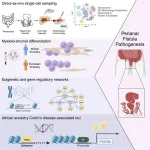
(Press-News.org) Mount Sinai researchers have published the first study to use single-cell analysis in identifying several pathophysiological mechanisms of abnormal passageways in the digestive system known as perianal fistulae, a common complication of Crohn’s disease. These findings were published in the journal Med on April 24.
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes chronic inflammation at any part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and impacts more than half a million people in the United States. Perianal fistulae, abnormal connections between the anal canal and perianal skin, are a common complication of Crohn’s disease that often result in painful abscesses and impact patients’ quality of life.
This Mount Sinai study is the first to apply single-cell transcriptomics of perianal fistulous tracts, and to recruit Black patients with the chronic condition for a diverse and comprehensive study cohort. Patients with African ancestry have been substantially underrepresented in genome-wide association studies of Crohn’s disease, and inflammatory bowel disease overall, reflecting in part the lower prevalence of Crohn’s disease in African American populations compared to patients with European ancestry. However, patients of African ancestry are about twice as likely to have perianal fistulae, according to studies in adult and pediatric populations.
The researchers profiled more than 140,000 single cells from diverse Crohn’s disease patients with perianal fistulae. The team identified several key pathways underlying fistulizing Crohn’s disease, including cellular aging and loss of proliferation, reaction to microenvironmental stimuli, and a destructive gene signature in connective tissues that is unique to perianal fistulae. The researchers also determined that subpopulations of fibroblasts—cells forming the connective tissues—with this destructive gene signature may originate from mononuclear cells in the immune system, a phenomenon observed in greater magnitude from patients with African ancestry. The experts found evidence for key transcription factor binding events in relevant gene promoter regions that suggests a potential epigenetic phenomenon underlying this apparent difference in cell behavior between patients of African and European ancestry.
“Circulating blood monocytes can traffic to disease tissues and form a critical first step in fighting microbes throughout the body,” said corresponding author Judy H. Cho, MD, Dean and Ward-Coleman Chair in Translational Genetics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. “In this study, we have defined population-specific differences in how blood monocytes respond, which contribute to the higher rates of perianal fistulous complications in African American patients with Crohn’s disease.”
A range of anti-inflammatory medications can treat Crohn’s disease, but they show limited efficacy for closure of perianal fistula tracts. In severe cases, patients may require surgical removal of all or part of the rectum. But researchers said their findings provide avenues to identify new therapeutic options. The team said future studies should examine similar epigenetic patterns in white blood cells of the immune system from diverse, healthy patients and from patients with other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases to further explore the role of the transcription factor underlying race or ancestry-based disparities.
“We have leveraged transcriptomic, epigenetic, genetic, cellular, and tissue-based data from patients with a history of this devastating complication to better understand reasons for the discrepancy in prevalence between Black and white patients,” said first author Rachel M. Levantovsky, PhD, who is working on her MD in the Mount Sinai Medical Scientist Training Program. “Our discovery of unique fistula fibroblasts, distinct monocyte differentiation in African-ancestry individuals, and key transcription factor binding events helps us illuminate mechanistic underpinnings of perianal fistula—critical for the optimization of future treatment.”
The study was supported by funding from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases at the National Institutes of Health (U01DK062422, U24DK062429, R01DK123758, and F30DK127736), Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust, Sanford J. Grossman Charitable Trust, and David and Margot Lowy Foundation Trust.
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with more than 43,000 employees working across eight hospitals, more than 400 outpatient practices, more than 600 labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it. Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 11 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report’s® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2023-2024.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.
END
Mount Sinai researchers the first to apply single-cell analysis to reveal mechanisms of a common complication of Crohn’s disease
2024-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists unveil genetics behind development of gliding
2024-04-24
HOUSTON – (April 24, 2024) – People say “When pigs fly” to describe the impossible. But even if most mammals are landlubbers, the ability to glide or fly has evolved again and again during mammalian evolution, in species ranging from bats to flying squirrels. How did that come about? In a study published in the journal Nature this week, a team of researchers led by Princeton University and Baylor College of Medicine explains the genomic and developmental basis of the patagium, the thin skin membrane that allows some mammalian species to soar through the air.
“We don't quite understand how novel traits and adaptations originate from a molecular ...
Safety of ancestral monovalent COVID-19 vaccines in children
2024-04-24
About The Study: In this cohort study of pediatric enrollees across three commercial health insurance databases, statistical signals detected for myocarditis or pericarditis after BNT162b2 (ages 12-17 years) were consistent with previous reports, and seizures after BNT162b2 (ages 2-4 years) and mRNA-1273 vaccinations (ages 2-5 years) should be further investigated in a robust epidemiologic study with confounding adjustment. The Food and Drug Administration concludes that the known and potential benefits of COVID-19 vaccination outweigh the known and potential risks of COVID-19 infection.
Authors: Patricia C. Lloyd, Ph.D., Sc.M., of the Food and Drug Administration in Silver ...
Reversals in the decline of heart failure mortality in the US
2024-04-24
About The Study: This analysis shows that declines in heart failure-related mortality from 1999 to 2012 have been entirely undone by reversals from 2012 to 2021, meaning that contemporary heart failure mortality rates are higher than in 1999. The origins of these reversals preceded the COVID-19 pandemic, although the larger increases in 2020 to 2021 indicate that the pandemic may have accelerated them due to limitations to health care access and possible cardiac involvement.
Authors: Marat Fudim, M.D., M.H.S., of Duke University in Durham, North Carolina, is the ...
Recreational marijuana laws and teen marijuana use, 1993-2021
2024-04-24
About The Study: In this repeated cross-sectional study, there was no evidence that recreational marijuana laws were associated with encouraging youth marijuana use, based on both the logistic regression and interaction-weighted models.
Authors: D. Mark Anderson, Ph.D., of Montana State University in Bozeman, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.0698)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
Manchester scientists found novel one-dimensional superconductor
2024-04-24
In a significant development in the field of superconductivity, researchers at The University of Manchester have successfully achieved robust superconductivity in high magnetic fields using a newly created one-dimensional (1D) system. This breakthrough offers a promising pathway to achieving superconductivity in the quantum Hall regime, a longstanding challenge in condensed matter physics.
Superconductivity, the ability of certain materials to conduct electricity with zero resistance, holds profound potential for advancements of quantum technologies. However, achieving superconductivity in the quantum Hall regime, characterised by quantised electrical conductance, has proven to be a mighty ...
Tumor cells evade the immune system early on: Newly discovered mechanism could significantly improve cancer immunotherapies
2024-04-24
Tumors actively prevent the formation of immune responses by so-called cytotoxic T cells, which are essential in combating cancer. Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU) Hospital have now uncovered for the first time how this exactly happens. The study in the journal Nature provides rationales for new cancer immunotherapies and could make existing treatments more effective. A second paper in Nature confirms the findings.
In cancer, tumors often impair the body's immune response. For example, they can prevent immune cells from perceiving cancer cells as a threat or render them inactive. Immunotherapies aim ...
Children with skin diseases suffer stigma, bullying and depression
2024-04-24
· 73% of children with skin disease experience stigma and poor quality of life
· ‘Chronic skin conditions can be tremendously life-altering’
· Shame during childhood can affect them throughout their lives, dermatologist says
CHICAGO --- The majority of children and teens with chronic skin diseases such as acne, eczema, psoriasis, alopecia areata (hair loss) and vitiligo (pigment loss) feel stigmatized by peers for their condition and are sometimes bullied, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study. As a result, these children have a ...
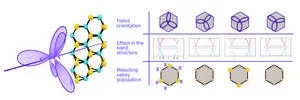
A novel universal light-based technique to control valley polarization in bulk materials
2024-04-24
Electrons inside solid materials can only take certain values of energy. The allowed energy ranges are called “bands” and the space between them, the forbidden energies, are known as “band-gaps”. Both of them together constitute the “band structure” of the material, which is a unique characteristic of each specific material.
When physicists plot the band structure, they usually see that the resulting curves resemble mountains and valleys. In fact, the technical term for a local energy maximum or minimum in the bands is called a “valley”, and the field which studies and exploits how electrons in the material ...
Vast DNA tree of life for flowering plants revealed by global science team
2024-04-24
Images
The most up-to-date understanding of the flowering plant tree of life is presented in a new study published today in the journal Nature by an international team of 279 scientists, including three University of Michigan biologists.
Using 1.8 billion letters of genetic code from more than 9,500 species covering almost 8,000 known flowering plant genera (ca. 60%), this achievement sheds new light on the evolutionary history of flowering plants and their rise to ecological dominance on Earth.
Led by scientists at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, the research team believes ...
Mini-colons revolutionize colorectal cancer research
2024-04-24
As our battle against cancer rages on, the quest for more sophisticated and realistic models to study tumor development has never been more critical. Until now, research has relied on animal models and simplified cell culture methods, which are valuable but cannot fully capture the complex interplay of factors involved in tumor development.
Even newer, more advanced models for studying cancer, such as organoids – tiny, lab-grown versions of organs – do not faithfully replicate the cell behaviors and tissue architectures seen in actual tumors.
This gap has significantly hindered our understanding ...