Spirometry clinical trial eligibility may differ with race-neutral equations
2024-05-19
(Press-News.org)
EMBARGOED UNTIL: 9:15 a.m. PT, May 19, 2024
Session: A27 – Emerging Treatments and Therapeutic Strategies in COP: Results of Clinical Trials and Observational Studies
Impact of Race-Neutral Spirometry Reference Equations on Eligibility for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Clinical Trials
Date and Time: Sunday, May 19, 9:15 a.m. PT
Location: San Diego Convention Center, Room 33A-C (Upper Level)
ATS 2024, San Diego – Equations that don’t use racially and ethnically adjusted spirometry results to help determine eligibility for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) clinical trials may lead to higher percentages of Black patients enrolled, according to research published at the ATS 2024 International Conference.
“While other researchers have initiated investigations into the effects of adhering to the recent American Thoracic Society (ATS) guidance on utilizing Global Lung Function Initiative (GLI) race-neutral spirometry reference equations in clinical practice, our research has identified a gap in the literature regarding the impact of these equations on inclusion criteria in clinical trials,” said lead author Frank Sciurba, MD, professor of medicine, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and medical director, Pulmonary Physiology Lab, UPMC.
In 2023, an expert panel convened by the ATS issued a statement recommending that race and ethnicity no longer be considered factors in interpreting the results of spirometry. For many years, race-specific equations or adjustments have been used to interpret pulmonary function test (spirometry) results. This approach requires results for Black patients to be lower—sometimes, up to 15 percent lower than for white patients.
“In our study, we saw a discernible pattern in which race-neutral equations tend to decrease the severity level for self-identified white subjects, while concurrently increasing severity for self-identified Black subjects,” said corresponding author Chad Karoleski, BA, research IT specialist, University of Pittsburgh Emphysema COPD Research Center. “This resulted in a GOLD stage shift which led to more Black subjects and fewer white subjects meeting typical spirometric inclusion criteria for COPD clinical trials.”
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) classifications are used to determine COPD clinical trial eligibility, with those testing at the GOLD 2 (moderate) and GOLD 3 (severe) levels typically deemed eligible.
To test the potential effects of the new guidelines the team looked at participants from the Combined Pittsburgh Lung Cohort, who had spirometry performed. The predicted values were calculated for both GLI ethnic-adjusted and GLI Global race-neutral equations to identify the FEV1 percent and resultant GOLD stage for each individual with each reference approach. They conducted an analysis of the shift in GOLD category overall and by self-reported race.
The researchers identified 3,716 (3,474 self- identified white and 242 self-identified Black) individuals with a baseline spirometry evaluation demonstrating an FEV1/FVC ratio <0.7 for inclusion in the study. When using the race-neutral reference equations instead of the race-adjusted equations, 5.8 percent of individuals became ineligible, while 2.1 percent were considered eligible, with all cases of decreasing GOLD stage occurring in white individuals and all cases of increasing GOLD stage occurring in Black individuals. Overall, 1.6 percent of white and 8.3 percent of Black patients gained eligibility, while six percent of whites and 2.9 percent of Blacks were no longer eligible.
Spirometry is the most common pulmonary function test used to diagnose lung disease and determine its severity. FEV1 is the volume of air expired in the first second of a forced exhalation and is typically represented as a percentage of age-, height- and sex-adjusted predicted value (and recently recommended to exclude racial adjustment). FEV1/FVC is a calculated ratio used in the diagnosis of obstructive disease. It represents the proportion of a person's vital capacity that they can exhale in the first second during a forced exhalation from full inhalation.
“We anticipate that our findings will stimulate further discussion and investigation into the development of appropriate inclusion criteria, guided by the ATS recommendation of using race-neutral spirometry reference equations,” said Mr. Karoleski. “Future research will be needed to determine the implication of these shifts on appropriate clinical trial selection, while the role of the race-independent classification STAR staging in clinical trial selection, based exclusively on FEV1/FVC ratio, also warrants evaluation.”
###
VIEW ABSTRACT
CONTACTS FOR MEDIA:
Dacia Morris Allison Hydzik
Director, Communications & Marketing Director, Science and Research Public Relations
American Thoracic Society UPMC
dmorris@thoracic.org hydzikam@upmc.edu
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-19
Finding and treating people with undiagnosed asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) improved their health and reduced their healthcare visits for respiratory symptoms in the year after diagnosis, according to a world-first clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"It's estimated that 70 per cent of people with asthma or COPD go undiagnosed." said study lead Dr. Shawn Aaron, a senior scientist and lung specialist at The Ottawa Hospital and professor at the University of ...
2024-05-19
A National Institutes of Health (NIH)-supported clinical trial has found that intravenous acetaminophen reduced sepsis patients’ risk of having organ injury or developing acute respiratory distress syndrome, a serious condition that allows fluid to leak into the lungs. Sepsis is the body’s uncontrolled and extreme response to an infection. While the trial did not improve mortality rates in all patients with sepsis regardless of severity, the researchers found that acetaminophen gave the greatest benefit to the patients most at risk for organ damage. With the therapy, those patients needed less assisted ...
2024-05-19
About The Study: Among people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at high risk of exacerbation, treatment with the β1-selective β-blocker bisoprolol did not reduce the number of self-reported COPD exacerbations requiring treatment with oral corticosteroids, antibiotics, or both.
Quote from corresponding author Graham Devereux, M.D.:
“People with COPD are at increased risk of cardiovascular conditions that benefit from treatment with beta-blockers. However, there is a well-documented ...
2024-05-19
About The Study: Among patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis treated with pamrevlumab (a fully human monoclonal antibody that binds to and inhibits connective tissue growth factor activity) or placebo, there was no statistically significant between-group difference for the primary outcome of absolute change in forced vital capacity from baseline to week 48.
Quote from corresponding author, Ganesh Raghu, M.D.:
“Current treatment with the two drugs approved by regulatory agencies ...
2024-05-19
About The Study: In critically ill sepsis patients, treatment with intravenous acetaminophen for 5 days was safe but did not improve the primary end point of days alive and free of any organ support (dialysis, assisted ventilation, and vasopressors) to day 28 compared with placebo.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lorraine B. Ware, M.D., email Lorraine.ware@vumc.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.8772)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
2024-05-19
Removing race from equations that estimate lung function will shift the categorization of disease severity across patient populations, moving more Black individuals into an advanced disease category, according to new research led by scientists at Harvard Medical School. At the same time, more white and Hispanic people would be reclassified as having less advanced illness.
The findings, the research team said, suggest that adjusting lung function tests to include race — as has been the case historically — likely normalized worse lung function and downplayed disease severity among Black people.
The work, to be published May 19 in the New England Journal ...
2024-05-18
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common form of arrythmia or irregular heartbeat worldwide, impacting millions of people in the U.S. alone. In a new study published in Heart Rhythm, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, analyzed real-world clinical data to measure the impact of evidence-based best-practices on patient outcomes for the most common AF procedure: radiofrequency (RF)-based ablation. One year after the procedure, 81.6 percent ...
2024-05-18
Wireless implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) eliminate the lead-related complications that come with a wired ICD, but they are unsuitable for patients with ventricular tachycardia, when the heart beats too quickly, or bradycardia, when the resting heart rate is seen as low. Research led by Amsterdam UMC, that is published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, shows that the first wireless modular system suitable for these patient groups is safe and exceeds performance expectations. Opening the door for a wider ...
2024-05-18
WASHINGTON, DC (May 18, 2024) — Patients seen by a female gastroenterologist for an initial consultation are less likely to use medical care in the emergency department, hospital or primary care office for two years after their visit when compared to patients initially seen by male gastroenterologists, according to a study to be presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024.
“If there really is something different about the way female and male gastroenterologists provide care that impacts patient outcomes, it will be important to share these learnings broadly among health care providers ...
2024-05-17
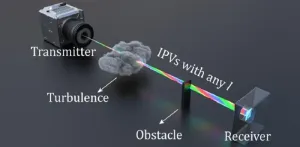
The future of optical communications just got brighter. In a groundbreaking development reported in Advanced Photonics, researchers from Nanjing University have introduced iso-propagation vortices (IPVs), a novel concept that offers a solution to a long-standing challenge faced by scientists and engineers: how to increase information processing capacity while overcoming the limitations of traditional vortex beams.
Challenge: divergence and beam size
Multiplexing of optical degrees of freedom, such as polarization and wavelength, has been a staple in enhancing communication capacity. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Spirometry clinical trial eligibility may differ with race-neutral equations