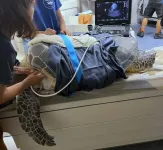
(Press-News.org) OTTAWA, Ontario, May 13, 2024 – Six out of seven sea turtle species are endangered, and humans are primarily responsible. Commercial fishing activities are the largest human-caused disturbance to sea turtles due to accidental capture.
Fishers are typically unaware if a sea turtle is caught in their net until it’s completely pulled out of the water. However, releasing sea turtles without veterinary evaluations can be harmful. When accidentally caught, the turtles’ normal diving processes are interrupted, which can cause abnormal gas in their organs, gas emboli, to form. Veterinarians around the globe are working to understand the possible consequences of this pathology and determine the best treatment for turtles depending on when they surface. Here, they used ultrasound imaging to get a closer look at sea turtles’ bodies in real time, focusing on the heart, liver, and kidney.
Katherine Eltz, a first-year doctoral student at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, determined that there are ways to differentiate gas levels over time in sea turtles. Eltz, whose home laboratory focuses on ultrasound imaging for decompression sickness mitigation in humans, collaborated with veterinarians who measured gas emboli in turtles in real time on fishing boats. She will present her work Monday, May 13, at 4:00 p.m. EDT as part of a joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and the Canadian Acoustical Association, running May 13-17 at the Shaw Centre located in downtown Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
“Veterinarians can examine whole-body MRI or X-ray scans and find specific bubbles in a variety of different organs,” said Eltz. “The benefit of ultrasound is that we can see bubbles flowing through vessels or stationary in tissues. The portability of ultrasound means that it can be brought onto fishing boats, which we took advantage of to collect half of the data used in this project.”
Her collaborators from the Oceanogràfic Foundation were the first to report decompression sickness in turtles. Eltz examined ultrasound data collected from sea turtles found off the coast of Brazil, Italy, and Spain, though this issue is found in sea turtles worldwide. The data collection from Eltz’s collaborators at Oceanogràfic comes from veterinarians who joined fishers off the coasts of these countries and imaged the turtles immediately to monitor their bubbles after surfacing.
Eltz’s results come from two experimental groups with different circumstances regarding time and gas severity. The brightness from the ultrasounds taken from the groups is a valuable quantitative metric to separate each ultrasound by grade. These findings can help veterinarians better treat sea turtles presenting with gas embolism. Ultrasound brightness could become a quantitative metric for veterinarians to determine which turtles need hyperbaric oxygen treatment and which can be released.
“The largest task still at hand is to work towards standardizing the acquisition of the ultrasound data collected for this project,” said Eltz. “Now, I can work with veterinarians to help adjust their methods, including improved image processing to standardize the data in post-processing.”
With a rich dataset from Oceanogràfic at her disposal, Eltz hopes to examine other possible factors that may be related to gas severity. These insights all help lead to better prediction of the outcomes for bycaught sea turtles.
###
----------------------- MORE MEETING INFORMATION -----------------------
Main meeting website: https://acousticalsociety.org/ottawa/
Technical program: https://eppro02.ativ.me/src/EventPilot/php/express/web/planner.php?id=ASASPRING24
ASA PRESS ROOM
In the coming weeks, ASA's Press Room will be updated with newsworthy stories and the press conference schedule at https://acoustics.org/asa-press-room/.
LAY LANGUAGE PAPERS
ASA will also share dozens of lay language papers about topics covered at the conference. Lay language papers are summaries (300-500 words) of presentations written by scientists for a general audience. They will be accompanied by photos, audio, and video. Learn more at https://acoustics.org/lay-language-papers/.
PRESS REGISTRATION
ASA will grant free registration to credentialed and professional freelance journalists. If you are a reporter and would like to attend the hybrid / in-person meeting or virtual press conferences, contact AIP Media Services at media@aip.org. For urgent requests, AIP staff can also help with setting up interviews and obtaining images, sound clips, or background information.
ABOUT THE ACOUSTICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA
The Acoustical Society of America is the premier international scientific society in acoustics devoted to the science and technology of sound. Its 7,000 members worldwide represent a broad spectrum of the study of acoustics. ASA publications include The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America (the world's leading journal on acoustics), JASA Express Letters, Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics, Acoustics Today magazine, books, and standards on acoustics. The society also holds two major scientific meetings each year. See https://acousticalsociety.org/.
ABOUT THE CANADIAN ACOUSTICAL ASSOCIATION/ASSOCIATION CANADIENNE D’ACOUSTIQUE
• fosters communication among people working in all areas of acoustics in Canada
• promotes the growth and practical application of knowledge in acoustics
• encourages education, research, protection of the environment, and employment in acoustics
• is an umbrella organization through which general issues in education, employment and research can be addressed at a national and multidisciplinary level
The CAA is a member society of the International Institute of Noise Control Engineering (I-INCE) and the International Commission for Acoustics (ICA) and is an affiliate society of the International Institute of Acoustics and Vibration (IIAV). Visit https://caa-aca.ca/.
###
END
Catch and release can give sea turtles the bends #ASA186
Veterinarians team up with fishers to evaluate the health of accidentally caught sea turtles
2024-05-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers unveil unique tidal disruption event with unprecedented early optical bump
2024-05-13
A research team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) presented a detailed analysis of a tidal disruption event (TDE) with unique characteristics, providing new insights into the behavior of TDEs and their multiwavelength emissions. The study was published online in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
When a star ventures too close to a supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy, it gets torn apart by the black hole's immense tidal forces, resulting ...
Researchers discover "topological hall effect" in two-dimensional quantum magnets
2024-05-13
In a recent study published in Nature Physics, researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with researchers of University of Science and Technology of China, have introduced the concept of the "Topological Kerr Effect" by using the low-temperature magnetic field microscopy system and the magnetic force microscopy imaging system supported by the steady-state high magnetic field experimental facility.
The study holds great promise for advancing our understanding of topological magnetic ...
Like dad and like mum…all in one plant
2024-05-13
In a new study, led by Charles Underwood from the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research (MPIPZ) in Cologne, Germany, scientists established a system to generate clonal sex cells in tomato plants and used them to design the genomes of offspring. The fertilization of a clonal egg from one parent by a clonal sperm from another parent led to plants containing the complete genetic information of both parents. The study is now published in Nature Genetics.
Hybrid seeds, combining two different parent lines with specific favorable traits, are popular in agriculture as they give rise to robust crops with enhanced productivity, and have been utilized by farmers ...
New molecule mimics the anti-clotting action of blood-sucking organisms
2024-05-13
DURHAM, N.C. – Nature gave ticks, mosquitos and leaches a quick-acting way to keep blood from clotting while they extract their meal from a host.
Now the key to that method has been harnessed by a team of Duke researchers as a potential anti-clotting agent that could be used as an alternative to heparin during angioplasty, dialysis care, surgeries and other procedures.
Publishing in the journal Nature Communications, the researchers describe a synthetic molecule that mimics the effects of compounds in the saliva of blood-sucking critters. Importantly, the new molecule can also ...
Transgender preteens report 13 hours of daily screen time
2024-05-13
Toronto, ON - A new national study found that transgender preteens, 12 and13 years old, reported 13 hours of daily recreational screen time, which was 4.5 hours more than their cisgender peers. Data were collected from 2019 to 2021, overlapping with the COVID-19 pandemic, and the study was published in Annals of Epidemiology.
“Transgender adolescents are more likely to experience school-based bullying and exclusion from peer groups due to their gender identity, leading them to spend less time in traditional school activities and more time on screens,” says lead author, Jason Nagata, MD, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. ...
World's largest hummingbird is actually two species
2024-05-13
For release: May 13, 2024
Ithaca, NY—The Giant Hummingbird of western South America is not one species but two, according to an international group of researchers. The northern population stays in the high Andes year-round while the southern population migrates from sea level up to 14,000 feet for the nonbreeding months. The two species appear identical. But looks deceive—their genomes and behaviors tell a different story. The paper announcing the find was published this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“These ...
New findings released from US 2020 Facebook and Instagram election study
2024-05-13
In the weeks before and after the 2020 presidential election, researchers ran a number of tests to try to understand how much Facebook and its corporate cousin, Instagram, may be contributing to the nation's political divide.
One of those experiments — led by Matthew Gentzkow and Hunt Allcott, economics professors at Stanford University — centered on more than 35,000 Facebook and Instagram users who were paid to stay off the platforms in the run-up to Election Day. There’s a lot that researchers could glean from the social media hiatus, including whether people’s political attitudes shifted and in what ways. If views changed dramatically, that ...
How miniature backpacks led to the discovery of the world’s largest hummingbird species
2024-05-13
Researchers from UNM’s Museum of Southwestern Biology (MSB) have uncovered the giant hummingbird’s extreme long-distance migration for the first time. Their eight-year study, Extreme elevational migration spurred cryptic speciation in giant hummingbirds published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, led them to another important discovery: The world’s largest hummingbird is a new species.
The team, led by Jessie Williamson, UNM Ph.D., 2022, included the Museum of Southwestern Biology at UNM, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile in Chile, and Centro de Ornitología ...
New synthetic biomarker technology differentiates between prior Zika and dengue infections
2024-05-13
A newly discovered Zika virus-specific synthetic molecule is capable of differentiating Zika-immune patient samples from samples of patients previously infected with the related dengue virus. The technology may lead to the development of better diagnostics and vaccine candidates, scientists announced today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study, led by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health and The Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation & Technology, is the first to apply an innovative “epitope surrogate” technology to Zika. Until now, researchers and clinicians have lacked diagnostic ...
Fruit fly testes offer potential tool against harmful insects
2024-05-13
A way to curb nagging insects has been flying under our radar—an enzyme from fruit fly testes.
The compound could control bugs that carry disease and harm crops by stunting their ability to procreate, Johns Hopkins University researchers found.
“We have a toe in the door to control fruit fly populations with this enzyme,” said Steven Rokita, a professor of chemistry at Johns Hopkins who led the research. “It could offer a good way to control fertility of all kinds of biological and agricultural pests, starting with mosquito populations.”
The findings are set to publish ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
[Press-News.org] Catch and release can give sea turtles the bends #ASA186Veterinarians team up with fishers to evaluate the health of accidentally caught sea turtles