(Press-News.org) Psychiatrists and mental health professionals have a new standard for managing major depression, thanks to refreshed clinical guidelines published today by the Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT).
The CANMAT guidelines are the most widely used clinical guidelines for depression in the world. The new version integrates the latest scientific evidence and advances in depression care since the previous guidelines were published in 2016. The update was led by researchers at the University of B.C. and the University of Toronto, alongside a national working group of more than 40 academic clinical experts and patient partners.
“These recommendations not only represent the evidence and broad consensus of leading experts in depression research and care, but, importantly, they also reflect the perspectives of patients with lived experience,” says co-lead author Dr. Raymond Lam, professor of psychiatry at UBC and co-director of the Mood Disorders Centre at the Djavad Mowafaghian Centre for Brain Health. “Our hope is that this update will empower clinicians with the latest recommendations that can help achieve better outcomes and improved quality of life for the millions of people affected by depression.”
More than one in 10 Canadians will experience depression at some point in their lives, making it one of the largest public health burdens in Canada. However, it is estimated that only 20 per cent of people receive adequate treatment.
The updated guidelines cover eight primary topic areas that map the patient care journey, from assessment and diagnosis through to the selection of treatments and strategies to prevent recurrence. The question-and-answer format is designed to be practical, accessible and easy for clinicians to use.
To develop the refreshed guidelines, the working group conducted a comprehensive literature review of new scientific evidence published since the previous 2016 guidelines. Drafts were revised based on review by patient partners, expert peer review and a defined expert consensus process.
The resulting recommendations are organized by lines of treatment based on the level of evidence supporting each therapy and factors such as safety, tolerability and feasibility. Guidance is provided to aid healthcare professionals in choosing the right treatment option with an emphasis on collaborative decision-making.
“Depression is a complex and highly individualized condition,” says Dr. Lam. “The guidelines highlight the importance of collaborating with patients in care decisions and providing a personalized treatment approach that carefully considers a person’s needs, preferences and treatment history.”
The guidelines underline the strong evidence base for well-established first-line treatments, including a number of medications, as well as psychological treatments such as cognitive behavioural therapy, interpersonal therapy and behavioural activation. Based on recent evidence, a number of new psychological and pharmacological treatments were added to the list of treatment options.
“Notable additions to the new guidelines are a strong emphasis on patient participation in choosing treatment, applying outcome measures throughout care, and an overview of digital mental health tools in the management of depression,” says co-lead author Dr. Sidney Kennedy, professor of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and director of the Centre for Depression and Suicide Studies at Unity Health Toronto.
The guidelines include further direction on how healthcare professionals can incorporate lifestyle interventions, such as exercise, nutrition and sleep hygiene. They also explore when neuromodulation treatments should be considered and what should be done when a patient doesn’t respond to initial treatments or develops treatment-resistant depression.
“Many well-established psychological and behavioural interventions have accumulated more support for their efficacy across different delivery formats,” says co-author Dr. Lena Quilty, associate professor of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and senior scientist at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health. “We are especially pleased to report on evidence for new interventions that target depression as well as commonly co-occurring challenges such as anxiety or disrupted cognitive processes. We hope that these additional alternatives provide more opportunities for integrated attention to these multi-faceted issues.”
CANMAT is a network of academic and clinical experts dedicated to improving clinical care for people with mood and anxiety disorders. The new depression guidelines were published today in The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. The researchers will be releasing updated versions of the CANMAT Pocket Guide to Depression for clinicians and the CHOICE-D Patient and Family Guide to Depression Treatment.
END
New guidelines for depression care emphasize patient-centred approach
2024-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Children sleep problems associated with psychosis in young adults
2024-05-08
Children who experience chronic lack of sleep from infancy may be at increased risk of developing psychosis in early adulthood, new research shows.
Researchers at the University of Birmingham examined information on nighttime sleep duration from a large cohort study of children aged between 6 months and 7 years old. They found that children who persistently slept fewer hours, throughout this time period, were more than twice as likely to develop a psychotic disorder in early adulthood, and nearly four times as likely to have a psychotic episode.
While ...
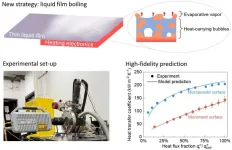
High-fidelity model for designing efficient thermal management surfaces
2024-05-08
In the past decade, fires from electronic devices and batteries, from small smartphones to electrical vehicles and airplanes, have repeatedly made headlines. Enhanced computational power has led to a large amount of waste heat generation and undesirable temperature rise of electronics. Poor heat management is the cause of over half of electronic device failures. To tackle this issue, it is crucial to develop advanced cooling technologies to effectively manage heat and maintain temperatures in the working conditions.
Among various cooling technologies, liquid-vapor phase-change cooling, which utilizes the boiling or evaporation of ...
Terahertz flexible multiplexing chip enabled by synthetic topological phase transitions
2024-05-08
This study is led by Prof. Xu (State Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University), Prof. Yu (College of Information Science and Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University), Prof. Han (Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Technology, Tianjin University and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Processing, School of Optoelectronic Engineering, Guilin University of Electronic Technology), and Prof. Sun ...
Potential causal effect of long-term PM1 exposure on hypertension hospitalization
2024-05-08
Hypertension is among the leading cardiovascular diseases. Despite extensive research, evidence concerning the relationship between long-term exposure to ambient particulate matter and hypertension remains limited and inconsistent, particularly with regard to submicron particulate matter (PM1). While randomized controlled trials are considered the gold standard for causal inference, environmental epidemiological studies typically rely on observational data. Traditional approaches in observational studies are less effective than randomized controlled trials in fully controlling for confounding factors to achieve results with causal interpretability. With the advancement of causal ...
Vertical atmospheric measurements and simulations demonstrate important contribution of combustion-related ammonium during haze pollution in Beijing
2024-05-08
Recently, Science Bulletin published a research conducted by Prof. Pingqing Fu and Dr. Libin Wu from Tianjin University, Peng Wang from Fudan University, and their Chinese and foreign collaborators. They explored the source of ammonium in PM2.5 at different heights of the atmospheric boundary layer in Beijing, and found that combustion-related ammonia is very important to ammonium in PM2.5 during haze pollution in winter.
Air pollution and treatment in Beijing have been widely concerned by both the scientific community and the public. Although its PM2.5 has decreased significantly in the past few years, there is still haze pollution in Beijing, especially in winter. The chemical compositions ...
Simulated High-altitude exposure for 24-hours is well tolerated by adolescents and adults with single-ventricle physiology after Fontan-palliation
2024-05-08
The researchers conducted a study over four days, including overnight stays, with 18 subjects at :envihab, the DLR medical research centre in Cologne. At a simulated altitude of 2500 meters above sea level, the influence of hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) on various hemodynamic and metabolic parameters was investigated. The central venous pressure via a catheter and the blood flow in the lungs using real-time magnetic resonance imaging were evaluated. The results showed that neither the pulmonarypressure nor the blood flow changed significantly. All patients able to tolerate a longer stay at altitude of 24 to 30 hours without complications.
Oxygenation ...
Scientists find ancient, endangered lamprey fish in Queensland, 1400 km north of its previous known range
2024-05-08
The Australian brook lamprey (Mordacia praecox) is part of a group of primitive jawless fish. It’s up to 15 cm long, with rows of sharp teeth. Surprisingly, it doesn’t use these teeth to suck blood like most lamprey species – it’s non-parasitic.
As larvae, the Australian brook lamprey lives buried in the bottom of streams for around three years, filter-feeding. Its adult phase is about one year long, in which it doesn’t feed at all. Prior to this study – funded in part by the Australian Government through the National Environmental Science Program’s (NESP) Resilient Landscapes Hub – the species was widely believed to only live in a few streams ...
New $3.7m climate crop lab will create food for ‘tomorrow’s atmosphere today’
2024-05-08
A unique $3.7m plant lab will put researchers on the frontline in the fight against climate change and create crops for “tomorrow’s atmosphere today”.
The new flagship facility at the University of Essex will allow scientists to adapt plants for a hotter drier planet as food security is increasingly threatened.
It boasts a cutting-edge commercially standard vertical farm, an indoor field that replicates real environments anywhere in the globe, and suites that imitate a warming world – with researchers able to raise CO2 concentration and temperature levels at will.
Computer ...
New air-breathing spacecraft to provide better Earth observation and quicker communications
2024-05-08
Scientists at the University of Surrey are developing a new way to power low-orbit spacecraft using – literally – thin air.
Surrey Space Centre aims to enable extremely low-altitude spacecraft orbits in the upper atmosphere, thanks to funding from the UK Space Agency.
This new spacecraft concept could offer new capabilities in Earth observation, climate monitoring and satellite communications.
Dr Andrea Lucca Fabris, principal investigator from Surrey Space Centre and an electric propulsion specialist, said:
“There are benefits to flying in very low altitude orbits, like being able to operate Earth observation at much ...
Exploring the asteroid apophis with small satellites
2024-05-08
The author of a disaster novel couldn't have dreamed it up any better: On a Friday, the thirteenth of all days, the potentially dangerous asteroid (99942) Apophis will come extremely close to humanity. On 13 April 2029, there will only be around 30,000 kilometres between the cosmic rock and Earth. It will then be possible to see Apophis with the naked eye as a point of light in the evening sky, even from Würzburg.
What makes the asteroid so dangerous: its average diameter is an impressive 340 metres. If it were to hit the Earth, the ...