(Press-News.org) (WASHINGTON, May 17, 2024) – People who use metformin are less likely to develop a myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) over time, indicating that the treatment may help prevent the development of certain types of cancers, according to a study published in Blood Advances.
Metformin is a therapy used to treat high blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes that increases the effect of insulin, reduces how much glucose is released from the liver and helps the body absorb glucose. A meta-analysis of previous studies connected the therapy with a reduction in the risk of gastrointestinal, breast, and urologic cancers, while a retrospective study of U.S. veterans found that metformin users have a reduced risk for solid and hematological cancers.
“Our team was interested in understanding what other effects we see with commonly prescribed treatments like metformin,” said Anne Stidsholt Roug, MD, PhD, chief physician at Aarhus University Hospital and clinical associate professor at Aalborg University Hospital in Denmark. “The anti-inflammatory effect of metformin interested us, as MPNs are very inflammatory diseases. This is the first study to investigate the association between metformin use and risk of MPN.”
MPNs are a group of diseases that affect how bone marrow produces blood cells, resulting in an overproduction of red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets that can lead to bleeding problems, a greater risk of stroke or heart attack, and organ damage.
The researchers compared metformin use among patients diagnosed with MPNs and a matched population from the Danish general population between 2010 and 2018. Of the 3,816 MPN cases identified from the sample, a total of 268 (7.0%) individuals with MPN had taken metformin as compared to 8.2% (1,573 out of 19,080) of the control group of people who had taken metformin but were not diagnosed with MPN. Just 1.1% of MPN cases had taken metformin for more than five years, as compared to 2.0% of controls. The protective effect of metformin was seen in all subtypes of MPN when adjusting for potential confounders.
“We were surprised by the magnitude of the association we saw in the data,” said Daniel Tuyet Kristensen, MD, PhD student, at Aalborg University Hospital and lead author of the study. “We saw the strongest effect in people who had taken metformin for more than five years as compared to those who had taken the treatment for less than a year.” Dr. Kristensen added that this makes clinical sense, as MPNs are diseases that develop over a long period of time, like other types of cancer.
The researchers noted that while the protective effect of long-term metformin use was seen in all subtypes of MPN, the study was limited by its registry-based retrospective design. Further, they could not account for lifestyle factors that can affect cancer risk, such as smoking, obesity, and dietary habits.
Dr. Roug noted that while the study team were unable to assess exactly why metformin seems to protect against the development of MPN, they hope additional research will be conducted to better understand why this may be. Moving forward, the researchers aim to identify any similar trends with myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia in population-level data for future study.
# # #
Blood Advances (bloodadvances.org) is an online, open access journal publishing more peer-reviewed hematology research than any other academic journal worldwide. Blood Advances is part of the Blood journals portfolio (bloodjournals.org) from the American Society of Hematology (ASH) (hematology.org).
Contact:
Melissa McGue, American Society of Hematology
mmcgue@hematology.org; 202-552-4927
END
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 17, 2024 – Pickleball Legal Consultant is a job title that likely did not exist a decade ago, but as pickleball courts infiltrate neighborhoods to satiate an appetite for a sport whose namesake is a snack, communities take issue with the resulting influx of noise. Now homeowners’ associations and city councils face litigation by those whose lives are disrupted by pickleball’s din.
Charles Leahy, an attorney, retired mechanical engineer, and former HOA board member became ...
LAWRENCE — More than 300 million years ago, all sorts of arachnids crawled around the Carboniferous coal forests of North America and Europe. These included familiar ones we’d recognize, such as spiders, harvestmen and scorpions — as well exotic animals that now occur in warmer regions like whip spiders and whip scorpions.
But there were also quite bizarre arachnids in these habitats belonging to now extinct groups. Even among these stranger species now lost to time, one might have stood out for its up-armored legs.
The ancient critter recently was described in a new paper published ...
By Ian Scheffler
By now, the challenges posed by generative AI are no secret. Models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Anthropic’s Claude and Meta’s Llama have been known to “hallucinate,” inventing potentially misleading responses, as well as divulge sensitive information, like copyrighted materials.
One potential solution to some of these issues is “model disgorgement,” a set of techniques that force models to purge themselves of content that leads to copyright infringement or biased responses.
In ...
Stroke is the leading cause of disability worldwide and the second leading cause of death, but the right early intervention can prevent severe consequences. A new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, and collaborators developed a new test by combining blood-based biomarkers with a clinical score to identify patients experiencing large vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke with high accuracy. Their results are published in the journal Stroke: Vascular and Interventional Neurology.
“We have developed a game-changing, accessible tool that could help ensure that more people suffering from ...
Bethesda, MD (May 17, 2024) — The American Gastroenterological Association’s (AGA) new evidence-based Clinical Practice Guideline on Endoscopic Eradication Therapy of Barrett's Esophagus and Related Neoplasia, published today in Gastroenterology, establishes updated guidance for Barrett’s esophagus patients.
A precursor to esophageal cancer, Barrett’s esophagus is a condition in which the cells in the esophagus have been replaced with non-cancerous abnormal cells. These cells can progress to a condition called dysplasia, which may in turn become cancer. Dysplasia is considered low-grade or ...
A team of researchers from the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC) in Portugal, together with Åbo Akademi University in Finland, the AI4Life consortium, and other collaborators, have developed an innovative open-source platform called DL4MicEverywhere published today in the journal Nature Methods*. This platform provides life scientists with easy access to advanced artificial intelligence (AI) for the analysis of microscopy images. Itenables other researchers, ...
A ruined building in the middle of the Pyrenees records a tragedy for the people who lived there — a devastating fire which burned a settlement to the ground, destroying everything down to a hidden gold earring. Now archaeologists’ excavation of Building G, in the strategically placed Iron Age site of Tossal de Baltarga, reveals a way of life derailed by violence: potentially, a forgotten episode of the war between Carthage and Rome.
“The destruction was dated around the end of the third century BCE, the moment where the Pyrenees were involved in the Second Punic War and the passage of Hannibal’s troops,” ...
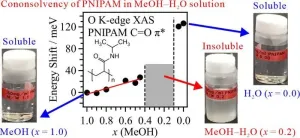
This study investigates the cononsolvency mechanism of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM), which is soluble in pure methanol (MeOH) and water but insoluble in aqueous MeOH solutions. Combining oxygen K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) with theoretical calculations executed in molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and inner-shell calculations, it was found that hydrophobic interactions between PNIPAM and MeOH clusters play a key role in PNIPAM aggregation and cononsolvency emergence.
PNIPAM is ...
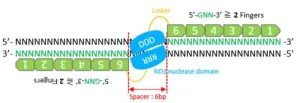
Genome editing is making inroads into biomedical research and medicine. By employing biomolecule modeling tools, a Japanese research team is accelerating the pace and cutting the cost of zinc finger nuclease (ZFN) technology, a primary gene editing tool.
In a recently published study, researchers from Hiroshima University and the Japanese National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology demonstrated how machine learning-driven modular assembly systems can improve gene editing.
The study was published on April 10 in the journal Advanced Science.
“Genome editing is ...
It has long been understood that pregnant women with diabetes are more likely to have children with obesity than women who do not have diabetes during pregnancy. But scientists have not fully understood the cause or why babies born to mothers with diabetes are also more likely to develop obesity and associated metabolic disorders later in life.
To help find answers, Keck School of Medicine of USC researcher Shan Luo, PhD, has been awarded $3.1 million in funding from the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute of Diabetes ...