DeepCRBP: Improved predicting function of circRNA-RBP binding sites with deep feature learning
2024-05-14
(Press-News.org)
There is growing evidence that it is essential to predict the interactions between circRNAs and RBP binding sites for diagnosing diseases and providing a potential target to treat diseases. Many studies have predicted the binding sites of circRNA-RBPs by using deep learning methods based on the sequence information of circRNAs for each RBP. However, the most of previous works only extract sequence feature, with a lack of exploiting the essential topological information from the secondary structure which contains rich spatial information.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Wen Zhang published their new research on 15 April 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
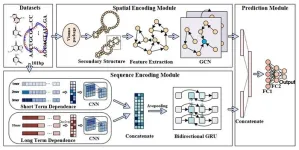
The team propose a novel deep feature learning method named DeepCRBP to learn the representations of circRNAs for better predicting the binding sites of circRNA-RBPs. DeepCRBP is consisted of spatial encoding module and sequence encoding module in which capture the local and global contextual feature in the circRNA sequences for rich semantic and high discrimination power, and synergistically construct molecular graph to represent the secondary structure of circRNAs for deriving essential topological information, respectively. The performance of DeepCRBP outperforms several state-of-the-art baseline methods.
DeepCRBP is composed of spatial encoding module, sequence encoding module and prediction module. In the spatial encoding module, circRNA sequences are converted into molecular graphs and then GCN is utilized to capture the prominent structure information. In the sequence encoding module, DeepCRBP utilizes multiple sequence encoding strategies to obtain the short term dependence information with local patterns and the long term dependence information with global patterns, respectively. In the prediction module, the representations extracted from the aforementioned modules are concatenated and fed into the 2-layer MLPs to predict the binding sites of circRNA-RBPs.
Future work can focus on applying the DeepCRBP to lncRNA or other RNA binding sites identification and developing general prediction software.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-2798-1
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-14
BOSTON (May 14, 2024) – A new editorial published this May in the British Journal of Sports Medicine by experts from Spaulding Rehabilitation, Boston University, Mayo Clinic, and the Concussion Legacy Foundation, argues that the term “subconcussion” is a dangerous misnomer that should be retired. The authors are appealing to the medical community and media to substitute the term with more specific terms so the public can better understand the risks of brain injuries and advance effective efforts to prevent chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE).
“The public has been led to believe through media coverage ...
2024-05-14
Researchers say the discovery of very high genetic diversity in leopards found in the Highveld region of South Africa has increased the need for conservation efforts to protect leopards in the country.
Declan Morris, a PhD candidate with the University of Adelaide’s School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, led the research project, which discovered that the two maternal lineages of leopards found in Africa overlap in the Highveld, leading to the high genetic diversity.
One lineage can be found across most of the African continent, while the other is confined ...
2024-05-14
Love it or hate it, Facebook Marketplace is the largest online resale site today with more than one billion monthly users. A new study conducted by UBC researchers sheds light on the intricate web of trust, privacy and safety factors shaping users’ experiences on this popular platform.
Researchers interviewed 42 Facebook Marketplace buyers and sellers in the U.S. and Canada to uncover the factors associated with trading decisions.
“Concerns for physical and financial safety, as well as well-being, were top ...
2024-05-14
[New York, NY, May 13, 2024] — Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have made a significant discovery, identifying genetic connections between inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD). Published in Genome Medicine (DOI 10.1186/s13073-024-01335-2) on May 13, their study highlights the potential for joint therapeutic strategies to target these two challenging disorders.
The team, led by Meltem Ece Kars, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at The Charles Bronfman Institute for Personalized Medicine; Yuval Itan, PhD, Associate Professor of Genetics and Genomic ...
2024-05-14
Key takeaways
A new study from UCLA and Duke University shows local journalism that produces detailed coverage about aging infrastructure increases voter support for additional infrastructure investment.
Basic, undetailed reporting, like that from severely understaffed newsrooms or AI-generated stories, resulted in lower support for infrastructure spending.
Voters demonstrated a willingness to hold local politicians accountable when provided with context in local reporting.
Reading strong local journalism is tied to greater support for funding dams, sewers ...
2024-05-14
Diamond is the hardest material found in nature — diamond also has the highest thermal conductivity, allowing the most heat to flow through it rapidly.
An international team of scientists discovered using supercomputer simulations that by flexing diamond, its thermal conductivity can be drastically tuned up or down. Scientists worldwide are interested in studying elastic strain engineering to discover the properties that materials exhibit when they are under large tensile or shear stresses.
Findings like this could open ...
2024-05-14
FRANKFURT. Hardly any other molecule has a more turbulent past than thalidomide. It was the central ingredient in a drug approved in many countries in the 1950s as a sedative and sleeping pill. However, it soon became apparent that pregnant women who had taken thalidomide often gave birth to children with severe deformities.
For the past few decades, however, medicine has nevertheless pinned great hopes on it again. Studies have shown, among other things, that it inhibits the growth of blood vessels and is therefore potentially suitable for cutting off tumors from their nutrient supply. It then also proved very effective in the treatment of multiple myeloma, ...
2024-05-14
UK survey examines consumer attitudes towards and willingness to consume insect-based foods.
Only 13% of respondents said they would be willing to regularly consume insects, with younger respondents less willing to give insects a try, as were those with higher sensitivity to food disgust.
*Please mention the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024, Venice,12-15 May) if using this material*
New research being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May), finds that insect-based foods remain unappealing ...
2024-05-14
New research being presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May) has found that many people who are living with obesity conceal their body in their WhatsApp profile pictures.
Profile pictures of pets, family members, landscapes, flowers and cartoon characters may indicate the individual has body dysmorphic disorder, says lead Dr Antonella Franceschelli, of Unicamillus International Medical University, Rome, Italy.
Body dysmorphic disorder is a condition in which a person has a distorted image of their body. They feel dissatisfied with their physical appearance, may experience shame or anxiety about their body and, in the case ...
2024-05-14
There is an urgent need to harness the potential of TikTok and other social media channels to provide scientific information about obesity to young people in engaging and accessible way, the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May) will hear.
The popularity and broad reach of such platforms provides the opportunity to reach diverse audiences, including teenagers and young adults, explains lead researcher Dr Antonella Franceschelli, of Unicamillus International Medical University, Rome, Italy.
The percentage of obese children and adolescents worldwide more than quadrupled among girls (from 1.7% to 6.9%) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] DeepCRBP: Improved predicting function of circRNA-RBP binding sites with deep feature learning