(Press-News.org) SASKATOON--Using an innovative new method, a University of Saskatchewan (USask) researcher is building tiny pseudo-organs from stem cells to help diagnose and treat Alzheimer’s.
When Dr. Tyler Wenzel (PhD) first came up with the idea of building a miniature brain from stem cells, he never could have predicted how well his creations would work.
Now, Wenzel’s “mini-brain” could revolutionize the way Alzheimer’s and other brain-related diseases are diagnosed and treated.
“Never in our wildest dreams did we think that our crazy idea would work,” he said. “These could be used as a diagnostic tool, built from blood.”
Wenzel, a postdoctoral fellow in the College of Medicine’s Department of Psychiatry, developed the idea for the “mini-brain” - or more formally, a one-of-a-kind cerebral organoid model – while working under the supervision of Dr. Darrell Mousseau (PhD).
Human stem cells can be manipulated to develop into practically any other cell in the body. Using stem cells taken from human blood, Wenzel was able to create a tiny artificial organ – roughly three millimetres across and resembling visually what Wenzel described as a piece of chewed gum someone has tried to smooth out again.
These “mini-brains” are built by creating stem cells from a blood sample, and then transforming these stem cells into functioning brain cells. Using small synthetic organoids for research is not a novel concept – but the “mini-brains” developed in Wenzel’s lab are unique. As outlined in Wenzel’s recent published article in Frontiers of Cellular Neuroscience, the brains from Wenzel’s lab are comprised of four different types of brain cells while most brain organoids are comprised of only neurons.
In testing, Wenzel's "mini-brains" more accurately reflect a fully-fledged adult human brain, so they can be used to more closely examine neurological conditions of adult patients, such as Alzheimer disease.
And for those “mini-brains” created from the stem cells of individuals who have Alzheimer’s, Wenzel determined that the artificial organ displayed the pathology of Alzheimer’s – just on a smaller scale.
“If stem cells have the capacity to become any cell in the human body, the question then came ‘could we create something that resembles an entire organ?’” Wenzel said. “While we were developing it, I had the crazy idea that if these truly are human brains, if a patient had a disease like Alzheimer’s and we grew their ‘mini-brain,’ in theory that tiny brain would have Alzheimer’s.”
Wenzel said this technology has the potential to change the way health services are provided to those with Alzheimer’s, particularly in rural and remote communities. This groundbreaking research has already received support from the Alzheimer Society of Canada.
If Wenzel and his colleagues can create a consistent way to diagnose and treat neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s using only a small blood sample – which has a relatively long shelf life and can be couriered – instead of requiring patients to travel to hospitals or specialized clinics, it could be a tremendous resource savings for the healthcare system and a burden off of patients.
“In theory, if this tool works the way we think it does, we could just get a blood sample shipped from La Loche or La Ronge to the university and diagnose you like that,” he said.
The early proof-of-concept work on the “mini-brains” has been extremely promising – which means the next step for Wenzel is expanding the testing to a larger pool of patients.
The researchers are also interested in trying to expand the scope of the “mini-brain” research. According to Wenzel, if they can confirm the “mini-brains” accurately reflect other brain diseases or neurological conditions, they could potentially be used to speed up diagnoses or test the efficacy of drugs on patients.
As an example, Wenzel pointed to the substantial wait times to see a psychiatrist in Saskatchewan. If the “mini-brains” could be used to test which antidepressant works best on a patient suffering from depression, it could dramatically reduce the time required to see a doctor and receive a prescription.
A former high school science teacher who made the move into the world of research and academia, Wenzel said it’s the “nature of research” to come up with a hypothesis and hit close to the mark in an experiment that excites him his work.
The astounding success of the early “mini-brains,” however, has been so staggering that Wenzel admitted he still struggles to wrap his own brain around it.
“I’m still in disbelief, but it’s also extremely motivating that something like this happened,” Wenzel said. “It gives me something that I think will impact society and have actual relevance and create some change … it has a strong potential to shift the landscape of medicine.”
-30-
For more information, contact:
Daniel Hallen
USask Media Relations
daniel.hallen@usask.ca
306-966-6922
END
MEDIA INQUIRES
Laura Muntean
laura.muntean@ag.tamu.edu
601-248-1891
FOR ...
MIT researchers, including several undergraduate students, have discovered three of the oldest stars in the universe, and they happen to live in our own galactic neighborhood.
The team spotted the stars in the Milky Way’s “halo” — the cloud of stars that envelopes the entire main galactic disk. Based on the team’s analysis, the three stars formed between 12 and 13 billion years ago, the time when the very first galaxies were taking shape.
The researchers have coined the stars ...
Within the Biodiversity Community Integrated Knowledge Library (BiCIKL) project, 14 European institutions from ten countries, spent the last three years elaborating on services and high-tech digital tools, in order to improve the findability, accessibility, interoperability and reusability (FAIR-ness) of various types of data about the world’s biodiversity. These types of data include peer-reviewed scientific literature, occurrence records, natural history collections, DNA data and more.
By ensuring all those data are readily available and efficiently interlinked to each other, the project consortium’s intention is to provide better tools to the scientific community, ...
Metal halide perovskites have emerged in recent years as a low-cost, highly efficient semiconducting material for solar energy, solid-state lighting and more. Despite their growing use, a fundamental understanding of the origins of their outstanding properties is still lacking. A Husker scientist is aiming to find answers that could lead to the development of new materials and new applications.
Yinsheng Guo, assistant professor of chemistry at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, also wants to transform how physical chemistry is taught to undergraduate and graduate students, who often struggle to understand and apply what ...
Reston, VA—The protein galectin-1 (Gal-1) has been identified as a new PET imaging biomarker for immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy, allowing physicians to predict the tumor responses before beginning treatment. Information garnered from Gal-1 PET imaging could also be used to facilitate patient stratification and optimize immunotherapy, enabling targeted interventions and improving patient outcomes. This research was published in the May issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Immunotherapies, such as ICB, have produced promising clinical ...
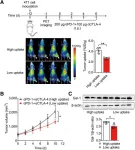
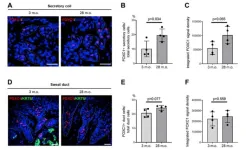
“In this study, we first obtained evidence that, in mouse, aging primarily reduced the number of active sweat glands.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 14, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 8, entitled, “Characterization of age-associated gene expression changes in mouse sweat glands.”
Evaporation of sweat on the skin surface is the major mechanism for dissipating heat in humans. The secretory capacity of sweat glands (SWGs) ...
DALLAS, May 13, 2024 — Fewer than half of all women are aware that heart disease is their leading cause of death. That is why the American Heart Association, celebrating one hundred years of lifesaving service, created its community-based Woman of Impact™ initiative as an outgrowth of its year-round Go Red for Women® activist movement. The movement spotlights the lack of awareness and the clinical care gaps in women’s heart health. This year’s National Winner of the Go Red for Women 2024 Woman of Impart initiative is a 26-year-old heart transplant recipient, stroke survivor and American Heart Association local volunteer, Hana Hooper from Puget ...
The blood-retinal barrier is designed to protect our vision from infections by preventing microbial pathogens from reaching the retina where they could trigger an inflammatory response with potential vision loss. But researchers at the University of Missouri School of Medicine have discovered the virus that causes COVID-19 can breach this protective retinal barrier with potential long-term consequences in the eye.
Pawan Kumar Singh, PhD, an assistant professor of ophthalmology, leads a team researching new ways to prevent and treat ocular infectious diseases. Using a humanized ...
Scientists have discovered a new insight into the genetic pathway of childhood cancer, offering new hope for tailored treatments.
Researchers from the University of Sheffield have created a stem cell model designed to investigate the origins of neuroblastoma, a cancer primarily affecting babies and young children.
Neuroblastoma is the most common childhood tumour occurring outside the brain, affecting the lives of approximately 600 children in the European Union and the United Kingdom each year.
Until now, studying genetic changes and their role in neuroblastoma initiation has been challenging due to the lack of suitable laboratory ...
As people age, they become more prone to blood clotting diseases, when blood cells called platelets clump together when they don’t need to and can cause major issues such as strokes and cardiovascular disease. For decades, scientists have studied why older people’s blood cells behave in this way, using their insights to develop the myriad of blood-thinning drugs now on the market for treating the leading cause of death in the United States.
Now, UC Santa Cruz Professor of Biomolecular Engineering Camilla Forsberg and her research group have ...