(Press-News.org)
For many patients with a deadly type of brain cancer called glioblastoma, chemotherapy resistance is a big problem.
Current standard treatments, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy using the drug temozolomide, have limited effectiveness and have not significantly changed in the past five decades. Although temozolomide can initially slow tumor progression in some patients, typically the tumor cells rapidly become resistant to the drug.
But now, Virginia Tech researchers with the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC may have moved a step closer to a solution.
Working with glioblastoma cell cultures, including glioblastoma stem cells derived from patient specimens, and laboratory mouse models harboring human cancer cells, scientists have pinpointed an effective molecular signaling pathway that is thought to be crucial for cancer cell survival during temozolomide treatment. The findings are now online in iScience, an open-access journal of Cell Publishing.
“In the past 50 years, treatment options for glioblastoma have remained largely unchanged, relying on surgery, radiation, and temozolomide,” said Zhi Sheng, senior author of the study and assistant professor at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute. “However, temozolomide's effectiveness is limited, and resistance to the chemotherapy inevitably develops in patients. Since it's the only currently available approved chemotherapy that can effectively reach the brain, finding ways to restore its effectiveness is crucial in addressing the treatment failure in glioblastoma.”
Researchers examined the Phosphoinositide 3 Kinase (PI3K) molecular signaling pathway, which is like a communication system inside cells. It tells cells how to grow, survive, and divide. When this pathway is activated, it can promote cancer growth, so scientists and clinicians generally thought blocking it could be a way to treat cancer.
Their results have not been successful.
In the new research, Fralin Biomedical Research Institute scientists found that in some brain cancer patients who didn’t respond to treatment, levels were high of a specific form of the signaling protein called PI3K-beta that helps regulate cellular processes.
When they blocked just PI3K-beta in cell cultures and mouse models harboring cancer cells, the tumor cells became more sensitive to temozolomide treatment. In addition, using a drug that blocks PI3K-beta along with the usual treatment slowed down the cancer cells' growth.
Researchers are uncertain why PI3K, in its various forms, are very similar in structure yet do different things in the body.
“The reason previous treatments targeting the PI3K pathway failed is because they didn't distinguish between PI3K-beta and its related proteins,” Sheng said. “This research shows that PI3K-beta is specific to glioblastoma, making it the crucial target for effective treatment.”
Going forward, overcoming the blood-brain barrier remains a hurdle for delivering P13K-beta inhibitors into the brain, which will be crucial for translating the findings into the clinic to help patients.
“We will resolve these issues in our future studies,” Sheng said.
Co-first authors of the study are Kevin Pridham, a former postdoctoral associate at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute, and Kasen Hutchings and Patrick Beck, two former medical students at the Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine who are pursuing their medical careers in radiology in Las Vegas and pediatrics in Philadelphia, respectively.
Cell specimens were provided by Carilion Clinic. Study results are in part based on data generated by The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, the Dependency Map, the Genotype-Tissue Expression, or the Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas. The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health.
END
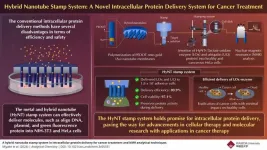
In today's medical landscape, precision medicine and targeted therapies are gaining traction for their ability to tailor treatments to individual patients while minimizing adverse effects. Conventional methods, such as gene transfer techniques, show promise in delivering therapeutic genes directly to cells to address various diseases. However, these methods face significant drawbacks, hindering their efficacy and safety.
Intracellular protein delivery offers a promising approach for developing safer, more targeted, and effective therapies. By directly transferring proteins into target cells, this method circumvents issues such as silencing ...
HOUSTON – (May 20, 2024) – Rice University chemist Julian West is one of a dozen up-and-coming young scientists featured in Chemical & Engineering News’ (C&EN) 2024 Talented 12, an annual issue of the weekly news magazine that highlights rising stars across all chemistry research disciplines.
West, an assistant professor and the Norman Hackerman-Welch Young Investigator in Rice’s Department of Chemistry, is a synthetic chemist whose lab designs novel chemical reactions. Drawing inspiration from biology, West’s research group has found ways to simplify the production of entire libraries of feedstock chemicals ...
VANCOUVER, Wash. – Using more robots to close labor gaps in the hospitality industry may backfire and cause more human workers to quit, according to a Washington State University study.
The study, involving more than 620 lodging and food service employees, found that “robot-phobia” – specifically the fear that robots and technology will take human jobs – increased workers’ job insecurity and stress, leading to greater intentions to leave their jobs. The impact was more pronounced with employees who had ...
In some severe cases of COVID-19, the lungs undergo extreme damage, resulting in a range of life-threatening conditions like pneumonia, inflammation, and acute respiratory distress syndrome. The root cause of those wide-ranging reactions in the lungs has until now remained unclear.
A new study by researchers at Columbia and the Columbia University Irving Medical Center sheds light on this mystery. The study found that ferroptosis, a form of cell death first named and identified at Columbia in 2012, is the major cell death mechanism that underlies COVID-19 lung disease. The finding indicates that deliberately halting ...
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have succeeded in delivering targeted cancer treatment via small membrane bubbles that our cells use to communicate. A new study published in Nature Biomedical Engineering shows that the treatment reduces tumour growth and improves survival in mice.
When our cells communicate, they send out small membrane bubbles known as extracellular vesicles which contain various signalling molecules. Interest in these tiny bubbles, sometimes referred to as the body’s ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – A quarter of parents report that caffeine is basically part of their teen’s daily life, according to a national poll.
Two in three parents think they know whether their teen’s caffeine intake is appropriate and which products have too much caffeine. Yet a third aren’t able to identify recommended caffeine limits, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
“Our report suggests parents may not always be aware of how much they should be limiting caffeine consumption for teens,” said poll co-director and Mott ...
Compartments of consistently sized, tightly packed microspheres are what makes some brown algae shimmer like opal. The Kobe University discovery not only sheds light on the mechanism behind the alga’s structural coloration, it is also the first to spot the effect in an order of brown algae other than the two where it was known to occur.
Most brown algae are indeed yellowish-brown, but scuba divers noticed that a species resembling Sporochnus in the order Sporochnales shimmers like peacock feathers in yellow, ...
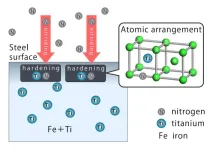
Decarbonization of automobiles not only requires a shift from gasoline engines to electric motors, but also quality steel parts that help the motors run while lessening the weight of vehicles. High-performance steel materials can offer quieter rides and resist the wear and tear from high-speed rotation in motors. To create them, the process of modifying the steel surface with carbon, nitrogen, and alloy elements needs to be optimized.
To understand the interactions between elements in steel, a systematic investigation ...
Dr. Hyuk-June Moon from the Bionics Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), in collaboration with Prof. Olaf Blanke’s team at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL), has successfully induced self-location illusions with multi-sensory virtual reality (VR) in the MRI scanner and observed corresponding changes in the human brain's grid cell activity.
The brain is known to contain grid cells and place cells, which perform global positioning system (GPS) functions that allow us to recognize where we are. While ...
WASHINGTON, DC (May 20, 2024) — Gallbladder cancer rates have been stable or declining for most Americans over the last two decades, but cases have steadily risen among Blacks, with growing numbers not being diagnosed until later stages, according to a study scheduled for presentation at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024.
“Gallbladder cancer diagnosis at late stage can be highly detrimental,” said lead author Yazan Abboud, MD, internal medicine resident at Rutgers University New Jersey Medical School. “This could be due to a lack of timely ...