Innovative GREENSKY model elevates UAV efficiency in next-gen wireless networks
2024-04-23
(Press-News.org)
Researchers from the University of Missouri-Kansas City, School of Computing and Engineering, and independent researchers have developed a groundbreaking model, dubbed GREENSKY, that significantly enhances the energy efficiency and operational time of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in cellular networks.
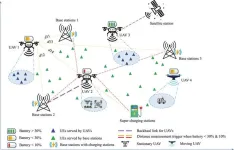
In the ever-evolving landscape of wireless communication, UAVs play a pivotal role, especially in rural, remote, and disaster-struck areas where traditional network infrastructure is absent. The GREENSKY model optimizes UAV charging behavior between static ground base stations and mobile supercharging stations, enhancing energy use and enabling longer operational periods without frequent recharging.
By integrating Mixed Integer Linear Programming, the GREENSKY model optimizes the recharging and routing processes for UAVs, thereby maximizing flight duration while minimizing energy consumption. The model strategically uses existing cellular base stations as opportunistic charging points, significantly reducing travel distances to recharge and ensuring UAVs can operate longer with less energy. Results show that GREENSKY achieves a significant reduction in energy consumption—9.1% less than traditional heuristic solutions.
Lead researcher Pratik Thantharate explains, "Our model is designed to make UAV networks more sustainable and efficient. By optimizing how and where UAVs recharge, we can extend their operational time dramatically, which is crucial for continuous and reliable service in critical areas."
The development of this optimization model not only increases the efficiency of UAV networks but also pushes forward the innovation in energy management for UAVs serving as aerial base stations.This approach not only promises enhanced connectivity for underserved regions but also paves the way for smarter, energy-conscious technology deployments in 5G and beyond.
As UAVs become more embedded in various industries, the introduction of the GREENSKY model offers a more efficient, cost-effective approach to UAV energy management and task execution. The implications of the GREENSKY model extend beyond improved service reliability. By effectively leveraging both static and mobile charging stations, the model facilitates a smarter and more robust framework for future aerial communication networks. This approach not only promises enhanced connectivity for underserved regions but also paves the way for smarter, energy-conscious technology deployments in 5G and beyond.
References
Authors: Pratik Thantharate, Anurag Thantharate, Atul Kulkarni
Affiliation: School of Computing and Engineering, University of Missouri, Kansas City, MO, USA
Title of original paper: Innovative GREENSKY Model Elevates UAV Efficiency in Next-Gen Wireless Networks
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geits.2023.100130
Journal: Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S277315372300066X
DOI: 10.1016/j.geits.2023.100130
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-23
A study analyzing a large sample of Medicare admissions at nearly 2,000 acute care hospitals nationwide during 2019 found that most hospitals—nearly four out of five—admitted a significantly different proportion of Black fee-for-service Medicare patients age 65 and older compared to the proportion of the same group of patients admitted to any hospital in that hospital’s market area.
The researchers say that understanding hospital choices within neighborhoods and markets could ...
2024-04-23
In a study of patients who smoked when they were diagnosed with laryngeal cancer, those who quit smoking before starting chemotherapy or radiation responded better to treatment, were less likely to need their voice boxes surgically removed, and lived significantly longer than those who continued to smoke. The research, from the University of Oklahoma, is published in the journal Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.
The study’s lead author, Lurdes Queimado, M.D., Ph.D., said the findings underscore the importance of integrating tobacco cessation programs into treatment plans for cancer of the larynx, an area of the throat involved in breathing, swallowing ...
2024-04-23
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Sandia National Laboratories and the Kansas City National Security Campus completed a crucial weapons component development milestone, prior to full rate production.
The Mark 21 Replacement Fuze interfaces with the W87-0 warhead for deployment onto the Minuteman III and, eventually, the Sentinel Intercontinental Ballistic Missile.
The first production unit of the replacement fuze was approved through the National Nuclear Security Administration’s rigorous Quality Assurance Inspection Procedure ...
2024-04-23
WASHINGTON, D.C. – The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) today announced the approval of funding awards totaling more than $150 million to support new patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER) studies, research to strengthen the rigor and quality of patient-centered CER and a project to implement the findings of PCORI-funded research into practice.
Among the nine awards for patient-centered CER, two include support for large, two-phased trials comparing approaches to treatments for heart failure and asthma. Two other large studies will compare health system strategies to improve hypertension control, and another will evaluate ...
2024-04-23
Human beings are likely to adopt the thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors of those around them.
Simple decisions like what local store is best to shop at to more complex ones like vaccinating a child are influenced by these behavior patterns and social discourse.
“We choose to be in networks, both offline and online, that are compatible with our own thinking,” explained Amin Rahimian, assistant professor of industrial engineering at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering. “The social contagion of behavior through networks can help ...
2024-04-23
In a new study published in Nature Chemistry, UNC-Chapel Hill researcher Ronit Freeman and her colleagues describe the steps they took to manipulate DNA and proteins — essential building blocks of life — to create cells that look and act like cells from the body. This accomplishment, a first in the field, has implications for efforts in regenerative medicine, drug delivery systems, and diagnostic tools.
“With this discovery, we can think of engineering fabrics or tissues that can be sensitive to changes in their environment and behave in dynamic ways,” says Freeman, whose lab is in the Applied Physical Sciences Department of the UNC College ...
2024-04-23
To properly protect forests and evaluate the state of natural resources, conservation practices and environmental policies, it is important to have accurate information on an area’s forest extent. One of the challenges facing researchers when it comes to evaluating the accuracy of forest extent, however, is that models use different remote sensing products that may have different definitions for what determines forest extent. In addition, on the ground surveys may sometimes come into conflict with what remote, satellite-based products are describing as forests.
To help quantify this problem, a group of researchers from ...
2024-04-23
The brain processes information on many scales. Individual cells electrochemically transmit signals in circuits but at the large scale required to produce cognition, millions of cells act in concert, driven by rhythmic signals at varying frequencies. Studying one frequency range in particular, beta rhythms between about 14-30 Hz, holds the key to understanding how the brain controls cognitive processes—or loses control in some disorders—a team of neuroscientists argues in a new review article.
Drawing on experimental ...
2024-04-23
We use computers to help us make (hopefully) unbiased decisions. The problem is that machine-learning algorithms do not always make fair classifications, if human bias is embedded in the data used to train them — which is often the case in practice. To ease this "garbage in, garbage out" situation, a research team presented a flexible framework for mitigating bias in machine classification. Their research was published Apr. 8 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Existing attempts to mitigate classification bias, according to the team, are often held back by their reliance on specific metrics of fairness and predetermined ...
2024-04-23
In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated the ability to make a thermal fusion plasma with electron temperatures hotter than 10 million degrees Celsius, roughly the temperature of the core of the sun. Zap Energy’s unique approach, known as a sheared-flow-stabilized Z pinch, has now joined those rarefied ranks, far exceeding this plasma temperature milestone in a device that is a fraction of the scale of other fusion systems.
A new research paper, published this month in Physical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Innovative GREENSKY model elevates UAV efficiency in next-gen wireless networks