(Press-News.org) New research being presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May) suggests that it is possible to predict if someone is going to gain weight based on their size of their fat cells.
Individuals with large fat cells tend to lose weight over time, while those with small fat cells gain weight, the Swedish study found.
The size and number of fat cells are known to determine fat mass – how much body fat someone has. But their impact on long-term changes in body weight are unknown.
To explore this further, Professor Peter Arner, of the Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, Dr Daniel P Andersson, Department of Endocrinology, Karolinska University Hospital Huddinge, Stockholm, and colleagues measured cell volume (FCV, the size of the fat cells) and fat cell number (FCN) in abdominal fat of 260 subjects (30% men) with an average age of 44 years and an average BMI of 32 kg/m².
An average of 15 years (range 5-28 years) later, the participants were seen again and body weight (BW), BMI and total body fat (BF) measured. Individuals undergoing bariatric surgery or receiving anti-obesity drugs (n=69) were excluded from the analysis.
Initial fat cell volume and fat cell number were significantly related to changes in all three measures over time – BW, BMI and BF.
Having a high number of fat cells that were large was associated with decreases in the three measures, while having few, but small, fat cells correlated with increases in weight, BMI and body fat. This was the case whether or not individuals were living with obesity.
The effects of FCV and FCN were additive and together explained 32-35% of the variations in changes over time in BW/BMI/BF.
The associations between FCV and changes in BW, BMI and BF was still significant when initial age, physical activity, length of follow-up and sex were taken into account. In other words, large cells were linked to future weight loss and small cells to future weight gain.
Professor Arner says: “We can only speculate as to why the size of a person’s fat cells seems to predict their future weight. Body weight decreases when energy expenditure exceeds intake and the body burns off fat to compensate. Our results suggest that the loss of large fat cells makes more of an impact on weight than the loss of small ones.
“It is a bit like having a room filled to the top by few large balloons or many small ones. It is easier to make empty space in the room by letting out air from the big rather than the small balloons.”
As to why having small cells might make it easier to gain weight, Professor Arner says: “Conversely it is easier to fill up the room if many small balloons increase their volume a bit, as compared with having few large balloons and filling them up just a bit.”
The researchers conclude that FCV has a strong influence on long-term changes in body weight. Thus, measuring FCV early in life could be important for weight management later in life.
Professor Arner adds: “It could be of great clinical value to have information about fat cell size before starting a weight management programme. If it is the case that those with large fat cells find it easier to lose weight, those with smaller cells could be given extra support.
“Unfortunately, there isn’t an easy way of measuring fat cell size at present – but it is something we are working on and we’re close to coming up with a solution.”
There are advantages, however, to having small fat cells. Professor Arner says: “It is well known that people with small fat cells have a better metabolic profile than people who are the same weight but have large fat cells.
“This means that if someone with small fat cells does gain weight, it may not raise their risk of conditions such as type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure as much as if they had large fat cells.”
END
Size of a person’s fat cells may hold clues to their future weight
Individuals with large fat cells tend to lose weight over time, while those with small fat cells gain weight, Swedish study finds
2024-05-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Do sex differences in how adipose tissue responds to insulin explain why type 2 diabetes is more common in men?
2024-05-11
New research being presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May), and published in the International Journal of Obesity, could help explain why type 2 diabetes is more common in men than in women.
“Previous studies have shown that men develop type 2 diabetes (TD2) at a younger age and at a lower weight than women and, overall, men appear to be at higher risk of the condition,” says lead researcher Dr Daniel P Andersson, at the Department of Endocrinology, Karolinska University Hospital Huddinge, Stockholm, Sweden. “One reason for ...
Poor muscle health is common in people living with obesity – and increases the risk of an early death, Swedish study of people in UK finds
2024-05-11
New research being presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May) has found that poor muscle health is associated with a higher risk of an early death in people living with obesity.
Individuals with adverse muscle composition were up to three times more likely to die during the course of the study than those with healthy muscles, a Swedish study of people in the UK concluded.
“We found that just by looking at muscle composition we can predict which individuals with obesity are most likely to die during the next few years,” says lead researcher Dr Jennifer Linge, of AMRA Medical, ...
The American Journal of Health Economics releases a special issue on health equity
2024-05-10
The May 2024 issue of the American Journal of Health Economics collects articles on the topic of health equity. The edition was inspired in part by the COVID-19 pandemic, writes guest editor Mónica García-Pérez, and the ways in which that “health crisis exposed the sources of disparities among different US populations that affect access to health care, quality of care, and final health outcomes.”
Consisting of five papers, the issue devotes particular attention to the topics of “race/ethnicity, ...
Optical power evolution in fiber-optic networks: New framework for better modeling and control
2024-05-10
With the emergence of internet services such as AI-generated content and virtual reality, the demand for global capacity has surged, significantly intensifying pressures on fiber-optic communication systems. To address this surge and reduce operational costs, efforts are underway to develop autonomous driving optical networks (ADONs) with highly-efficient network operations. One of the most important tasks for an ADON is to accurately model and control the optical power evolution (OPE) over fiber links, since it ...
Therapeutic opportunities for hypermutated urothelial carcinomas beyond immunotherapy
2024-05-10
“These results argue that combinations based on immunotherapy may also provide an opportunity for targeting urothelial cancers with low TMB, and provide efficacy superior to classic chemotherapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 10, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on April 25, 2024, entitled, “Therapeutic opportunities for hypermutated urothelial carcinomas beyond immunotherapy.”
In this new editorial, researcher Ioannis A. Voutsadakis from Sault Area Hospital and Northern Ontario School of Medicine discusses tumor mutation burden (TMB)—a ...
UC Santa Cruz study discovers cellular activity that hints recycling is in our DNA
2024-05-10
By Rose Miyatsu, UC Santa Cruz Genomics Institute
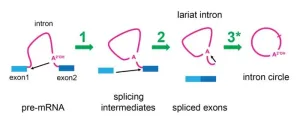
Although you may not appreciate them, or have even heard of them, throughout your body, countless microscopic machines called spliceosomes are hard at work. As you sit and read, they are faithfully and rapidly putting back together the broken information in your genes by removing sequences called “introns” so that your messenger RNAs can make the correct proteins needed by your cells.
Introns are perhaps one of our genome’s biggest mysteries. They are DNA sequences that interrupt the sensible protein-coding information ...
A retrospective look at Human Computer Interaction - free public lecture by Professor Manolya Kavakli
2024-05-10
Professor Manolya Kavakli is an expert in gamification
Her talk will examine the complex relationship between humans, computers and tech
She will examine how digital developments have the potential to improve lives and modernise industry.
The latest inaugural lecture at Aston University will look at the complex relationship between humans, computers and technology.
Professor Manolya Kavakli will discuss progress so far and offer insights into how to ease into digital transformation for the challenges that lie ahead.
The professor is an expert in gamification, the process of using elements of gaming in non-gaming situations such as learning and training.
She ...
Reducing prejudice in war zones proves challenging
2024-05-10
There are 62.5 million internally displaced persons worldwide, according to 2022 data by the UNHCR, the United Nations Refugee Agency. These individuals were forced to leave their homes but remain in the same country.
Prior research has shown that internally displaced persons often experience prejudice and discrimination, as residents in their new locale fear that the migrants may be insurgents or criminals, or compete for jobs.
Now, a new Dartmouth study involving Afghanistan indicates that changing such attitudes is an uphill battle. Given the decades of fighting there, Afghanistan has had one of the largest populations ...
Chapman professor contributes to breakthrough hemostasis and wound healing research
2024-05-10
A breakthrough study, published in Science Translational Medicine, features a biomedical engineering innovation with the potential to transform trauma care and surgical practices. Chapman University’s Fowler School of Engineering Founding Dean and Professor, Andrew Lyon, is a member of this multidisciplinary, multi-university scientific research team developing platelet-like particles that integrate into the body’s clotting pathways to stop hemorrhage. Sanika Pandit, an alumna of Chapman University, is also among the 15 authors in this research.
Addressing a longstanding gap in surgical and trauma care, this advancement holds potential for patient implementation. Patients ...
Melanoma in darker skin tones: Race and sex play a role, Mayo study finds
2024-05-10
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Melanoma, an aggressive form of skin cancer that accounts for 75% of all skin-cancer-related deaths, is often detected later in people with darker skin complexions — and the consequences can be devastating, a Mayo Clinic study reveals.
While melanoma may be found less frequently in people with darker complexions than fair ones, this potentially serious form of cancer can strike anyone. The study, which consisted of 492,597 patients with melanoma, suggests that added vigilance in early screening is particularly needed for Black men, whose cancers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
JBNU researchers review advances in pyrochlore oxide-based dielectric energy storage technology
Novel cellular phenomenon reveals how immune cells extract nuclear DNA from dying cells
Printable enzyme ink powers next-generation wearable biosensors
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
People’s gut bacteria worse in areas with higher social deprivation
Unique analysis shows air-con heat relief significantly worsens climate change
Keto diet may restore exercise benefits in people with high blood sugar
Manchester researchers challenge misleading language around plastic waste solutions
Vessel traffic alters behavior, stress and population trends of marine megafauna
Your car’s tire sensors could be used to track you
Research confirms that ocean warming causes an annual decline in fish biomass of up to 19.8%
Local water supply crucial to success of hydrogen initiative in Europe
New blood test score detects hidden alcohol-related liver disease
High risk of readmission and death among heart failure patients
Code for Earth launches 2026 climate and weather data challenges
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
Have abortion-related laws affected broader access to maternal health care?
Do muscles remember being weak?
Do certain circulating small non-coding RNAs affect longevity?
How well are international guidelines followed for certain medications for high-risk pregnancies?
New blood test signals who is most likely to live longer, study finds
Global gaps in use of two life-saving antenatal treatments for premature babies, reveals worldwide analysis
Bug beats: caterpillars use complex rhythms to communicate with ants
High-risk patients account for 80% of post-surgery deaths
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
New method to remove toxic PFAS chemicals from water
The nanozymes hypothesis of the origin of life (on Earth) proposed
Microalgae-derived biochar enables fast, low-cost detection of hydrogen peroxide
[Press-News.org] Size of a person’s fat cells may hold clues to their future weightIndividuals with large fat cells tend to lose weight over time, while those with small fat cells gain weight, Swedish study finds