 function.
Results
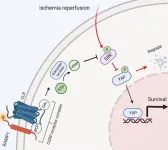
Liver injury was exacerbated in RAMP1-KO mice compared with the sham group, as evidenced by increased cell death and elevated serum transaminase and inflammation levels. HIRI was promoted in RAMP1-KO mice via the induction of hepatocyte apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation. The absence of RAMP1 led to increased activation of the extracellular signal–regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and yes-associated protein (YAP) phosphorylation, ultimately promoting apoptosis. SCH772984, an ERK/MAPK phosphorylation inhibitor, and PY-60, a YAP phosphorylation inhibitor, reduced apoptosis in in-vitro and in-vivo experiments.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that RAMP1 protects against HIRI by inhibiting ERK and YAP phosphorylation signal transduction, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target for HIRI and providing a new avenue for intervention.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2310-8819/JCTH-2023-00339
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
Follow us on X: https://twitter.com/xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/xia&he-publishing-inc/
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-23
Thermophilic fungi are chief components of mycoflora in a variety of natural and manmade composting systems, including rotting hay, stored grains, wood mulch, nesting material of birds and animals, municipal refuse, and self-heating accumulated organic matter. Thermophilic fungi are also a potential source of natural products, which complement the metabolite libraries of mesophilic fungi and bacteria.
The research team led by Prof. Dr. Xuemei Niu (State Key Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Bio-Resources in Yunnan, Yunnan University) has been working on the discovery of secondary metabolites in thermophilic fungi and their biological ...
2024-04-23
DALLAS, April 23, 2024 — Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, is the most common type of irregular heartbeat, estimated to affect about 12.1 million U.S. adults by 2030.[1] The abnormal firing of electrical impulses causes part of the heart to quiver, or fibrillate, often leading to complications and up to a fivefold increased risk of stroke. To help ensure all patients with AFib receive the most appropriate care, the American Heart Association is launching a new effort to educate and engage pharmacists, an important but underrepresented voice in AFib care.
This ...
2024-04-23
We experience the world and connect with others through social interactions. Engaging in activities, such as conversations, cooperative tasks, and intimate relationships, deeply affect brain activity leading to coordinated neural activity within an individual's brain (intra-brain synchronization) and between the brains of multiple individuals (inter-brain synchronization).
Researchers study brain synchronizations to understand the neural processes behind social behaviors. This knowledge can help diagnose and treat conditions like social anxiety and communication-related disorders. However, investigations on brain synchronization ...
2024-04-23
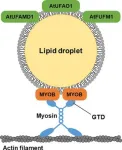
Lipids are biomolecules essential for the proper functioning of the living cell, ranging from comprising cell membranes to forming integral components of cell signaling pathways. Plant cells possess cell subcellular structures or organelles called lipid droplets (LDs) in the leaves and seeds, which store excess lipids (fats).
Recent studies have shown that LDs also localize unique plant proteins that perform essential molecular functions. For example, seed LDs localize plant proteins called oleosins, which help seeds weather freezing temperatures and germinate properly. With an expanding body of proof ...
2024-04-23
NEW YORK, April 23, 2024 — Single-photon emitters (SPEs) are akin to microscopic lightbulbs that emit only one photon (a quantum of light) at a time. These tiny structures hold immense importance for the development of quantum technology, particularly in applications such as secure communications and high-resolution imaging. However, many materials that contain SPEs are impractical for use in mass manufacturing due to their high cost and the difficulty of integrating them into complex devices.
In 2015, scientists discovered SPEs within a material called hexagonal boron nitride (hBN). Since then, hBN has gained widespread attention and ...
2024-04-23
Palaeontologists at University College Cork (UCC), Ireland, have solved a hundred-year-old mystery of how some fossil frogs preserve their fleshy parts – it’s all down to their skin.
Palaeontologists Daniel Falk and Prof. Maria McNamara, together with scientists from Ireland, Germany and the UK, studied 45-million-year-old fossil frogs from the Geiseltal site in central Germany. Remarkably, the fossils show full body outlines of the soft tissues. The team discovered that the excellent condition of the fossil frogs is due to preservation of ancient skin remnants.
The team studied the fossils with high-precision ...
2024-04-23
Existing drugs studied in patients with rare immune diseases
This month the first study within the DRIMID consortium (DRIMID stands for Drug Rediscovery for Rare Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases) has started. This study will investigate the efficacy and safety of the drug filgotinib (approved for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis) in three rare immune diseases (Behçet's disease, idiopathic inflammatory myositis, IgG4-related disease). DRIMID aims to investigate whether this drug - despite the absence of formal ...
2024-04-23
A new study conducted by researchers at Loma Linda University Children’s Health has shed light on the alarming rates of pediatric injuries resulting from mechanical bull riding. The study, titled "Mechanical Bull Injuries in Pediatric Patients: A Call for Safety Regulations," highlights the urgent need for enhanced safety measures and regulations.
The findings were published in the journal Children's Health Care and revealed that mechanical bull riding poses a significant risk to children, with traumatic brain injuries being the most common outcome.
“Mechanical bulls, even when ...
2024-04-23
ROCKVILLE, Md.— Compared to their civilian counterparts, excessive pregnancy weight gain is more frequent among military health care beneficiaries, in particular active duty personnel, and is associated with costly maternal/neonatal complications. Women in this sample with excessive pregnancy weight gain were also three times more likely to have substantial postpartum weight retention, according to a new study published in the journal Obesity, The Obesity Society’s (TOS) flagship journal.
Substantial weight retention ...
2024-04-23
Body odor from the armpits comes from bacteria metabolizing sweat produced by the apocrine glands. These bacteria are native to our skin, but the odors produced differ among people. Generally, people use deodorants on their armpits, but perhaps there is a way to get rid of the bacteria.
To find out, a research team led by Osaka Metropolitan University Professor Satoshi Uematsu and Associate Professor Kosuke Fujimoto at the Graduate School of Medicine collected body fluid samples from the armpits of 20 men that were deemed healthy. In advance, a subjective olfactory panel classified ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] RAMP1 protects hepatocytes against ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting the ERK/YAP pathway