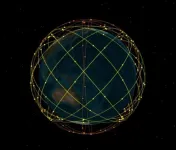
(Press-News.org) A study has outlined the critical needs and essential technologies for a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellation to augment satellite navigation systems, significantly improving the Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) services. This research specifically targets the diverse demands of different users for LEO augmented GNSS, the possible contribution of LEOs to PNT performances, and the key technologies referring to the LEO-based navigation augmentation system.
The Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), including the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), are the most widely used in providing PNT services. However, GNSS signals from geostationary orbit (GEO), inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO), and medium earth orbit (MEO) satellites often face interference issues due to their low received signal power. Besides, the PNT service performance is relatively poor in polar regions because of the limited inclination angles of all MEO and IGSO satellites. This vulnerability compromises the accuracy and reliability of PNT services provided by the GNSS.
In a study (DOI: 10.1186/s43020-024-00133-w) published in Satellite Navigation on 29 April 2024, researchers from the Xi'an Research Institute of Surveying and Mapping introduced the augmentation to satellite navigation systems by integrating LEO constellations. This development is set to significantly refine the precision and reliability of global PNT services.
The integration of LEO constellations with the GNSS, can fulfil the requirements of some special PNT users that cannot be fulfilled with existing GNSS. The study's findings indicate that different kinds of PNT users have different demands for LEO navigation enhancement, and the special demands of particular user groups must be taken into consideration. The research also proposes the key technologies for the construction of LEO navigation augmentation constellation.
Dr. Yuanxi Yang, the lead researcher and correspondent for the article, highlighted the impact of these enhancements: "LEO constellations can significantly enhance not only the accuracy, continuity and availability of PNT service, but also the reliability, integrity and safety for PNT users" stated Dr. Yang.
This breakthrough marks a critical progress in satellite navigation technology, promising to improve the quality of existing GNSS. The reasonable design of LEO satellites ensures a more secure satellite-based PNT service system, fulfilling more requirements of special users.
###
References
DOI
10.1186/s43020-024-00133-w
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43020-024-00133-w
Funding information
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42388102; No. 41931076), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFB0505800) and the Laoshan Laboratory (Grant No. LSKJ202205101).
About Satellite Navigation
Satellite Navigation (E-ISSN: 2662-1363; ISSN: 2662-9291) is the official journal of Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The journal aims to report innovative ideas, new results or progress on the theoretical techniques and applications of satellite navigation. The journal welcomes original articles, reviews and commentaries.
END
Advancing satellite-based PNT service: low earth orbit satellite constellations augment the GNSS
2024-05-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers show that slow-moving earthquakes are controlled by rock permeability
2024-05-07
Earthquakes are the most dramatic and noteworthy results of tectonic plate movement. They are often destructive and deadly, or at the very least physically felt — they’re literally groundbreaking geological events. However not all tectonic movement results in effects that humans can perceive.
Slow slip events occur when pent up tectonic forces are released over the course of a few days or months, like an earthquake unfolding in slow motion. The more gradual movement means people won’t feel the earth shaking beneath their feet and buildings won’t collapse. But the lack of destruction does not make slow slip events less scientifically ...
Seeking medical insights in the physics of mucus
2024-05-07
WASHINGTON, May 7, 2024 – As much as we might not want to think about it, mucus is everywhere in our bodies. It coats our airways and our digestive systems and serves as a first line of defense against pathogens, a habitat for our microbiomes, and a conveyor belt for our insides to keep everything moving smoothly.
The front-line role of mucus means it is often the site of the first symptoms of infection or disease. Understanding how mucus changes, and what it changes in response to, can help diagnose illnesses and develop treatments. Designing a study to measure the physical properties of mucus, however, is nothing to sneeze at.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, ...
Study sheds light on cancer cell ‘tug-of-war’
2024-05-07
WASHINGTON, May 7, 2024 – Understanding how cancerous cells spread from a primary tumor is important for any number of reasons, including determining the aggressiveness of the disease itself. The movement of cells into the extracellular matrix (ECM) of neighboring tissue is an essential step in cancer progression that directly correlates to the onset of metastasis.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, a team of researchers from Germany and Spain used a breast cancer cell line panel and primary tumor explants from breast and cervical cancer patients to ...
Social determinants of health and the availability of cancer clinical trials in the US
2024-05-07
About The Study: Substantial geographic disparities in cancer clinical trials availability exist throughout the United States, with the most socially vulnerable counties being far less likely to have any trial and having only a fraction of trials available, a disparity that has worsened over time.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Rishi Robert Sekar, M.D., M.S., email rsekar@med.umich.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.10162)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Multilevel characteristics of cumulative symptom burden in young survivors of childhood cancer
2024-05-07
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that symptoms are prevalent years after young childhood cancer survivors’ initial cancer diagnosis, and interventions to reduce caregiver anxiety and neighborhood adversity and improve resilience may alleviate symptom burden.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, I-Chan Huang, Ph.D., email i-chan.huang@stjude.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.10145)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Why getting in touch with our ‘gerbil brain’ could help machines listen better
2024-05-07
Macquarie University researchers have debunked a 75-year-old theory about how humans determine where sounds are coming from, and it could unlock the secret to creating a next generation of more adaptable and efficient hearing devices ranging from hearing aids to smartphones.
In the 1940s, an engineering model was developed to explain how humans can locate a sound source based on differences of just a few tens of millionths of a second in when the sound reaches each ear.
This model worked on the theory that we must ...
It flickers, then it tips – study identifies early warning signals for the end of the African humid period
2024-05-07
The transition from the African Humid Period (AHP) to dry conditions in North Africa is the clearest example of climate tipping points in recent geological history. They occur when small perturbations trigger a large, non-linear response in the system and shift the climate to a different future state, usually with dramatic consequences for the biosphere. That was also the case in North Africa, where the grasslands, forests, and lakes favored by humans disappeared, causing them to retreat to areas like the mountains, oases, and the Nile Delta. This ...
Aquatic weed among ‘world’s worst’ expands in Northeastern US
2024-05-07
WESTMINSTER, Colorado – 7 May 2024 – An article in the latest issue of Invasive Plant Science and Management provides new insights on a northern hydrilla (Hydrilla verticillata) subspecies (lithuanica) and its establishment outside the Connecticut River. Considered among the “world’s worst” aquatic weeds, northern hydrilla hinders recreational activities by forming dense canopies. If unchecked, it has the potential to displace native species and host a bacterium that produces ...
Emergency department packed to the gills? Someday, AI may help
2024-05-07
UCSF-led study finds artificial intelligence is as good as a physician at prioritizing which patients need to be seen first.
Emergency departments nationwide are overcrowded and overtaxed, but a new study suggests artificial intelligence (AI) could one day help prioritize which patients need treatment most urgently.
Using anonymized records of 251,000 adult emergency department (ED) visits, researchers at UC San Francisco evaluated how well an AI model was able to extract symptoms from patients’ ...
Asthma education is key to reducing deaths worldwide, say respiratory health associations
2024-05-07
NEW YORK, NY - May 7, 2024 – On World Asthma Day 2024 the message is clear: "Asthma Education Empowers." The Forum of International Respiratory Societies (FIRS), of which the American Thoracic Society is a founding member, stresses the crucial role of education in empowering people with asthma to manage their condition effectively and to know when to seek medical assistance.
FIRS also urges health care professionals to enhance their awareness of the preventable morbidity and mortality from asthma and of the published evidence on effective asthma management, so they are equipped to provide reliable information and optimal treatment for their patients.
Asthma ...