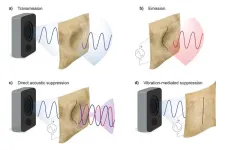
We are living in a very noisy world. From the hum of traffic outside your window to the next-door neighbor’s blaring TV to sounds from a co-worker’s cubicle, unwanted noise remains a resounding problem.
To cut through the din, an interdisciplinary collaboration of researchers from MIT and elsewhere developed a sound-suppressing silk fabric that could be used to create quiet spaces.
The fabric, which is barely thicker than a human hair, contains a special fiber that vibrates when a voltage is applied to it. The researchers leveraged those vibrations to suppress sound in two different ways.
In one, the vibrating fabric generates sound waves that interfere with an unwanted noise to cancel it out, similar to noise-canceling headphones, which work well in a small space like your ears but do not work in large enclosures like rooms or planes.
In the other, more surprising technique, the fabric is held still to suppress vibrations that are key to the transmission of sound. This prevents noise from being transmitted through the fabric and quiets the volume beyond. This second approach allows for noise reduction in much larger spaces like rooms or cars.
By using common materials like silk, canvas, and muslin, the researchers created noise-suppressing fabrics which would be practical to implement in real-world spaces. For instance, one could use such a fabric to make dividers in open workspaces or thin fabric walls that prevent sound from getting through.
“Noise is a lot easier to create than quiet. In fact, to keep noise out we dedicate a lot of space to thick walls. [First author] Grace’s work provides a new mechanism for creating quiet spaces with a thin sheet of fabric,” says Yoel Fink, a professor in the departments of Materials Science and Engineering and Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, a Research Laboratory of Electronics principal investigator, and senior author of a paper on the fabric.
The study’s lead author is Grace (Noel) Yang SM ’21, PhD ’24. Co-authors include MIT graduate students Taigyu Joo, Hyunhee Lee, Henry Cheung, and Yongyi Zhao; Zachary Smith, the Robert N. Noyce Career Development Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT; graduate student Guanchun Rui and professor Lei Zhu of Case Western University; graduate student Jinuan Lin and Assistant Professor Chu Ma of the University of Wisconsin at Madison; and Latika Balachander, a graduate student at the Rhode Island School of Design. The an open-access paper about the research appeared recently in Advanced Materials.
Silky silence
The sound-suppressing silk builds off the group’s prior work to create fabric microphones.
In that research, they sewed a single strand of piezoelectric fiber into fabric. Piezoelectric materials produce an electrical signal when squeezed or bent. When a nearby noise causes the fabric to vibrate, the piezoelectric fiber converts those vibrations into an electrical signal, which can capture the sound.
In the new work, the researchers flipped that idea to create a fabric loudspeaker that can be used to cancel out soundwaves.
“While we can use fabric to create sound, there is already so much noise in our world. We thought creating silence could be even more valuable,” Yang says.
Applying an electrical signal to the piezoelectric fiber causes it to vibrate, which generates sound. The researchers demonstrated this by playing Bach’s “Air” using a 130-micrometer sheet of silk mounted on a circular frame.
To enable direct sound suppression, the researchers use a silk fabric loudspeaker to emit sound waves that destructively interfere with unwanted sound waves. They control the vibrations of the piezoelectric fiber so that sound waves emitted by the fabric are opposite of unwanted sound waves that strike the fabric, which can cancel out the noise.
However, this technique is only effective over a small area. So, the researchers built off this idea to develop a technique that uses fabric vibrations to suppress sound in much larger areas, like a bedroom.
Let’s say your next-door neighbors are playing foosball in the middle of the night. You hear noise in your bedroom because the sound in their apartment causes your shared wall to vibrate, which forms sound waves on your side.
To suppress that sound, the researchers could place the silk fabric onto your side of the shared wall, controlling the vibrations in the fiber to force the fabric to remain still. This vibration-mediated suppression prevents sound from being transmitted through the fabric.
“If we can control those vibrations and stop them from happening, we can stop the noise that is generated, as well,” Yang says.
A mirror for sound
Surprisingly, the researchers found that holding the fabric still causes sound to be reflected by the fabric, resulting in a thin piece of silk that reflects sound like a mirror does with light.
Their experiments also revealed that both the mechanical properties of a fabric and the size of its pores affect the efficiency of sound generation. While silk and muslin have similar mechanical properties, the smaller pore sizes of silk make it a better fabric loudspeaker.
But the effective pore size also depends on the frequency of sound waves. If the frequency is low enough, even a fabric with relatively large pores could function effectively, Yang says.
When they tested the silk fabric in direct suppression mode, the researchers found that it could significantly reduce the volume of sounds up to 65 decibels (about as loud as enthusiastic human conversation). In vibration-mediated suppression mode, the fabric could reduce sound transmission up to 75 percent.
These results were only possible due to a robust group of collaborators, Fink says. Graduate students at the Rhode Island School of Design helped the researchers understand the details of constructing fabrics; scientists at the University of Wisconsin at Madison conducted simulations; researchers at Case Western Reserve University characterized materials; and chemical engineers in the Smith Group at MIT used their expertise in gas membrane separation to measure airflow through the fabric.
Moving forward, the researchers want to explore the use of their fabric to block sound of multiple frequencies. This would likely require complex signal processing and additional electronics.
In addition, they want to further study the architecture of the fabric to see how changing things like the number of piezoelectric fibers, the direction in which they are sewn, or the applied voltages could improve performance.
“There are a lot of knobs we can turn to make this sound-suppressing fabric really effective. We want to get people thinking about controlling structural vibrations to suppress sound. This is just the beginning,” says Yang.
This work is funded, in part, by the National Science Foundation (NSF), the Army Research Office (ARO), the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA), and the Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation.
####
Written by Adam Zewe, MIT News
Paper: “Single Layer Silk and Cotton Woven Fabrics for Acoustic Emission and Active Sound Suppression”
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/adma.202313328
END