(Press-News.org)
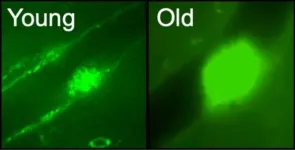
“In this study, we first obtained evidence that, in mouse, aging primarily reduced the number of active sweat glands.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 14, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 8, entitled, “Characterization of age-associated gene expression changes in mouse sweat glands.”
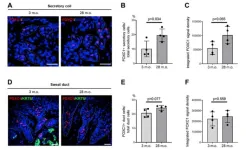
Evaporation of sweat on the skin surface is the major mechanism for dissipating heat in humans. The secretory capacity of sweat glands (SWGs) declines during aging, leading to heat intolerance in the elderly, but the mechanisms responsible for this decline are poorly understood. In this new study, researchers Alexandra G. Zonnefeld, Chang-Yi Cui, Dimitrios Tsitsipatis, Yulan Piao, Jinshui Fan, Krystyna Mazan-Mamczarz, Yutong Xue, Fred E. Indig, Supriyo De, and Myriam Gorospe from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Aging investigated the molecular changes accompanying SWG aging in mice, where sweat tests confirmed a significant reduction of active SWGs in old mice relative to young mice.
“We first identified SWG-enriched mRNAs by comparing the skin transcriptome of Eda mutant Tabby male mice, which lack SWGs, with that of wild-type control mice by RNA-sequencing analysis.”
This comparison revealed 171 mRNAs enriched in SWGs, including 47 mRNAs encoding ‘core secretory’ proteins such as transcription factors, ion channels, ion transporters, and trans-synaptic signaling proteins. Among these, 28 SWG-enriched mRNAs showed significantly altered abundance in the aged male footpad skin, and 11 of them, including Foxa1, Best2, Chrm3, and Foxc1 mRNAs, were found in the ‘core secretory’ category. Consistent with the changes in mRNA expression levels, immunohistology revealed that higher numbers of secretory cells from old SWGs express the transcription factor FOXC1, the protein product of Foxc1 mRNA.
“In sum, our study identified mRNAs enriched in SWGs, including those that encode core secretory proteins, and altered abundance of these mRNAs and proteins with aging in mouse SWGs.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205776
Corresponding Authors: Chang-Yi Cui, Myriam Gorospe
Corresponding Emails: cuic@mail.nih.gov, gorospem@grc.nia.nih.gov
Keywords: FOXA1, BEST2, FOXC1, ectodysplasin/Eda, Tabby
Go Behind the Study with the author interview.
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Aging publishes research papers in all fields of aging research including but not limited, aging from yeast to mammals, cellular senescence, age-related diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s diseases and their prevention and treatment, anti-aging strategies and drug development and especially the role of signal transduction pathways such as mTOR in aging and potential approaches to modulate these signaling pathways to extend lifespan. The journal aims to promote treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X, formerly Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
DALLAS, May 13, 2024 — Fewer than half of all women are aware that heart disease is their leading cause of death. That is why the American Heart Association, celebrating one hundred years of lifesaving service, created its community-based Woman of Impact™ initiative as an outgrowth of its year-round Go Red for Women® activist movement. The movement spotlights the lack of awareness and the clinical care gaps in women’s heart health. This year’s National Winner of the Go Red for Women 2024 Woman of Impart initiative is a 26-year-old heart transplant recipient, stroke survivor and American Heart Association local volunteer, Hana Hooper from Puget ...
The blood-retinal barrier is designed to protect our vision from infections by preventing microbial pathogens from reaching the retina where they could trigger an inflammatory response with potential vision loss. But researchers at the University of Missouri School of Medicine have discovered the virus that causes COVID-19 can breach this protective retinal barrier with potential long-term consequences in the eye.
Pawan Kumar Singh, PhD, an assistant professor of ophthalmology, leads a team researching new ways to prevent and treat ocular infectious diseases. Using a humanized ...
Scientists have discovered a new insight into the genetic pathway of childhood cancer, offering new hope for tailored treatments.
Researchers from the University of Sheffield have created a stem cell model designed to investigate the origins of neuroblastoma, a cancer primarily affecting babies and young children.
Neuroblastoma is the most common childhood tumour occurring outside the brain, affecting the lives of approximately 600 children in the European Union and the United Kingdom each year.
Until now, studying genetic changes and their role in neuroblastoma initiation has been challenging due to the lack of suitable laboratory ...
As people age, they become more prone to blood clotting diseases, when blood cells called platelets clump together when they don’t need to and can cause major issues such as strokes and cardiovascular disease. For decades, scientists have studied why older people’s blood cells behave in this way, using their insights to develop the myriad of blood-thinning drugs now on the market for treating the leading cause of death in the United States.
Now, UC Santa Cruz Professor of Biomolecular Engineering Camilla Forsberg and her research group have ...
Researchers have found that 2023 was the hottest summer in the Northern Hemisphere in the past two thousand years, almost four degrees warmer than the coldest summer during the same period.
Although 2023 has been reported as the hottest year on record, the instrumental evidence only reaches back as far as 1850 at best, and most records are limited to certain regions.
Now, by using past climate information from annually resolved tree rings over two millennia, scientists from the University of Cambridge and the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz have shown how exceptional the summer of 2023 was.
Even allowing for natural climate variations over hundreds of years, 2023 was still ...
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 4PM GMT (11AM ET) on 14 May 2024.
Peer reviewed | Observational | People
Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) is present in hundreds of copies in the genome, but has not previously been part of genetic analyses. A new study of 500,000 individuals indicates that people who have more copies of rDNA are more likely to develop inflammation and diseases during their lifetimes.
Standard genetic analysis techniques have not studied areas of the human genome that are repetitive, such as ribosomal ...
Three out of four U.S. adults support the use of emerging technologies that estimate a future child’s likelihood of developing health conditions influenced by multiple genes — such as diabetes, heart disease, and depression — before an embryo is implanted during in vitro fertilization (IVF), according to a new public opinion survey led by researchers at Harvard Medical School.
Results of the survey, to be published May 14 in JAMA Network Open, underscore the need for public education and conversation about the positive ...
Children with neurodevelopmental disorders report congenital abnormalities, such as defects of the heart and/or urinary tract, at least ten times more frequent compared to other children. This is one of the findings from an analysis from Radboud university medical center of data from over 50,000 children. Thanks to this new database, it's now much clearer which health problems are associated with a particular neurodevelopmental disorder and which are not. The study has been published in Nature Medicine.
Two to three percent of the population have a neurodevelopmental disorder, such as autism or intellectual ...
May 14 2024 – A study in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (JAACAP), published by Elsevier, found that pharmacological treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) reduced violence- and public-order related crimes. However, it did not reduce other types of crimes, among patients with ADHD in early to late adolescence considered to be in the grey zone (or on the margin) for such treatment.
This study uses variation in healthcare providers treatment preference as the basis for a quasi-experimental design that examines the effect of pharmacological ...
A team led by Dr. Eddie Imada, assistant professor of research in pathology and laboratory medicine, has been awarded a three-year, $1.5 million United States Department of Defense grant for research on a cellular process called alternative polyadenylation and its role in prostate cancer.
The grant was awarded under DoD’s long-running Prostate Cancer Research Program, a Congressionally-directed medical research funding project aimed at improving prostate cancer prevention, detection and patient care. Thousands of current and former servicemen ...