(Press-News.org) HOUSTON – (April 24, 2024) – People say “When pigs fly” to describe the impossible. But even if most mammals are landlubbers, the ability to glide or fly has evolved again and again during mammalian evolution, in species ranging from bats to flying squirrels. How did that come about? In a study published in the journal Nature this week, a team of researchers led by Princeton University and Baylor College of Medicine explains the genomic and developmental basis of the patagium, the thin skin membrane that allows some mammalian species to soar through the air.
“We don't quite understand how novel traits and adaptations originate from a molecular and genetic perspective. We wanted to investigate how an evolutionary novelty arises,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Ricardo Mallarino, assistant professor of molecular biology at Princeton.
To better understand patagium evolution, the team focused on marsupials. That is because the ability to glide has developed repeatedly, using similar anatomical changes, in closely related marsupials like the sugar glider – a tiny marsupial small enough to fit in your pocket, and popular as an exotic pet.
The Baylor team led the genome sequencing for 15 marsupial species, determining the DNA sequences in both gliding species and their non-gliding relatives. Comparing those sequences revealed accelerated evolution near a gene called Emx2.
“What’s interesting is that the sequence of the gene itself doesn’t seem to be where the most relevant changes are taking place. Instead, the key changes are in short DNA sequences, called ‘enhancers,’ that lie nearby in the genome. It’s those changing enhancers that alter how and where in the body Emx2 is active, and that drives the evolution of gliding,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Erez Lieberman Aiden, professor of molecular and human genetics and director of the Center for Genome Architecture at Baylor.
“Understanding the underlying changes that happen at the genomic level to give rise to these convergent traits is important because it can tell us whether evolution is targeting the path of least resistance. You can have the same outcome but different paths to get there,” said co-first author Jorge Moreno, a graduate student in Mallarino’s lab.
Next, the researchers wanted to test these ideas. To do so, they used one of the most unique characteristics of marsupials – their pouch. “Marsupial joeys are born at a much earlier stage in development than typical mammals,” said co-first author Dr. Olga Dudchenko, assistant professor of molecular and human genetics at Baylor and a researcher at the Center for Theoretical Biological Physics at Rice University. “Instead of continuing development in their mother’s womb, they crawl into her pouch, and stay there until they are ready to take on the world independently. The fact that they are right there in the pouch makes it much easier to study how individual genes, like Emx2, affect the marsupial’s development.”
The researchers showed that Emx2 gives rise to the marsupial patagium using a genetic program that probably exists in all mammals. For instance, Emx2 is active in the skin on the sides of both mice and sugar gliders, but in sugar gliders, it is expressed for far longer. As Dudchenko, also at the Center for Genome Architecture at Baylor, notes, “By modifying those critical Emx2 enhancers, one species after another has tapped into this universal program in order to develop the ability to glide.”
Encouraging news for pigs hoping to reach for the skies.
Other authors of this work include Charles Y. Feigin, Sarah A. Mereby, Zhuoxin Chen, Raul Ramos, Axel A. Almet, Harsha Sen, Benjamin J. Brack, Matthew R. Johnson, Sha Li, Wei Wang, Jenna M. Gaska, Alexander Ploss, David Weisz, Arina D. Omer, Weijie Yao, Zane Colaric, Parwinder Kaur, Judy St. Leger, Qing Nie, Alexandria Mena, Joseph P. Flanagan, Greta Keller, Thomas Sanger, Bruce Ostrow, Maksim V. Plikus and Evgeny Z. Kvon.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R35GM133758, UM1HG009375, RM1HG011016-01A1, F32 GM139240-01, T32GM007388, R01-AR079150); the Searle Scholars Program; the Sloan Foundation and the Vallee Scholars Program; the Welch Foundation (Q-1866), the U.S.-Israel Binational Science Foundation (2019276); the National Science Foundation (DGE-2039656, NSF DBI-2021795, NSF PHY-2210291); the LEO Foundation (LF-AW-RAM-19-400008, LF-OC-20-000611); and the W.M. Keck Foundation (WMKF-5634988).
# # #
END
Scientists unveil genetics behind development of gliding
A key gene helps explain how the ability to glide has emerged over-and-over during marsupial evolution
2024-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Safety of ancestral monovalent COVID-19 vaccines in children
2024-04-24
About The Study: In this cohort study of pediatric enrollees across three commercial health insurance databases, statistical signals detected for myocarditis or pericarditis after BNT162b2 (ages 12-17 years) were consistent with previous reports, and seizures after BNT162b2 (ages 2-4 years) and mRNA-1273 vaccinations (ages 2-5 years) should be further investigated in a robust epidemiologic study with confounding adjustment. The Food and Drug Administration concludes that the known and potential benefits of COVID-19 vaccination outweigh the known and potential risks of COVID-19 infection.
Authors: Patricia C. Lloyd, Ph.D., Sc.M., of the Food and Drug Administration in Silver ...
Reversals in the decline of heart failure mortality in the US
2024-04-24
About The Study: This analysis shows that declines in heart failure-related mortality from 1999 to 2012 have been entirely undone by reversals from 2012 to 2021, meaning that contemporary heart failure mortality rates are higher than in 1999. The origins of these reversals preceded the COVID-19 pandemic, although the larger increases in 2020 to 2021 indicate that the pandemic may have accelerated them due to limitations to health care access and possible cardiac involvement.
Authors: Marat Fudim, M.D., M.H.S., of Duke University in Durham, North Carolina, is the ...
Recreational marijuana laws and teen marijuana use, 1993-2021
2024-04-24
About The Study: In this repeated cross-sectional study, there was no evidence that recreational marijuana laws were associated with encouraging youth marijuana use, based on both the logistic regression and interaction-weighted models.
Authors: D. Mark Anderson, Ph.D., of Montana State University in Bozeman, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.0698)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
Manchester scientists found novel one-dimensional superconductor
2024-04-24
In a significant development in the field of superconductivity, researchers at The University of Manchester have successfully achieved robust superconductivity in high magnetic fields using a newly created one-dimensional (1D) system. This breakthrough offers a promising pathway to achieving superconductivity in the quantum Hall regime, a longstanding challenge in condensed matter physics.
Superconductivity, the ability of certain materials to conduct electricity with zero resistance, holds profound potential for advancements of quantum technologies. However, achieving superconductivity in the quantum Hall regime, characterised by quantised electrical conductance, has proven to be a mighty ...
Tumor cells evade the immune system early on: Newly discovered mechanism could significantly improve cancer immunotherapies
2024-04-24
Tumors actively prevent the formation of immune responses by so-called cytotoxic T cells, which are essential in combating cancer. Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU) Hospital have now uncovered for the first time how this exactly happens. The study in the journal Nature provides rationales for new cancer immunotherapies and could make existing treatments more effective. A second paper in Nature confirms the findings.
In cancer, tumors often impair the body's immune response. For example, they can prevent immune cells from perceiving cancer cells as a threat or render them inactive. Immunotherapies aim ...
Children with skin diseases suffer stigma, bullying and depression
2024-04-24
· 73% of children with skin disease experience stigma and poor quality of life
· ‘Chronic skin conditions can be tremendously life-altering’
· Shame during childhood can affect them throughout their lives, dermatologist says
CHICAGO --- The majority of children and teens with chronic skin diseases such as acne, eczema, psoriasis, alopecia areata (hair loss) and vitiligo (pigment loss) feel stigmatized by peers for their condition and are sometimes bullied, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study. As a result, these children have a ...
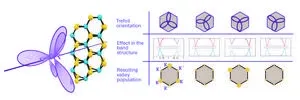
A novel universal light-based technique to control valley polarization in bulk materials
2024-04-24
Electrons inside solid materials can only take certain values of energy. The allowed energy ranges are called “bands” and the space between them, the forbidden energies, are known as “band-gaps”. Both of them together constitute the “band structure” of the material, which is a unique characteristic of each specific material.
When physicists plot the band structure, they usually see that the resulting curves resemble mountains and valleys. In fact, the technical term for a local energy maximum or minimum in the bands is called a “valley”, and the field which studies and exploits how electrons in the material ...
Vast DNA tree of life for flowering plants revealed by global science team
2024-04-24
Images
The most up-to-date understanding of the flowering plant tree of life is presented in a new study published today in the journal Nature by an international team of 279 scientists, including three University of Michigan biologists.
Using 1.8 billion letters of genetic code from more than 9,500 species covering almost 8,000 known flowering plant genera (ca. 60%), this achievement sheds new light on the evolutionary history of flowering plants and their rise to ecological dominance on Earth.
Led by scientists at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, the research team believes ...
Mini-colons revolutionize colorectal cancer research
2024-04-24
As our battle against cancer rages on, the quest for more sophisticated and realistic models to study tumor development has never been more critical. Until now, research has relied on animal models and simplified cell culture methods, which are valuable but cannot fully capture the complex interplay of factors involved in tumor development.
Even newer, more advanced models for studying cancer, such as organoids – tiny, lab-grown versions of organs – do not faithfully replicate the cell behaviors and tissue architectures seen in actual tumors.
This gap has significantly hindered our understanding ...
Lead-vacancy centers in diamond as building blocks for large-scale quantum networks
2024-04-24
Much like how electric circuits use components to control electronic signals, quantum networks rely on special components and nodes to transfer quantum information between different points, forming the foundation for building quantum systems. In the case of quantum networks, color centers in diamond, which are defects intentionally added to a diamond crystal, are crucial for generating and maintaining stable quantum states over long distances.
When stimulated by external light, these color centers in diamond emit photons carrying information about their internal electronic states, especially the spin states. The interaction between the emitted photons and the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
Lower music volume levels in fitness class and perceived exercise intensity
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
Share of migratory wild animal species with declining populations despite UN treaty protections worsens from 44% to 49% in two years; 24% face extinction, up 2%
One in 20 babies experiences physical abuse, global review finds
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
[Press-News.org] Scientists unveil genetics behind development of glidingA key gene helps explain how the ability to glide has emerged over-and-over during marsupial evolution