(Press-News.org) It’s one thing to dream up a quantum internet that could send hacker-proof information around the world via photons superimposed in different quantum states. It’s quite another to physically show it’s possible.
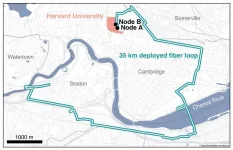
That’s exactly what Harvard physicists have done, using existing Boston-area telecommunication fiber, in a demonstration of the world’s longest fiber distance between two quantum memory nodes to date. Think of it as a simple, closed internet between point A and B, carrying a signal encoded not by classical bits like the existing internet, but by perfectly secure, individual particles of light.
The groundbreaking work, published in Nature, was led by Mikhail Lukin, the Joshua and Beth Friedman University Professor in the Department of Physics, in collaboration with Harvard professors Marko Lončar and Hongkun Park, who are all members of the Harvard Quantum Initiative, alongside researchers at Amazon Web Services.
The Harvard team established the practical makings of the first quantum internet by entangling two quantum memory nodes separated by optical fiber link deployed over a roughly 22-mile loop through Cambridge, Somerville, Watertown, and Boston. The two nodes were located a floor apart in Harvard’s Laboratory for Integrated Science and Engineering.
Quantum memory, analogous to classical computer memory, is an important component of an interconnected quantum computing future because it allows for complex network operations and information storage and retrieval. While other quantum networks have been created in the past, the Harvard team’s is the longest fiber network between devices that can store, process and move information.
Each node is a very small quantum computer, made out of a sliver of diamond that has a defect in its atomic structure called a silicon-vacancy center. Inside the diamond, carved structures smaller than a hundredth the width of a human hair enhance the interaction between the silicon-vacancy center and light.
The silicon-vacancy center contains two qubits, or bits of quantum information: one in the form of an electron spin used for communication, and the other in a longer-lived nuclear spin used as a memory qubit to store entanglement (the quantum-mechanical property that allows information to be perfectly correlated across any distance). Both spins are fully controllable with microwave pulses. These diamond devices – just a few millimeters square – are housed inside dilution refrigeration units that reach temperatures of -459 Fahrenheit.
Using silicon-vacancy centers as quantum memory devices for single photons has been a multi-year research program at Harvard. The technology solves a major problem in the theorized quantum internet: signal loss that can’t be boosted in traditional ways. A quantum network cannot use standard optical-fiber signal repeaters because copying of arbitrary quantum information is impossible – making the information secure, but also very hard to transport over long distances.
Silicon vacancy center-based network nodes can catch, store and entangle bits of quantum information while correcting for signal loss. After cooling the nodes to close to absolute zero, light is sent through the first node and, by nature of the silicon vacancy center’s atomic structure, becomes entangled with it.
“Since the light is already entangled with the first node, it can transfer this entanglement to the second node,” explained first author Can Knaut, a Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences student in Lukin’s lab. “We call this photon-mediated entanglement.”
Over the last several years, the researchers have leased optical fiber from a company in Boston to run their experiments, fitting their demonstration network on top of the existing fiber to indicate that creating a quantum internet with similar network lines would be possible.
“Showing that quantum network nodes can be entangled in the real-world environment of a very busy urban area, is an important step towards practical networking between quantum computers,” Lukin said.
A two-node quantum network is only the beginning. The researchers are working diligently to extend the performance of their network by adding nodes and experimenting with more networking protocols.
The paper is titled “Entanglement of Nanophotonic Quantum Memory Nodes in a Telecom Network.” The work was supported by the AWS Center for Quantum Networking’s research alliance with the Harvard Quantum Initiative, the National Science Foundation, the Center for Ultracold Atoms (an NSF Physics Frontiers Center), the Center for Quantum Networks (an NSF Engineering Research Center), the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, and other sources.
END
A simple internet with significant possibilities
Physicists demo first metro-area quantum computer network in Boston
2024-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unwrapping the origin story of the baobab
2024-05-15
The baobab (Adansonia) is a genus of trees with eight extant (in existence currently) species and a long history of humans marveling at them. For as much admiration the baobabs get, there is an equal amount of mystery surrounding their origin.
Genomic and ecological analyses recently done by a global research team led by Sino-Africa Joint Research Center, CAS (hosted by Wuhan Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences), suggest that Madagascar, is the origin from where all other baobab species hail. With a deeper understanding of the baobabs' genetics, researchers are hoping to uncover some clues on what ...
The origin and long-distance travels of upside down trees
2024-05-15
The iconic baobabs, also known as upside-down trees, or the tree of life, have much cultural significance, inspiring innumerable arts, folklore, and traditions. A research published in Nature, involving international collaboration between Wuhan Botanical Garden (China), Royal Botanic Gardens (Kew, UK), University of Antananarivo (Madagascar) and Queen Mary University of London (UK) reveal a remarkable example of species radiation in Madagascar followed by long distance dispersal to Africa and Australia. With speciation, an astonishing divergence of pollination mechanisms evolved, that exploit hawkmoths, bats and lemurs for ...
Some mice may owe their monogamy to a newly evolved type of cell
2024-05-15
NEW YORK, NY — What makes the oldfield mouse steadfastly monogamous throughout its life while its closest rodent relatives are promiscuous? The answer may be a previously unknown hormone-generating cell, according to a new study published online today in Nature from scientists at Columbia's Zuckerman Institute.
"The hormone from these cells was actually first discovered in humans many decades ago, but nobody really knew what it did," said Andrés Bendesky, MD, PhD, a principal investigator at Columbia's Zuckerman Institute. "We’ve discovered ...
Mortality in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 vs influenza in fall-winter 2023-2024
2024-05-15
About The Study: This study found that in fall-winter 2023-2024, the risk of death in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 was greater than the risk of death in patients hospitalized for seasonal influenza.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ziyad Al-Aly, M.D., email ziyad.alaly@va.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.7395)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # ...
First ‘warm-blooded’ dinosaurs may have emerged 180 million years ago
2024-05-15
The ability to regulate body temperature, a trait all mammals and birds have today, may have evolved among some dinosaurs early in the Jurassic period about 180 million years ago, suggests a new study led by UCL and University of Vigo researchers.
In the early 20th century, dinosaurs were considered slow-moving, “cold-blooded” animals like modern-day reptiles, relying on heat from the sun to regulate their temperature. Newer discoveries indicate some dinosaur types were likely capable of generating their own body heat but when this adaptation occurred is unknown.
The new study, published in the journal Current Biology, looked at ...
Next-generation sustainable electronics are doped with air
2024-05-15
Semiconductors are the foundation of all modern electronics. Now, researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a new method where organic semiconductors can become more conductive with the help of air as a dopant. The study, published in the journal Nature, is a significant step towards future cheap and sustainable organic semiconductors.
“We believe this method could significantly influence the way we dope organic semiconductors. All components are affordable, easily accessible, and potentially environmentally friendly, which is a prerequisite for future sustainable ...
Disparities in patient portal engagement among patients with hypertension treated in primary care
2024-05-15
About The Study: This cohort study of patients with hypertension found clear sociodemographic disparities in patient portal engagement among those treated in primary care. Without special efforts to engage patients with portals, interventions that use patient portals to target hypertension may exacerbate disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Rasha Khatib, Ph.D., M.H.S., email rasha.alkhatib@aah.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.11649)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
Dose-dependent association between body mass index and mental health and changes over time
2024-05-15
About The Study: This study revealed a U-shaped association between adolescent body mass index and mental health, which was consistent across sex and grades and became stronger over time. These insights emphasize the need for targeted interventions addressing body image and mental health, and call for further research into underlying mechanisms.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Shanquan Chen, Ph.D., email Shanquan.chen@lshtm.ac.uk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.0921)
Editor’s ...
The doctor is in…. but what’s behind them?
2024-05-15
Americans have gotten used to seeing their doctors and other health care providers using telehealth video visits in the past four years. But a new study reveals that what a doctor has behind them during a telehealth visit can make a difference in how the patient feels about them and their care.
Even if the doctor is miles away from their usual in-person clinic or exam room, they should make it look like they’re there, the study suggests.
Even better: sitting in an office with their diplomas hanging ...
Structural evolution and high-temperature sensing performance of polymer-derived SiAlBCN ceramics
2024-05-15
The group of Gang Shao from Zhengzhou University, China recently investigated the structural evolution of pentagonal polymer-derived SiAlBCN ceramics (PDCs) and outlined PDC-based sensor technology for high-temperature extreme environments. The high-performance temperature sensing materials including high sensitivity, fast response, wide detection range are scarce and needful. This research developed a ceramic-based temperature with attractive performance that can be applied in high-temperature environments ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
[Press-News.org] A simple internet with significant possibilitiesPhysicists demo first metro-area quantum computer network in Boston