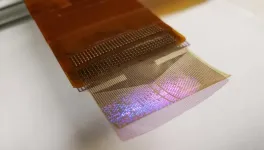
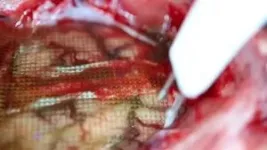
(Press-News.org) A thin film that combines an electrode grid and LEDs can both track and produce a visual representation of the brain’s activity in real-time during surgery–a huge improvement over the current state of the art. The device is designed to provide neurosurgeons visual information about a patient’s brain to monitor brain states during surgical interventions to remove brain lesions including tumors and epileptic tissue.
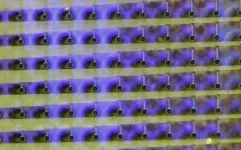
Each LED in the device mirrors the activity of a few thousand neurons. In a series of proof-of-concept experiments in rodents and large non-primate mammals, researchers showed that the device can effectively track and display neural activity in the brain corresponding to different areas of the body. In this case, the LEDs developed by the team light up red in the areas that need to be removed by the surgeon. Surrounding areas that control critical functions and should be avoided show up in green.
The study also showed that the device can visualize the onset and map the propagation of an epileptic seizure on the surface of the brain. This would allow physicians to isolate the ‘nodes’ of the brain that are involved in epilepsy. It also would allow physicians to deliver necessary treatment by removing tissue or by using electrical pulses to stimulate the brain.
“Neurosurgeons could see and stop a seizure before it spreads, view what brain areas are involved in different cognitive processes, and visualize the functional extent of tumor spread. This work will provide a powerful tool for the difficult task of removing a tumor from the most sensitive brain areas,” said Daniel Cleary, one of the study’s coauthors, a neurosurgeon and assistant professor at Oregon Health and Science University. Cleary was a medical resident and a postdoctoral researcher at the University of California San Diego.
The device was conceived and developed by a team of engineers and physicians from University of California San Diego and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and was led by Shadi Dayeh, the paper’s corresponding author and a professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at UC San Diego. The team describes their work in the April 24 issue of the journal Science Translational Medicine.
During brain surgery, physicians need to map brain function to define which areas of the organ control critical functions and can’t be removed. Currently, neurosurgeons work with a team of electrophysiologists during the procedure. But that team and their monitoring equipment are located in a different part of the operating room. Brain areas that need to be protected and those that need to be operated on are either marked by electrophysiologists on a paper that is brought to the surgeon or communicated verbally to the surgeon, who then places sterile papers on the brain surface to mark these regions. “Both are inefficient ways of communicating critical information during a procedure, and could impact its outcomes,” said Dr. Angelique Paulk of MGH, who is a co-author and co-inventor of the technology.
In addition, the electrodes currently used to monitor brain activity during surgery do not produce detailed fine grained data. So surgeons need to keep a buffer zone, known as resection margin, of 5 to 7 millimeters (about ¼ of an inch) around the area they are removing inside the brain. This means that they might leave some harmful tissue in. The new device provides a level of detail that would shrink this buffer zone to less than a millimeter.
“We invented the brain microdisplay to display with precision critical cortical boundaries and to guide neurosurgery in a cost-effective device that simplifies and reduces the time of brain mapping procedures,” said Shadi Dayeh, the paper’s corresponding author and a professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering.
Researchers installed the LEDs on top of another innovation from the Dayeh lab, the platinum nanorod electrode grid (PtNRGrid). Using the PtNRGrids since 2019, Dayeh’s team pioneered human brain and spinal cord mapping with thousands of channels to monitor brain neural activity. They reported early safety and effectiveness results in a series of articles in Science Translational Medicine in 2022 in tens of human subjects. (New sensor grids record human brain signals with record breaking resolution and Microelectrode array can enable safer spinal cord surgery)--ahead of Neuralink and other companies in this space.
The PtNRGrid also includes perforations, which enable physicians to insert probes to stimulate the brain with electrical signals, both for mapping and for therapy.
How it’s made
Dayeh and his team used their expertise in working with Gallium Nitride to develop a manufacturing technique for high-efficiency LEDs that do not heat up when they light up and do not damage brain tissues. The material itself is grown on a flat and rigid substrate called Qromis substrate technology. Dayeh’s team at UC San Diego was able to embed thousands of LEDs in flexible films and release them from the substrate in the form of a flexible display panel. Researchers then used inkjet printing to deposit quantum dot inks on the surface of the LEDs to convert their blue light to multiple other colors. “This enables richer and more nuanced visual representation of neural activity patterns,” said Dayeh.
“These Gallium nitride-based inorganic micro-LEDs, substantially brighter and power-efficient than organic LEDs, can maintain clear visibility under surgical lights that may exceed the brightness of direct sunlight. The iEEG microdisplay, just a few tens of microns thick, captures brain activity at 20,000 samples per second across thousands of channels and visualizes it at a video rate of 40 Hz. This enables precise and real-time displays of cortical dynamics during critical surgical interventions,” said Youngbin Tchoe, the first author and co-inventor, formerly a postdoc in the Dayeh group at UC San Diego and now an assistant professor at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology.
The microdisplays measure 5 by 5 square millimeters and 32 by 32 square millimeters and include either 1024 or 2048 of these LEDs, laminated on the back of the PtNRGrid. In addition to the LEDs, the device includes acquisition and control electronics as well as software drivers to analyze and project cortical activity directly from the surface of the brain.
“The brain iEEG-microdisplay can impressively both record the activity of the brain to a very fine degree and display this activity for a neurosurgeon to use in the course of surgery. We hope that this device will ultimately lead to better clinical outcomes for patients with its ability to both reveal and communicate the detailed activity of the underlying brain during surgery,” said study coauthor Jimmy Yang, a neurosurgeon and assistant professor at The Ohio State University.
Next steps
Dayeh’s team is working to build a microdisplay that will include 100,000 LEDs, with a resolution equivalent to that of a smartphone screen. Each LED in those displays would reflect the activity of a few hundred neurons. These brain microdisplays will cost a fraction of a high-end smartphone.
This brain microdisplay will also include a foldable portion. This would allow surgeons to operate within the foldable portion and monitor the impact of the procedure as the other, unfolded portion of the microdisplay shows the status of the brain in real time.
Researchers are also working on one limitation of the study. The close proximity of the LED sensors and the PtNRGrids led to a slight interference and noise in the data. The team plans to build customized hardware to change the frequency of the pulses that turn on the LEDs to make it easier to screen out that signal, which is not relevant to the brain’s electrical activity.
The work was supported by the National Institutes of Health primarily by Dayeh’s Director’s New Innovator Award No. NIBIB DP2-EB029757 titled “Bringing Light to Functional Mapping in Resective Neurosurgery”. The research was supported in part by the BRAIN® Initiative NIH grants R01NS123655, K99NS119291, UG3NS123723, and 5R01NS109553.
The brain microdisplay was fabricated in the Nano3 cleanroom facilities at UC San Diego’s Qualcomm Institute and was tested in large mammals at UC San Diego’s Center of the Future of Surgery.
An electroencephalogram microdisplay to visualize neuronal activity on the brain surface
Youngbin Tchoe, Tianhai Wu, Hoi Sang U, David M Roth, Dogwood Kin, Jiwan Lee, Patricia Pizarro, Karen J. Tonsfeldt, Keundong Lee, Po Chun Chen, Andrew M. Bourhis, Ian Galton, Eric Halgren, Shadi A. Dayeh: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, UC San Diego
Dayeh also has an appointment in the Department of Neurological Surgery at UC San Diego.
Youngbin Tchoe, now at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea
David M. Roth, Department of Anesthesiology, UC San Diego
Daniel R. Cleary, Oregon Health and Science University
Brian Coughlin, Angelique Paulk and Sydney Cash, Department of Neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital
Jimmy Yang, Department of Neurological Surgery, The Ohio State University
Karen Tonsfeld, Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences at the Center for Reproductive Science and Medicine at UC San Diego
Eric Halgren, Departments of Radiology and Neurosciences, UC San Diego
UC San Diego and Massachusetts General Hospital have filed a provisional patent application on the device. Tchoe, Cleary, Paulk, Halgren, Cash and Dayeh have equity in Cortical Sciences Inc, which was cofounded by the team to commercialize PtNRGrids. Dayeh was a paid consultant to MaXentric Technologies. Cleary and Tonsfeld have equity in Surgical Simulations LLC. The MGH Translational Research Center has clinical research support agreements with Neuralink, Paradromics and Synchorn, for which Cash provides consultative input.
END
A flexible microdisplay can monitor brain activity in real-time during brain surgery
The device represents a huge leap ahead to visualize brain activity to guide neurosurgeons
2024-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Diversity and productivity go branch-in-branch
2024-04-24
Kyoto, Japan -- Climate change can be characterized as the Grim Reaper or some other harbinger of dire times for humanity and natural environment, including forests. Previous studies reporting a decline in forest productivity due to climate warming and long-term drought may suggest that trees' survival hangs in the balance.
Now, a study by an international group, including Kyoto University, found that forests with higher trait diversity not only adapt better to climate change but may also thrive.
The study, conducted by researchers from Lakehead ...
Color variants in cuckoos: the advantages of rareness
2024-04-24
Every cuckoo is an adopted child – raised by foster parents, into whose nest the cuckoo mother smuggled her egg. The cuckoo mother is aided in this subterfuge by her resemblance to a bird of prey. There are two variants of female cuckoos: a gray morph that looks like a sparrowhawk, and a rufous morph. Male cuckoos are always gray.
“With this mimicry, the bird imitates dangerous predators of the host birds, so that they keep their distance instead of attacking,” says Professor Jochen Wolf from LMU Munich. Together with researchers at CIBIO (Centro de Investigação ...
Laser technology offers breakthrough in detecting illegal ivory
2024-04-24
A new way of quickly distinguishing between illegal elephant ivory and legal mammoth tusk ivory could prove critical to fighting the illegal ivory trade. A laser-based approach developed by scientists at the Universities of Bristol and Lancaster, could be used by customs worldwide to aid in the enforcement of illegal ivory from being traded under the guise of legal ivory. Results from the study are published in PLOS ONE today [24 April].
Despite the Convention on the International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) ban on ivory, poaching associated with its illegal trade has ...
Why can’t robots outrun animals?
2024-04-24
Robotics engineers have worked for decades and invested many millions of research dollars in attempts to create a robot that can walk or run as well as an animal. And yet, it remains the case that many animals are capable of feats that would be impossible for robots that exist today.
“A wildebeest can migrate for thousands of kilometres over rough terrain, a mountain goat can climb up a literal cliff, finding footholds that don't even seem to be there, and cockroaches can lose a leg and not slow down,” ...
After spinal cord injury, neurons wreak havoc on metabolism
2024-04-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Conditions such as diabetes, heart attack and vascular diseases commonly diagnosed in people with spinal cord injuries can be traced to abnormal post-injury neuronal activity that causes abdominal fat tissue compounds to leak and pool in the liver and other organs, a new animal study has found.
After discovering the connection between dysregulated neuron function and the breakdown of triglycerides in fat tissue in mice, researchers found that a short course of the drug gabapentin, commonly prescribed for nerve pain, prevented ...
Network model unifies recency and central tendency biases
2024-04-24
Neuroscientists have revealed that recency bias in working memory naturally leads to central tendency bias, the phenomenon where people’s (and animals’) judgements are biased towards the average of previous observations. Their findings may hint at why the phenomenon is so ubiquitous.
Researchers in the Akrami Lab at the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre at UCL and the Clopath Lab at Imperial College London developed a network model with a working memory module and another accounting for sensory histories. The study, published in eLife, describes how the model shows neural circuits ...
Ludwig Lausanne scientists identify and show how to target a key tumor defense against immune attack
2024-04-24
April 24, 2024, NEW YORK – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has discovered how a lipid molecule found at high levels within tumors undermines the anti-cancer immune response and compromises a recently approved immunotherapy known as adoptive cell therapy (ACT) using tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, or TIL-ACT. In this individualized cell therapy, TILs—CD8+ T cells that kill cancer cells—are expanded in culture from a patient’s tumor samples and reinfused into the patient as a treatment.
Researchers led by Ludwig Lausanne’s Matteo ...
Can climate change accelerate transmission of malaria? Pioneering research sheds light on impacts of temperature
2024-04-24
In 2022, an estimated 249 million malaria cases killed 608,000 people in 85 countries worldwide including the United States, according to the World Health Organization.
Malaria continues to pose a considerable public health risk in tropical and subtropical areas, where it impacts human health and economic progress.
Despite concerns about the potential impact of climate change on increasing malaria risk, there is still limited understanding of how temperature affects malaria transmission – until now.
Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease caused by a parasite that spreads from bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. If left untreated in humans, malaria can cause severe symptoms, ...
A new attempt to identify salt gland development and salt resistance genes of Limonium bicolor ——Identification of bHLH gene family and its function analysis in salt gland development
2024-04-24
The secondary salinization of saline-alkali land is increasing globally. It is of strategic significance to explore the salt-tolerant molecular mechanism of halophytes and cultivate saline-alkali resistant crops for the improvement of saline-alkali land. The recretohalophyte Limonium bicolor has a unique salt-secreting structure, salt gland, which can directly excrete Na+ out of the body to effectively avoid salt stress. Exploring the development mechanism of salt gland structure in recretohalophyte is of great significance for analyzing the development of plant epidermis structure and improving the salt-resistant mechanism of plants.
Recently, Wang ...
The SAPIENS Podcast named finalist at the 16th Annual Shorty Awards
2024-04-24
SAPIENS: A Podcast for Everything Human has been named as a 16th Annual Shorty Awards finalist in the Science and Technology Podcast Category.
The Shorty Awards honor the best work in digital and social media by the most creative and influential brands, agencies, organizations, and individuals whose work has excelled in creativity, strategy, and effectiveness.
SAPIENS’s work has demonstrated outstanding performance across the judging criteria, which makes it a top contender for a Shorty Award in a most competitive year. The work is also eligible for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
[Press-News.org] A flexible microdisplay can monitor brain activity in real-time during brain surgeryThe device represents a huge leap ahead to visualize brain activity to guide neurosurgeons