(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. – An HIV vaccine candidate developed at the Duke Human Vaccine Institute triggered low levels of an elusive type of broadly neutralizing HIV antibodies among a small group of people enrolled in a 2019 clinical trial.
The finding, reported May 17 in the journal Cell, not only provides proof that a vaccine can elicit these antibodies to fight diverse strains of HIV, but that it can also initiate the process within weeks, setting in motion an essential immune response.
The vaccine candidate targets an area on the HIV-1 outer envelope called the membrane proximal external region (MPER), which remains stable even as the virus mutates. Antibodies against this stable region in the HIV outer coat can block infection by many different circulating strains of HIV.
“This work is a major step forward as it shows the feasibility of inducing antibodies with immunizations that neutralize the most difficult strains of HIV,” said senior author Barton F. Haynes, M.D., director of the Duke Human Vaccine Institute (DHVI). “Our next steps are to induce more potent neutralizing antibodies against other sites on HIV to prevent virus escape. We are not there yet, but the way forward is now much clearer.”
The research team analyzed data from a phase 1 clinical trial of a vaccine candidate developed by Haynes and S. Munir Alam, Ph.D., at DHVI.
Twenty healthy, HIV-negative people enrolled in the trial. Fifteen participants received two of four planned doses of the investigational vaccine, and five received three doses.
After just two immunizations, the vaccine had a 95% serum response rate and a 100% blood CD4+ T-cell response rate -- two key measurements that demonstrated strong immune activation. Most of the serum responses mapped to the portion of the virus targeted by the vaccine.
Importantly, broadly neutralizing antibodies were induced after just two doses.
The trial was halted when one participant experienced a non-life-threatening allergic reaction, similar to rare incidences reported with COVID-19 vaccinations. The team investigated the cause of the event, which was likely from an additive.
“To get a broadly neutralizing antibody, a series of events needs to happen, and it typically takes several years post-infection,” said lead author Wilton Williams, Ph.D., associate professor in Duke’s Department of Surgery and member of DHVI. “The challenge has always been to recreate the necessary events in a shorter space of time using a vaccine. It was very exciting to see that, with this vaccine molecule, we could actually get neutralizing antibodies to emerge within weeks.”
Other features of the vaccine were also promising, most notably how the crucial immune cells remained in a state of development that allowed them to continue acquiring mutations, so they could evolve along with the ever-changing virus.
The researchers said there is more work to be done to create a more robust response, and to target more regions of the virus envelope. A successful HIV vaccine will likely have at least three components, all aimed at distinct regions of the virus.
“Ultimately, we will need to hit all the sites on the envelope that are vulnerable so that the virus cannot escape,” Haynes said. ”But this study demonstrates that broadly neutralizing antibodies can indeed be induced in humans by vaccination. Now that we know that induction is possible, we can replicate what we have done here with immunogens that target the other vulnerable sites on the virus envelope.”
In addition to Haynes and Williams, study authors include S. Munir Alam, Gilad Ofek, Nathaniel Erdmann, David Montefiori, Michael S. Seaman, Kshitij Wagh, Bette Korber, Robert J. Edwards, Katayoun Mansouri, Amanda Eaton, Derek W. Cain, Mitchell Martin, Robert Parks, Maggie Barr, Andrew Foulger, Kara Anasti, Parth Patel, Salam Sammour, Ruth J. Parsons, Xiao Huang, Jared Lindenberger, Susan Fetics, Katarzyna Janowska, Aurelie Niyongabo, Benjamin M. Janus, Anagh Astavans, Christopher B. Fox, Ipsita Mohanty, Tyler Evangelous, Yue Chen, Madison Berry, Helene Kirshner, Elizabeth Van Itallie, Kevin Saunders, Kevin Wiehe, Kristen W. Cohen, M. Juliana McElrath, Lawrence Corey, Priyamvada Acharya, Stephen R. Walsh, and Lindsey R. Baden.
The study received funding support from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health (AI100645, AI144371, AI170752), and from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (OPP1094352/INV-007688).
The content of this press release is solely the responsibility of DHVI and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
###
END
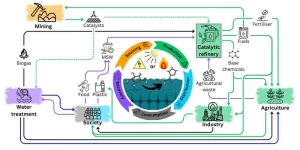
The chemical industry is a cornerstone of global development, driving innovation, and providing essential products that support our modern way of life.
However, its reliance on unsustainable fossil resources has posed significant threats to global ecosystems through climate change and chemical pollution.
A new commentary published in Cell Press’ OneEarth co-authored by Griffith University researchers puts forth a transformative solution: catalysis to leverage sustainable waste resources, ushering the industry from a linear to a circular economy.
“If ...
Rutgers researchers, aided by international collaborators, have tracked the devastation war has made on Ukraine’s hospital system.
Hundreds of hospitals in Ukraine have been forced to close or operate at a reduced capacity since Russia’s invasion of the Eastern European country in February 2022. Damage, destruction and supply shortages caused by the war have impaired the nation’s hospital system and taken a serious toll on human health.
In a study published in JAMA, Rutgers researchers and collaborators from the United States, Pakistan and Ukraine collected and compared data on hospital services provided both during ...
Recognising and respecting the different ways nature is valued can enable better environmental decision-making, according to new research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA).
International agreements such as the Sustainable Development Goals represent wide support for a sustainable future, living within planetary boundaries and ensuring a safer future for current and next generations.
However, there remain huge disagreements about how to advance such goals, often resulting in marginalisation, conflict and inaction.
The paper, published in the journal One Earth, ...
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that high ultraprocessed food (UPF) consumption in young children is associated with adiposity and other cardiometabolic risk factors, highlighting the need for public health initiatives to promote the replacement of UPFs with unprocessed or minimally processed foods.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nancy Babio, Ph.D., email nancy.babio@urv.cat.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.11852)
Editor’s ...
A significant link between the use of electronic cigarettes and earlier age of asthma onset in U.S. adults was reported by UTHealth Houston researchers May 17, 2024 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Network Open.
Led by first author Adriana Pérez, PhD, MS, professor of biostatistics and data science at UTHealth Houston School of Public Health, the research found that adults who were asthma-free at the beginning of the study and reported e-cigarette use in the past 30 days increased their risk of developing earlier age of asthma onset by 252%.
“While previous studies have reported that e-cigarette use increases ...
UNC Greensboro researcher Hemali Rathnayake, Ph.D., has been approved for grant funding from NCInnovation to continue her work in developing a cost-effective and efficient lithium refining process for converting lithium into battery-grade lithium carbonate.
The grant approval is conditioned on standard next steps, including executed grant agreements and formal notification to government partners. This funding is part of NCInnovation’s larger mission to unlock the innovative potential of North Carolina’s world-class universities.
“From ...
Plants have special corrective molecules at their disposal that can make retrospective modifications to copies of genes. However, it would appear that these “Tipp-Ex proteins” do not have permission to work in all areas of the cell, only being used in chloroplasts and mitochondria. A study by the University of Bonn has now explained why this is the case. It suggests that the correction mechanism would otherwise modify copies that have nothing wrong with them, with fatal consequences for the cell. The findings have now been ...
A new AI tool to more quickly and accurately classify brain tumours has been developed by researchers at The Australian National University (ANU).
According to Dr Danh-Tai Hoang, precision in diagnosing and categorising tumours is crucial for effective patient treatment.
“The current gold standard for identifying different kinds of brain tumours is DNA methylation-based profiling,” Dr Hoang said.
“DNA methylation acts like a switch to control gene activity, and ...
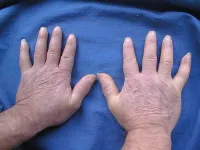
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells instead of protecting them. Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is one such autoimmune condition characterized by faulty circulatory and immune systems, leading to the occurrence of fibrosis (hardening and scarring of healthy tissue) of the skin and internal organs. SSc is known to affect patients throughout their lives, thereby, impairing their quality of life. Although precise mechanisms underlying SSc development and progression are not clearly understood, a complex interplay of immune, hormonal, environmental, and genetic factors is often implicated.
Moreover, ...
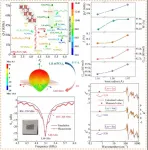
Microwave dielectric ceramics are the cornerstone of wireless communication devices, widely utilized in mobile communications, satellite radar, GPS, Bluetooth, and WLAN applications. Components made from these ceramic materials, such as filters, resonators, and dielectric antennas, are extensively used in wireless communication networks. As wireless communication frequencies extend into higher bands, signal delay issues become increasingly prominent. Low dielectric constants (εr) can reduce electromagnetic coupling effects, effectively minimizing signal delays. Consequently, developing new ceramic materials with ...