(Press-News.org) Natural scenery typically conjures up positive emotions and a sense of wellbeing for most individuals. A new study by INSEAD shows that verdant views can also nudge people to pick healthier food.
Published in Communications Psychology, a new journal by Nature, the study suggests that spending time in a natural setting, such as walking in a park (vs. on city streets), or simply viewing greenery outside the window (vs. an urban view), leads people to make healthier food choices afterward.
“Our studies suggest that it was not the urban view that led to unhealthy food choices but rather that nature influenced people to eat healthier,” says Pierre Chandon, one of the study’s co-authors and the L’Oréal Chaired professor of marketing at INSEAD.
Your window view matters
In one study, participants were randomly assigned to take a 20-minute walk either through a park or busy streets in Paris. Afterward, all participants were offered a buffet with a mix of healthy and less healthy snacks.
While participants across both groups ate about equal amounts, those who had walked in the park displayed a clear preference for healthier choices: 70% of their selections were healthier snacks, compared to just 39% for the city walkers.
In a further, more controlled experiment, participants were placed in simulated "hotel rooms" with different window views: a green pasture, a city street, or a control condition, a blank wall with closed curtains. They were asked to choose a lunch from an in-room service menu featuring healthy and unhealthy main courses, beverages, and desserts. The results mirrored the previous experiment. Those with a view of nature opted for healthier options, while those with urban or obscured views showed less healthy preferences.
Green may be the key
The idea for this research came from co-author Maria Langlois,who noticed how she and her teammates taking part in a 7200-km charity bike ride gravitated towards healthier, unprocessed foods while biking through natural environments. Langlois, who is now an assistant professor of marketing at SMU’s Cox School of Business, turned this observation into a series of rigorous field and online studies when she enrolled in INSEAD’s PhD program.
Interestingly, the research suggests that not all natural environments have the same effect. The vividness and level of greenery in the setting could play a part. For instance, when snow covers the natural or urban views, the scenery does not influence food choices.
The researchers conducted another experiment to find out whether nature exposure increases preferences for truly healthy and natural food, or for any processed food that claims to be healthy. They offered participants three types of snacks: diet and light, healthy and natural, or tasty and indulgent. Exposure to natural scenes decreased preference for both diet snacks while significantly shifting preferences from indulgent choices towards the healthier, natural options.
Implications for an increasingly urban world
These findings hold promise for promoting healthier eating habits. Schools, companies and other organisations could utilise nature imagery in cafeterias to nudge students and employees towards healthier options. Food marketers could use natural visual cues to promote healthy or natural products.
More importantly, the research reminds us of the crucial role of urban planning. By 2050, two-thirds of the world population are expected to live in cities. Incorporating green spaces into future urban landscapes will become even more essential.
END
Nature's nudge: Study shows green views lead to healthier food choices
2024-04-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI algorithms can determine how well newborns nurse, study shows
2024-04-29
A modified pacifier and AI algorithms to analyze the data it produces could determine if newborns are learning the proper mechanics of nursing, a recent study shows.
Specifically, the researchers from the University of California San Diego measured if babies are generating enough suckling strength to breastfeed and whether they are suckling in a regular pattern based on eight independent parameters.
The results, published in the April 18 online edition of IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering ...
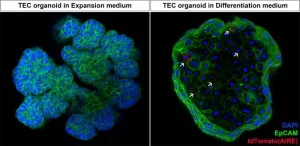
Scientists develop new organoid model to study thymus function
2024-04-29
Researchers from the Organoid group have developed a new organoid model that can be used to study the thymus. The organoids, derived from mouse thymus tissue, specifically model thymic epithelial cells (TECs). These cells are responsible for training the T cells of the immune system to properly respond to pathogens. It is the first laboratory model that enables long-term culture of TECs, which presents new opportunities to study their function. Ultimately, this could also bring new insights into the treatment ...
A revised classification of primary iron overload syndromes
2024-04-29
Background and Aims
The clinical introduction of hepcidin25 (Hep25) has led to a more detailed understanding of its relationship with ferroportin (FP) and divalent metal transporter1 in primary iron overload syndromes (PIOSs). In 2012, we proposed a classification of PIOSs based on the Hep25/FP system, which consists of prehepatic aceruloplasminemia, hepatic hemochromatosis (HC), and posthepatic FP disease (FP-D). However, in consideration of accumulated evidence on PIOSs, we aimed to renew the classification.
Methods
We ...
Expanding health equity by including nursing home residents in clinical trials
2024-04-29
INDIANAPOLIS – Clinical trials are constantly being designed and study participants enrolled to determine if medical treatments and therapies are safe and effective. Much has been written about the importance of including diverse populations in these trials.
However, the nearly 1.4 million individuals who live in the 15,600 nursing homes across the U.S. have been largely left out of clinical trials, despite the prevalence of such common conditions as hypertension, depression, diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease in this population.
A commentary by faculty of Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University, UCLA ...
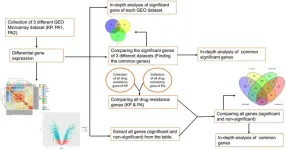
Identification and exploration of transcripts involved in antibiotic resistance mechanism of two critical superbugs
2024-04-29
Background and objectives
Infectious diseases caused by pathogenic strains of bacteria are a global cause of morbidity and mortality. Hospital-acquired infections caused by Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were found vulnerable during the COVID-19 pandemic. They are also responsible for the onset of certain life-threatening infectious diseases such as cystic fibrosis, endocarditis, bacteremia, and sepsis. Looking into the importance of these two superbugs there is a strong need for extensive comparative differential gene expression analysis ...
Quantum fiber optics in the brain enhance processing, may protect against degenerative diseases
2024-04-29
WASHINGTON, DC – (April 26, 2024) The effects of quantum mechanics—the laws of physics that apply at exceedingly small scales—are extremely sensitive to disturbances. This is why quantum computers must be held at temperatures colder than outer space, and only very, very small objects, such as atoms and molecules, generally display quantum properties. By quantum standards, biological systems are quite hostile environments: they’re warm and chaotic, and even their fundamental components—such as cells—are considered very large.
But ...
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai names Miriam Merad, MD, PhD, as Dean for Translational Research and Therapeutic Innovation
2024-04-29
New York, NY [April 29, 2024]—Miriam Merad, MD, PhD, a world-renowned immunologist, has been appointed Dean for Translational Research and Therapeutic Innovation of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The appointment reaffirms Icahn Mount Sinai’s commitment to pioneering medical progress and catalyzing the rapid advancement of research innovation.
Dr. Merad, the Mount Sinai Professor in Cancer Immunology, will also continue to serve as the founding Chair of the Department of Immunology and Immunotherapy, Director of the Marc and Jennifer Lipschultz Precision Immunology Institute, and Director ...
Details of hurricane Ian’s aftermath captured with new remote sensing method
2024-04-29
Category 4 Hurricane Ian made landfall in Florida’s Lee County on Sept. 28, 2022, battering the region with wind speeds of 155 miles per hour and storm surge up to 13 feet – the highest storm surge documented in Southwest Florida in the past 150 years.
In the aftermath of a disaster, rapidly assessing damage is critical for rescue, recovery and emergency planning. Damage assessments are typically conducted through field reconnaissance deployments, which can be labor-intensive, costly and risky. Moreover, field-based emergency response ...
Robots can’t outrun animals. A new study explores why
2024-04-29
The question may be the 21st century’s version of the fable of the tortoise and the hare: Who would win in a foot race between a robot and an animal?
In a new perspective article, a team of engineers from the United States and Canada, including University of Colorado Boulder roboticist Kaushik Jayaram, set out to answer that riddle. The group analyzed data from dozens of studies and came to a resounding “no.” In almost all cases, biological organisms, such as cheetahs, cockroaches and even humans, seem to be able to outrun their robot counterparts.
The researchers, led by Samuel Burden at the University of Washington and ...
The Human Immunome Project unveils scientific plan to decode and model the immune system
2024-04-29
NEW YORK, April 29, 2024 – The Human Immunome Project (HIP), a global nonprofit scientific initiative, released its Scientific Plan today, on World Immunology Day, the organization announced. The plan provides a detailed roadmap of how the Human Immunome Project and its network of global study sites will generate the world’s largest and most diverse immunological dataset and use these data to power publicly available AI models of the immune system.
“The immune system is the epicenter of human health, and our newly released ...