(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS – Clinical trials are constantly being designed and study participants enrolled to determine if medical treatments and therapies are safe and effective. Much has been written about the importance of including diverse populations in these trials.
However, the nearly 1.4 million individuals who live in the 15,600 nursing homes across the U.S. have been largely left out of clinical trials, despite the prevalence of such common conditions as hypertension, depression, diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease in this population.
A commentary by faculty of Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University, UCLA and the universities of North Carolina, Colorado and Massachusetts, published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society (JAGS), focuses on the importance of including nursing home residents, a population with significant medical complexity, in clinical trials. The essay highlights the benefits and challenges of conducting research on medical therapies in nursing homes. The authors identify key elements for successful nursing home clinical trials and propose a nursing home clinical trials network, noting that ensuring diversity, equity and inclusion in any trial design is imperative.
“Among the questions we want to ask are: Is this therapy appropriate for a nursing home population? Does it work in a nursing home population but are there issues around implementation? Are there challenges to delivering it in a nursing home setting?” notes corresponding author Kathleen Unroe, M.D., MHA, M.S., a Regenstrief Institute and IU School of Medicine researcher-clinician. “Nursing homes were not built to facilitate research. We as researchers need to fit in. We need to appreciate the realities of providing clinical care in this setting and adjust and adapt our protocols to work within that system.”
Among the topics discussed in the commentary:
The need for clinical trials in nursing homes
Gaps that can be filled with these clinical trials
Challenges conducting these clinical trials
Next steps in conducting clinical trials in nursing homes
A framework for making a nursing home clinical trials network a reality
“It is imperative that we build the science of nursing home care around testing, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. It is a unique setting that merits more focus given the essential role it plays in the continuum of care for seriously ill adults,” said commentary co-author Susan Hickman, PhD, director of Regenstrief Institute’s Center for Aging Research and a faculty member of IU schools of nursing and medicine.
Citing a missed opportunity, the authors write, “Inclusion of nursing home residents in COVID-19 therapeutics trials might have identified specific issues relating to dosing, administration and monitoring, spurred creation of training materials specifically for nursing home staff, and promoted the development of consistent policies to identify appropriate candidates and deliver treatments promptly, safely, and optimally.”
Dr. Unroe adds, “Nursing home residents should have access to evidence-based therapies. When we choose not to do the hard work to test them in the nursing home setting, we are setting ourselves up for a much more difficult implementation.” She notes that “Conducting trials in the nursing home may generate generalizable knowledge that also would be highly relevant to people who are cared for in assisted living facilities or even the broader geriatric population living at home.”
"Evaluation of medical therapies in the nursing home population: Gaps, challenges, and next steps” is part of a JAGS special collection, "A changing landscape for evaluation of new therapies for older adults and diverse populations: National and international perspectives."
Authors and affiliations:
Kathleen T. Unroe MD, MHA, MS1,2,3| Debra Saliba MD, MPH, AGSF4,5,6,7|Susan E. Hickman PhD2,3,8| Sheryl Zimmerman PhD9,10,11|Cari Levy MD, PhD12,13| Jerry Gurwitz MD14
1Division of General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA
2Indiana University Center for Aging Research, Regenstrief Institute Inc., Indianapolis, Indiana, USA
3Research in Palliative and End-of-Life Communication and Training (RESPECT) Center, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA
4US Department of Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System (VAGLAS) Health Services Research and Development Service (HSR&D) Center of Innovation, Los Angeles, California, USA
5David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, California, USA
6Anna and Harry Borun Center for Gerontological Research, University of California Division of Geriatrics, Los Angeles, California, USA
7RAND Corporation, Santa Monica, California, USA
8Indiana University School of Nursing, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA
9School of Social Work, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, USA
10Cecil G. Sheps Center for Health Services Research, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, USA
11Center for Excellence in Assisted Living (CEAL), School of Social Work, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, USA
12Division of Geriatric Medicine, University of Colorado School of Medicine Anschutz Campus, Aurora, Colorado, USA
13Denver Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Aurora, Colorado, USA
14Division of Geriatric Medicine, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, USA
Kathleen T. Unroe, M.D., MHA, M.S.
In addition to being a research scientist with the Indiana University Center for Aging Research at Regenstrief Institute, Kathleen Unroe, M.D., MHA, M.S., is an associate professor of medicine at Indiana University School of Medicine and a practicing geriatrician. Dr. Unroe is the founder and an executive officer of Probari, a healthcare start-up supporting nursing home care.
Susan Hickman, PhD
In addition to serving as director and a research scientist with the Indiana University Center for Aging Research at Regenstrief Institute, Susan Hickman, PhD, is a professor at Indiana University School of Nursing, a professor of medicine and the Cornelius and Yvonne Pettinga Professor of Aging Research at Indiana University School of Medicine and co-director of the IU Indianapolis Research in Palliative and End-of-Life Communicating and Training (RESPECT) Signature Center.
END
Expanding health equity by including nursing home residents in clinical trials
2024-04-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Identification and exploration of transcripts involved in antibiotic resistance mechanism of two critical superbugs
2024-04-29
Background and objectives
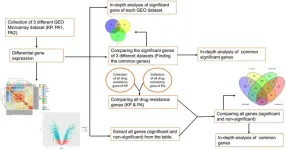
Infectious diseases caused by pathogenic strains of bacteria are a global cause of morbidity and mortality. Hospital-acquired infections caused by Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were found vulnerable during the COVID-19 pandemic. They are also responsible for the onset of certain life-threatening infectious diseases such as cystic fibrosis, endocarditis, bacteremia, and sepsis. Looking into the importance of these two superbugs there is a strong need for extensive comparative differential gene expression analysis ...
Quantum fiber optics in the brain enhance processing, may protect against degenerative diseases
2024-04-29
WASHINGTON, DC – (April 26, 2024) The effects of quantum mechanics—the laws of physics that apply at exceedingly small scales—are extremely sensitive to disturbances. This is why quantum computers must be held at temperatures colder than outer space, and only very, very small objects, such as atoms and molecules, generally display quantum properties. By quantum standards, biological systems are quite hostile environments: they’re warm and chaotic, and even their fundamental components—such as cells—are considered very large.
But ...
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai names Miriam Merad, MD, PhD, as Dean for Translational Research and Therapeutic Innovation
2024-04-29
New York, NY [April 29, 2024]—Miriam Merad, MD, PhD, a world-renowned immunologist, has been appointed Dean for Translational Research and Therapeutic Innovation of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The appointment reaffirms Icahn Mount Sinai’s commitment to pioneering medical progress and catalyzing the rapid advancement of research innovation.
Dr. Merad, the Mount Sinai Professor in Cancer Immunology, will also continue to serve as the founding Chair of the Department of Immunology and Immunotherapy, Director of the Marc and Jennifer Lipschultz Precision Immunology Institute, and Director ...
Details of hurricane Ian’s aftermath captured with new remote sensing method
2024-04-29
Category 4 Hurricane Ian made landfall in Florida’s Lee County on Sept. 28, 2022, battering the region with wind speeds of 155 miles per hour and storm surge up to 13 feet – the highest storm surge documented in Southwest Florida in the past 150 years.
In the aftermath of a disaster, rapidly assessing damage is critical for rescue, recovery and emergency planning. Damage assessments are typically conducted through field reconnaissance deployments, which can be labor-intensive, costly and risky. Moreover, field-based emergency response ...
Robots can’t outrun animals. A new study explores why
2024-04-29
The question may be the 21st century’s version of the fable of the tortoise and the hare: Who would win in a foot race between a robot and an animal?
In a new perspective article, a team of engineers from the United States and Canada, including University of Colorado Boulder roboticist Kaushik Jayaram, set out to answer that riddle. The group analyzed data from dozens of studies and came to a resounding “no.” In almost all cases, biological organisms, such as cheetahs, cockroaches and even humans, seem to be able to outrun their robot counterparts.
The researchers, led by Samuel Burden at the University of Washington and ...
The Human Immunome Project unveils scientific plan to decode and model the immune system
2024-04-29
NEW YORK, April 29, 2024 – The Human Immunome Project (HIP), a global nonprofit scientific initiative, released its Scientific Plan today, on World Immunology Day, the organization announced. The plan provides a detailed roadmap of how the Human Immunome Project and its network of global study sites will generate the world’s largest and most diverse immunological dataset and use these data to power publicly available AI models of the immune system.
“The immune system is the epicenter of human health, and our newly released ...
New research funding awarded to assess the role of race in predicting heart disease
2024-04-29
Highlights:
The American Heart Association awarded four new scientific research grants to evaluate the role of race in measuring heart disease risk.
The funded studies are focused on multi-ethnic groups and studying how race, considered a social rather than biological construct, affects health risk prediction when it is incorporated as a variable in algorithms.
This research is funded by a grant from the Doris Duke Foundation to study the complex issue of how race and ethnicity, when factored into cardiovascular clinical care algorithms ...
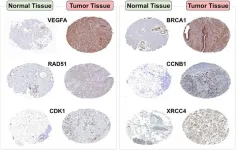
Exploring the role of seven key genes in breast cancer: insights from in silico and in vitro analyses
2024-04-29
Background and objectives
Breast cancer remains a significant global health concern, warranting further exploration into its genetic basis and potential therapeutic targets. This study aimed to elucidate the genetic associations of seven pivotal genes with breast cancer and discern their potential role in disease prognosis.
Methods
The genes VEGFA, BRCA1, RAD51, CCNB1, CHEK1, CDK1, and XRCC4 were curated from over 30 articles. Their association with breast cancer was analyzed using both in silico and in vitro techniques. The in silico assessment ...
The therapeutic effects of baicalein on the hepatopulmonary syndrome in the rat model of chronic common bile duct ligation
2024-04-29
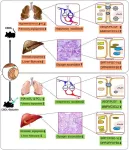
Background and Aims
Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) is characterized by arterial oxygenation defects due to pulmonary vascular dilation in liver disease. To date, liver transplantation remains the only effective treatment for HPS. This study aimed to explore the preventative role of baicalein in HPS development.
Methods
Sixty male rats were randomly assigned to three groups: sham, common bile duct ligation (CBDL), and baicalein, receiving intraperitoneal injections of baicalein (40 mg·kg−1·d−1, diluted in saline) for 21 days. Survival rate, liver and kidney function, and bile acid metabolism levels were evaluated. Liver and lung angiogenesis ...
Development and characterization of honey-containing nanoemulsion for topical delivery
2024-04-29
Background and objectives
Honey is a viscous, hygroscopic liquid in nature. It has the ability to treat wounds, wrinkles, aging, and inflammation. This study’s objective was to create and characterize a nanoemulsion containing honey and evaluate its stability.
Methods
A pseudo-ternary phase diagram was retraced with several concentrations of the Smix, water, and liquid paraffin oil to formulate nanoemulsions containing honey. From the results of pre-formulation stability studies, formulation HNE-19, with a hydrophilic lipophilic balance ...