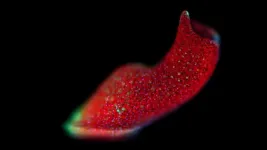
(Press-News.org) Many organisms are far more complex than just a single species. Humans, for example, are full of a variety of microbes. Some creatures have even more special connections, though. Acoels, unique marine worms that regenerate their bodies after injury, can form symbiotic relationships with photosynthetic algae that live inside them. These collections of symbiotic organisms are called a holobiont, and the ways that they “talk” to each other are something scientists are trying to understand – especially when the species in question are an animal and a solar-powered microbe.
Bo Wang, assistant professor of bioengineering in the Schools of Engineering and of Medicine at Stanford, has started to find some answers. His lab, in conjunction with the University of San Francisco, studies Convolutriloba longifissura, a species of acoel that hosts the symbiotic algae Tetraselmis. According to new research, published in Nature Communications, the researchers found that, when C. longifissura regenerates, a genetic factor that takes part in the acoel regeneration also controls how the algae inside of them reacts.
“We don’t know yet how these species talk to each other or what the messengers are. But this shows their gene networks are connected,” said Wang, who is a senior author of the paper.
Splitting worms
Because holobiont is a relatively new concept, scientists still aren’t sure what the nature of some relationships are. The odd name “acoel” is Greek for “no gut,” as the worms have no stomach to speak of. Instead, all things that they eat go directly into their internal tissues – which is also where algae float, photosynthesizing inside their bodies. This relationship provides a safe zone for the algae and extra energy from photosynthesis to the acoel.
“There was no guarantee that there was communication because the algae are not within the acoel’s cells, they’re floating around them,” says James Sikes, a researcher at the University of San Francisco and co-senior author of the paper. Sikes has been working with acoels for about 20 years, and their symbiotic relationship differentiates them from other animals that regenerate, like planarian flatworms and axolotls.
When these acoels reproduce asexually, they first bisect themselves. The head region grows a tail and becomes a new acoel. The tail, however, acts like the mythological Hydra and grows two new heads, which, then, split into two separate animals.
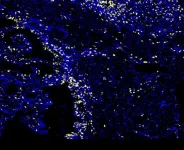
Animal regeneration requires communication across many different cell types, but in this case, it may also involve another organism entirely. Researchers were curious about how the algal colonies inside reacted to this process – in particular, whether they continued to photosynthesize as normal, and if not, what was controlling that? This was especially puzzling as the team found that photosynthesis wasn’t required for acoels to regenerate – they could do it in the dark. But there has to be conversation between the species for their long-term survival.
“Testing if photosynthesis was affected was an adventure. None of us knew what we were doing,” says Dania Nanes Sarfati, lead author of the paper, who was a doctoral student in Wang’s lab and Stanford Bio-X Bowes Fellow. “One of the most exciting things was that we could actually measure algal photosynthesis happening inside the animal.”
In addition, through sequencing, the team was able to differentiate the genes of the two species and figure out which pathways were responding to injury. These measurements helped them realize that the algae inside were undergoing a major reconstruction of their photosynthetic machinery during the regeneration – but the process by which it was being controlled was shocking.
The role of runt
When the results came back, Wang said the unpredictable happened. During regeneration, both the acoel’s regrowth and the algal photosynthesis appeared to be controlled by a common transcription factor in acoels called runt.
In the early stage, right after injury, runt is activated, kicking off the regeneration process. Meanwhile, algal photosynthesis drops off, but there is an upregulation in algal genes associated with photosynthesis – likely to compensate for the loss in photosynthesis due to the split. However, when the researchers knocked down runt, it halted both regeneration and the algal responses.
What’s special about runt is that it’s highly conserved, meaning the same factor is responsible for regeneration in many different organisms, including non-symbiotic acoels. But now it’s clear that instead of just controlling the acoel’s regenerative process, it also controls the communication with another species.
How holobionts communicate
Understanding how partners in symbiotic relationships communicate at the molecular level opens up many new questions for this field of research. “Are there rules of symbiosis? Do they exist?” said Nanes Sarfati. “This research sparks these kinds of questions, which we can link to other organisms.”
Wang believes it introduces more ways of investigating how symbiotic species interact and couple with each other to form holobionts. Some of these interactions could be potentially driven by chemicals, proteins, or environmental factors. But more concerningly, these interactions are now becoming vulnerable points under the challenge of climate change, causing symbiotic partners to separate. Sikes highlighted that he, Wang, and Nanes Sarfati all began from the animal side of the symbiotic relationship but realized that algae respond to host injury as well, potentially sparking similar questions in other systems.
“We often assume we know a lot, but we’re humbled when we look at different species,” Wang said. “They can do things in completely unexpected ways, which highlights the need to study more organisms and is becoming possible with technology.”
Additional Stanford co-authors include former graduate student Yuan Xue, PhD ‘21; PhD student Eun Sun Song; Stephen Quake, the Lee Otterson Professor of Bioengineering in the Schools of Engineering and Medicine and professor of applied physics in the School of Humanities and Sciences; and Adrien Burlacot, assistant professor (by courtesy) of biology in the School of Humanities and Sciences.
Burlacot is also a principal investigator at the Carnegie Institution for Science. Quake is also co-president of the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub, and a member of Stanford Bio-X, the Cardiovascular Institute, the Wu Tsai Human Performance Alliance, the Stanford Cancer Institute, and the Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute. Wang is also a member of Bio-X and the Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute.
This research was funded by a Bio-X Bowes Fellowship, a Stanford Interdisciplinary Graduate Fellowship, the Beckman Young Investigator Program, the Carnegie Institution for Science, and the National Institutes of Health.
END
Regenerating worms have genetic control over their algal partners
2024-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pre- and post-surgical immunotherapy improves outcomes for patients with operable lung cancer
2024-05-15
Compared with pre-surgical (neoadjuvant) chemotherapy alone, adding perioperative immunotherapy – given before and after surgery – significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) in patients with resectable early-stage non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC), according to researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Results from the Phase III CheckMate 77T study were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine. At a median follow-up of 25.4 months, the median EFS with chemotherapy alone was 18.4 months, while the median had not yet ...
'Trojan horse' weight loss drug more effective than available therapies
2024-05-15
“I consider the drugs available on the marked today as the first generation of weight-loss drugs. Now we have developed a new type of weight-loss drug that affects the plasticity of the brain and appears to be highly effective.”
So says Associate Professor and Group Leader Christoffer Clemmensen, from the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research at the University of Copenhagen, who is senior author of the new study, which has been published in the prestigious scientific journal Nature.
In the study, Christoffer Clemmensen and colleagues demonstrate a new use of the weight loss hormone GLP-1. GLP-1 can be used as a ‘Trojan ...
Reduced risk of breast cancer following bariatric surgery in women with hyperinsulinemia
2024-05-15
Bariatric surgery is associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer in women with obesity. These are the findings of a study conducted at the University of Gothenburg. The risk reduction is greatest for those with high blood insulin levels at the time of surgery.
The study, published in JAMA Surgery, is based on data from 2,867 women with obesity, half of whom had undergone bariatric surgery at 25 surgical departments. The remaining women, comprising the control group, received standard obesity treatment at 480 healthcare centers. The groups were otherwise comparable in terms of age and body composition.
The results show that a total of ...
Copper can't be mined fast enough to electrify the US
2024-05-15
Copper cannot be mined quickly enough to keep up with current U.S. policy guidelines to transition the country's electricity and vehicle infrastructure to renewable energy, according to a University of Michigan study.
The Inflation Reduction Act, signed into law in 2022, calls for 100% of cars manufactured to be electric vehicles by 2035. But an electric vehicle requires three to five times as much copper as an internal combustion engine vehicle—not to mention the copper required for upgrades to the electric grid.
"A ...
Guideline issued for people with epilepsy who may become pregnant
2024-05-15
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MAY 15, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A new guideline has been issued to help neurologists and other clinicians determine the best antiseizure medications for people with epilepsy who may become pregnant. The guideline is published in the May 15, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology (AAN), and was developed through a collaboration between the AAN, the American Epilepsy Society (AES) and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM). It was endorsed by the Child Neurology Society.
The guideline partially updates two 2009 AAN and AES ...
Only 20% of U.S. nonprofit hospitals invested in housing as part of the federal community benefit mandate
2024-05-15
Waltham — May 15, 2024 — A nationwide assessment of how nonprofit hospitals are addressing housing-related needs in their communities appears in the latest issue of Medical Care, the official journal of the Medical Care Section of the American Public Health Association. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Approximately 60% of hospitals in the United States are 501(c)(3) nonprofit organizations ...
The crystallization of memory: Study reveals how practice forms new memory pathways in the brain
2024-05-15
A new study led by UCLA Health has shown that repetitive practice not only is helpful in improving skills but also leads to profound changes in the brain’s memory pathways.
The research, published in the journal Nature and co-led by Rockefeller University, sought to unravel how the brain’s ability to retain and process information, known as working memory, improves through training.
To test this, researchers tasked mice with identifying and recalling a sequence of odors over the course of two weeks. Researchers then tracked neural activity in the animals as they practiced the task by using a novel, custom-built microscope that can image cellular activity ...
Dartmouth-led study provides new insights into phage therapy design
2024-05-15
Results from a new Dartmouth-led study, involving collaborators at the University of Pittsburgh and Yale University and published in the journal PLOS Biology, are providing new insights into the therapeutic potential of bacteriophage (phage) therapy for treating diseases like cystic fibrosis (CF).
A major challenge of treating people with CF—an inherited disease that causes sticky, thick mucus to build up in the lungs—are the persistent infections the disease causes which can lead to respiratory failure and death.
“Opportunistic ...
This time, it’s personal: Enhancing patient response to cancer immunotherapy
2024-05-15
LA JOLLA (May 15, 2024)—Immunotherapy has revolutionized the way we treat cancer in recent years. Instead of targeting the tumor itself, immunotherapies work by directing patients’ immune systems to attack their tumors more effectively. This has been especially impactful in improving outcomes for certain difficult-to-treat cancers. Still, fewer than half of all cancer patients respond to current immunotherapies, creating an urgent need to identify biomarkers that can predict which patients are most likely to benefit.
Recently, scientists have noticed that patients whose tumors have a mutation in a gene called ARID1A are ...
A novel multifunctional catalyst turns methane into valuable hydrocarbons
2024-05-15
Methane, a greenhouse gas that contributes significantly towards global warming, is also an important source of energy and an essential chemical resource. When used as a chemical feedstock, methane is typically converted into methanol first and then into hydrocarbons. However, this sequential conversion requires complex industrial setups. More importantly, since methane is a very stable molecule, its conversion into methanol requires tremendous amounts of energy when using conventional means, such ...