(Press-News.org) A team led by Dr. Eddie Imada, assistant professor of research in pathology and laboratory medicine, has been awarded a three-year, $1.5 million United States Department of Defense grant for research on a cellular process called alternative polyadenylation and its role in prostate cancer.
The grant was awarded under DoD’s long-running Prostate Cancer Research Program, a Congressionally-directed medical research funding project aimed at improving prostate cancer prevention, detection and patient care. Thousands of current and former servicemen are diagnosed with, and die of, prostate cancer every year.
At first glance, polyadenylation isn’t an obvious culprit in cancer. It is an evolutionarily ancient and routine process that adds a tail of RNA nucleotide “letters”—all of them adenosines, represented by the letter “A” in the genetic code—to one end of a gene’s newly made RNA transcript. This polyA tail and other routine modifications turn the transcript into a messenger RNA (mRNA). Scientists know that polyadenylation increases the stability of the mRNA and helps it exit the cell nucleus so it can be translated into a protein in the cytoplasm.
On the other hand, polyadenylation is not a straightforward process: For about two-thirds of human genes, the place where the raw RNA transcript is trimmed and polyadenylated – known as polyadenylation sites – sometimes differs resulting in what is termed alternative polyadenylation. This “alternative polyadenylation” can lead to a host of changes including greater or lesser production of the protein encoded by the gene, or even different versions of the protein. In some cases that appears to be a normal, healthy way of fine-tuning various cell processes, including cell division and cell maturation. In other cases, alternative polyadenylation seems dysfunctional; it has been linked to multiple diseases including cancers.
Dr. Imada says his project may be the first in-depth, genome-wide exploration of alternative polyadenylation’s role in prostate cancer. He and his team will use computational analysis of RNA sequences from healthy individuals and from patient tumor samples to see how changes in polyadenylation site usage affect prostate cancer progression and treatment response.
Potential payoffs of the research include uncovering new molecular targets that can lead to new treatments for prostate cancer—which often becomes resistant to current treatments—as well as better ways of enhancing therapy selection for existing treatments such as immunotherapies.
END
WCM awarded grant to study RNA processing in prostate cancer
2024-05-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Artificial intelligence tool to improve heart failure care
2024-05-14
UVA Health researchers have developed a powerful new risk assessment tool for predicting outcomes in heart failure patients. The researchers have made the tool publicly available for free to clinicians.
The new tool improves on existing risk assessment tools for heart failure by harnessing the power of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) to determine patient-specific risks of developing unfavorable outcomes with heart failure.
“Heart failure is a progressive condition that affects not only quality of life but quantity as well. All heart failure patients are not the same. Each patient ...
People without an inner voice have poorer verbal memory
2024-05-14
Previously, it was commonly assumed that having an inner voice had to be a human universal. But in recent years, researchers have become aware that not all people share this experience.
According to postdoc and linguist Johanne Nedergård from the University of Copenhagen, people describe the condition of living without an inner voice as time-consuming and difficult because they must spend time and effort translating their thoughts into words:
“Some say that they think in pictures and then translate the pictures into words when they need to say ...
Courtship through flute song in Indigenous Southern Plains culture #ASA186
2024-05-14
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 14, 2024 – Every love story is unique, and in traditional Indigenous Southern Plains culture, it begins with an original ballad performed on the flute. In order to win a lover’s affection, and respect among the tribe, each pursuer must compose one good flute serenade.
Paula Conlon, a former music professor at the University of Oklahoma, has researched the history and cultural significance of the Indigenous flute since the 1980s. Conlon will present her work Tuesday, May 14, at 9:45 a.m. EDT as part of a joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and the Canadian Acoustical ...
SwRI investigating unusual substorm in Earth’s magnetotail using MMS data
2024-05-14
SAN ANTONIO — May 14, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute is investigating an unusual event in the Earth’s magnetotail, the elongated portion of the planet’s magnetosphere trailing away from the Sun. Using data from NASA’s Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission, SwRI scientists are examining the nature of substorms, fleeting disturbances in the magnetotail that release energy and often cause aurorae.
Since their launch in 2015, the MMS spacecraft have been surveying the magnetopause, the boundary between the magnetosphere ...
Mislabelled shark meat rampant in Australian markets, study finds
2024-05-14
Researchers at Macquarie University have found a significant portion of shark meat sold in Australian fish markets and takeaway shops is mislabelled, including several samples from threatened species.
The findings, published in the journal Marine and Freshwater Research this month, highlight the ineffectiveness of seafood labelling and the grave implications for both consumer choice and shark conservation.
Researchers collected 91 samples of shark meat from 28 retailers across six Australian states and territories and used DNA ...
90% of Floridians believe climate change is happening
2024-05-14
The latest edition of Florida Atlantic University’s “Florida Climate Resilience Survey,” found that 90% of Floridians believe that climate change is happening. In comparison, a recent Yale University survey showed 72% of all Americans believe climate change is happening. The FAU survey includes questions on beliefs about climate change, experience with extreme weather events and support for climate-related policies.
The Florida Climate Resilience Survey also shows belief in human-caused climate change has surged among Florida Independents while slipping among Republicans in the state since last fall.
But despite these changes, the latest edition of the survey ...
Using artificial intelligence to speed up and improve the most computationally-intensive aspects of plasma physics in fusion
2024-05-14
The intricate dance of atoms fusing and releasing energy has fascinated scientists for decades. Now, human ingenuity and artificial intelligence are coming together at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) to solve one of humankind’s most pressing issues: generating clean, reliable energy from fusing plasma.
Unlike traditional computer code, machine learning — a type of artificially intelligent software — isn’t simply a list of instructions. Machine learning is software that can analyze data, infer relationships between features, learn from this new knowledge and adapt. PPPL researchers ...
A new perspective reviews pork’s place in global sustainable healthy diets
2024-05-14
A new food systems perspective study1 published in Advances in Nutrition from the University of Washington is the first to explore the place of fresh pork in in the global food sustainability framework.
Merging data on food composition, food trends, prices and incomes, the study concluded that pork meat is an affordable high-quality protein and may have a lower environmental (GHGE) impact than previously believed. The perspective also makes clear pork is well positioned to meet the rising global demand for animal protein.
Pork is one of the most consumed meats globally,2 providing high quality protein and several priority ...
Heat’s effects on police and judges
2024-05-14
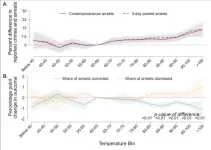
High temperatures affect the decision-making of police officers and judges. Previous research has shown that heat can increase criminal activity, with the leading theory proposing that heat reduces emotional control and increases aggression. A. Patrick Behrer and Valentin Bolotnyy investigate the effects of heat on the behavior of those who respond to criminal activity. The authors analyzed records of 10 million arrests across the state of Texas from 2010 through 2017, along with the legal outcomes that followed each arrest. These data were merged with daily temperature data. Police made fewer arrests per reported crime on the hottest days in the sample, and these arrests were ...
Scientists unlock mysteries of orangutan communication
2024-05-14
In a new study published in PeerJ Life & Environment, scientists have revealed the intricate vocal patterns of Bornean orangutans, shedding new light on the complexities of their communication. Titled "Vocal Complexity in the Long Calls of Bornean Orangutans," the research, led by Dr. Wendy Erb from the K. Lisa Yang Center for Conservation Bioacoustics at the Cornell Lab of Ornithology, unveils the remarkable diversity and variability within orangutan long call vocalizations.
Orangutans, the charismatic great apes of Southeast Asia, are known for their complex social behaviors and vocal communication. However, understanding the nuances of their vocal repertoire ...