(Press-News.org) Human beings are likely to adopt the thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors of those around them.
Simple decisions like what local store is best to shop at to more complex ones like vaccinating a child are influenced by these behavior patterns and social discourse.
“We choose to be in networks, both offline and online, that are compatible with our own thinking,” explained Amin Rahimian, assistant professor of industrial engineering at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering. “The social contagion of behavior through networks can help us understand how and why new norms, products, and ideas are adopted.”
Initially, researchers thought highly clustered ties that are close together in networks created the perfect environment for the spread of complex behaviors that require significant social reinforcement. However, Rahimian, alongside a team of researchers from Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Harvard University, counter these ideas. Long ties, which are created through randomly rewired edges that make them ‘longer,’ accelerate the spread of social contagions. For example, in the age of social media, long ties can facilitate broader reach across different demographics and heterogeneous populations. Rather than just communicating with one’s neighbor, one may also be connecting with someone in another state – even another country.
By using mathematical and statistical methods, the researchers were able to analyze the rate of spread over circular lattices with long ties and show that having a small probability of adoption below the contagion threshold is enough to ensure that random rewiring accelerates the spread of these contagions.
“Mechanisms that we identify for spread on circular lattices remain valid in higher dimensions,” explained Rahimian.
Similar network dynamics arise in the study of neural activity in the brain.
“We are interested in the implications of these results for a better understanding of network structures that facilitate the spread of bursting activity in various brain regions," explained Jonathan Rubin, professor in Pitt’s Department of Mathematics.
This research suggests those wanting to achieve fast, total spread would benefit from implementing intervention points across network neighborhoods with long-tie connections to other network regions, explained Dean Eckles, associate professor of marketing at MIT.
“Further work could study such strategies for seeding complex behaviors,” Eckles continued.
The paper, “Long ties accelerate noisy threshold-based contagions,” was recently published in Nature Human Behavior.
Other researchers on the project include:
Elchanan Mossel, Professor of Mathematics at MIT
Subhabrata Sen, Assistant Professor of Statistics at Harvard University END
Infected: understanding the spread of behavior
2024-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UNC-Chapel Hill researchers create artificial cells that act like living cells
2024-04-23
In a new study published in Nature Chemistry, UNC-Chapel Hill researcher Ronit Freeman and her colleagues describe the steps they took to manipulate DNA and proteins — essential building blocks of life — to create cells that look and act like cells from the body. This accomplishment, a first in the field, has implications for efforts in regenerative medicine, drug delivery systems, and diagnostic tools.
“With this discovery, we can think of engineering fabrics or tissues that can be sensitive to changes in their environment and behave in dynamic ways,” says Freeman, whose lab is in the Applied Physical Sciences Department of the UNC College ...
New research develops forest extent map for Mexico
2024-04-23
To properly protect forests and evaluate the state of natural resources, conservation practices and environmental policies, it is important to have accurate information on an area’s forest extent. One of the challenges facing researchers when it comes to evaluating the accuracy of forest extent, however, is that models use different remote sensing products that may have different definitions for what determines forest extent. In addition, on the ground surveys may sometimes come into conflict with what remote, satellite-based products are describing as forests.
To help quantify this problem, a group of researchers from ...
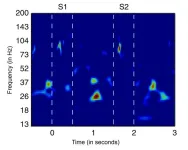
In the brain, bursts of beta rhythms implement cognitive control
2024-04-23
The brain processes information on many scales. Individual cells electrochemically transmit signals in circuits but at the large scale required to produce cognition, millions of cells act in concert, driven by rhythmic signals at varying frequencies. Studying one frequency range in particular, beta rhythms between about 14-30 Hz, holds the key to understanding how the brain controls cognitive processes—or loses control in some disorders—a team of neuroscientists argues in a new review article.
Drawing on experimental ...
New mitigation framework reduces bias in classification outcomes
2024-04-23
We use computers to help us make (hopefully) unbiased decisions. The problem is that machine-learning algorithms do not always make fair classifications, if human bias is embedded in the data used to train them — which is often the case in practice. To ease this "garbage in, garbage out" situation, a research team presented a flexible framework for mitigating bias in machine classification. Their research was published Apr. 8 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Existing attempts to mitigate classification bias, according to the team, are often held back by their reliance on specific metrics of fairness and predetermined ...
Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
2024-04-23
In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated the ability to make a thermal fusion plasma with electron temperatures hotter than 10 million degrees Celsius, roughly the temperature of the core of the sun. Zap Energy’s unique approach, known as a sheared-flow-stabilized Z pinch, has now joined those rarefied ranks, far exceeding this plasma temperature milestone in a device that is a fraction of the scale of other fusion systems.
A new research paper, published this month in Physical ...
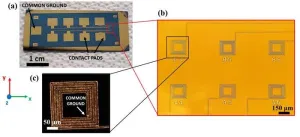
Magnetic microcoils unlock targeted single-neuron therapies for neurodegenerative disorders
2024-04-23
WASHINGTON, April 23, 2024 — Neural stimulation is a medical technique used to treat many illnesses affecting the nervous system. It involves applying energy to neurons to encourage them to grow and make connections with their neighbors. Treatments for epilepsy can often include neural stimulation, and similar treatments exist for Parkinson’s disease, chronic pain, and some psychiatric illnesses.
In the Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Minnesota deployed an array of microscopic coils — microcoils — to create ...
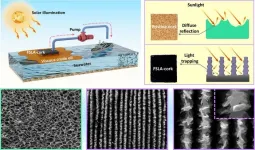
Laser-treated cork absorbs oil for carbon-neutral ocean cleanup
2024-04-23
WASHINGTON, April 23, 2024 – Oil spills are deadly disasters for ocean ecosystems. They can have lasting impacts on fish and marine mammals for decades and wreak havoc on coastal forests, coral reefs, and the surrounding land. Chemical dispersants are often used to break down oil, but they often increase toxicity in the process.
In Applied Physics Letters, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Central South University, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and Ben-Gurion University of the Negev used laser treatments to transform ordinary ...
COVID-19 vaccination and incidence of pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection and hospitalization
2024-04-23
About The Study: The findings of this study including 3.9 million children suggest that vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 was associated with significant reductions in COVID-19 incidence and hospitalizations among children in California.
Authors: Justin V. Remais, Ph.D., of the University of California, Berkeley, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7822)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and ...
Long-term taste and smell outcomes after COVID-19
2024-04-23
About The Study: Taste dysfunction as measured objectively was absent one year after exposure to COVID-19 while some smell loss remained in nearly one-third of individuals with this exposure, likely explaining taste complaints of many individuals with post–COVID-19 condition in this study of 340 individuals with and 434 individuals without prior COVID-19. Infection with earlier untyped and Alpha variants was associated with the greatest degree of smell loss.
Authors: Shima T. Moein, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Pennsylvania ...
Artificial intelligence to be used for the detection of common eye disease
2024-04-23
Dry Eye Disease (DED) is one of the more common eye diseases, affecting up to 30% of the world’s population. This disease can affect many different types of people and can wind up being a great hindrance to their overall quality of life. Early screening and prognosis is vital to the patient’s progression with the disease. However, this can be difficult. In this study, researchers aim to use artificial intelligence (AI) to aid in early screening and prognosis of DED. Not only can the use of AI make screening more accessible for ...