(Press-News.org) EMBARGOED UNTIL: 9:15 a.m. PT, May 20, 2024
Session: B20 – Lung Screening: One Size Does Not Fit All
Association of Electronic Cigarette Use After Conventional Smoking Cessation with Lung Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Date and Time: Monday, May 20, 2024, 9:15 a.m. PT
Location: San Diego Convention Center, Room 30A-B (Upper Level)
ATS 2024, San Diego – Former cigarette smokers who use e-cigarettes or vaping devices may be at higher risk for lung cancer than those who don’t vape, according to research published at the ATS 2024 International Conference.
“This is the first large population-based study to demonstrate the increased risk of lung cancer in e-cigarette users after smoking cessation,” said corresponding author Yeon Wook Kim, MD, assistant professor, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Republic of Korea.
E-cigarettes have gained popularity globally as an alternative to conventional cigarette smoking, and some smokers turn to vaping to help in smoking cessation. However, there is little knowledge about the long-term consequences of vaping, and epidemiological evidence for the association between e-cigarette use and lung cancer is lacking.
Biological studies suggest the possible dangers of e-cigarettes, including pulmonary toxicity and lung cancer. E-cigarettes and heating elements have been shown to contain carbonyl compounds (e.g., formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, acrolein and diacetyl) and toxic metals (e.g., chromium, nickel and lead), which are known to be carcinogenic. These toxins are also present in conventional cigarettes.
“Our results indicate that when integrating smoking cessation interventions to reduce lung cancer risk, the potential harms of using e-cigarettes as an alternative to smoking must be considered,” said Dr. Kim.
To determine these individuals’ risk, the researchers evaluated 4,329,288 individuals with a history of conventional smoking who participated in the Republic of Korea’s National Health Screening Program at two time points: 2012-2014 and 2018. They conducted follow-up in December 2021.
The research team categorized participants into six groups according to their smoking history and habit change. They used statistical analyses to assess each group’s risk of developing lung cancer and of dying from it.
During follow-up, they found that 53,354 individuals had developed lung cancer and 6,351 died from lung cancer. Ex-cigarette smokers who had quit five years or more and used e-cigarettes were at greater risk of lung cancer-related death than ex-smokers who had quit five years or more and hadn’t used e-cigarettes. For smokers who had quit less than five years, those who used e-cigarettes were found to have both a higher risk of both lung cancer and lung cancer mortality than non-e-cigarette users.
Dr. Kim and colleagues also conducted a stratified analysis in which they looked at individuals ages 50-80 with a smoking history of 20 or more pack-years , because these individuals would be likely to be referred for lung cancer screening according to the 2021 US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the 2023 American Cancer Society (ACS) guidelines. Ex-smokers in this group who had quit smoking for five years or more and used e-cigarettes reported a higher risk of both lung cancer and lung cancer-related death than those who didn’t use e-cigarettes. In addition, ex-smokers who used e-cigarettes and had quit smoking less than five years before had a higher comparative risk of lung cancer.
The authors conclude that, “Clinicians must highlight the potential harmful effects of alternative e-cigarettes use when integrating smoking cessation interventions to reduce lung cancer risk.”
###
VIEW ABSTRACT
CONTACTS FOR MEDIA:
Dacia Morris
Director, Communications & Marketing, American Thoracic Society
dmorris@thoracic.org
Minjae Jung
Department of Public Relations, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
02245@snubh.org
END
Ex-cigarette smokers who vape may be at higher risk for lung cancer
2024-05-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The impacts of climate change on food production
2024-05-20
A new peer-reviewed study from researchers at The University of Texas at Arlington; the University of Nevada, Reno; and Virginia Tech shows that climate change has led to decreased pollen production from plants and less pollen more diversity than previously thought, which could have a significant impact on food production.
“This research is crucial as it examines the long-term impacts of climate change on plant-pollinator interactions,” said Behnaz Balmaki, lead author of the study and an assistant professor of research in biology at UTA. “This study investigates how shifts in flowering times and extreme weather events affect the availability of critical food ...
Mothers live longer as child mortality declines
2024-05-20
ITHACA, N.Y. – The dramatic decline in childhood mortality during the 20th century has added a full year to women’s lives, according to a new study.
“The picture I was building in my mind was to think about what the population of mothers in the U.S. looked like in 1900,” said Matthew Zipple, a Klarman Postdoctoral Fellow in neurobiology and behavior at Cornell University and author of “Reducing Childhood Mortality Extends Mothers’ Lives,” which published May 9 in Scientific Reports.
“It was a population made up of two approximately equal-sized ...
Study reveals promising development in cancer-fighting nanotechnologies
2024-05-20
A new study conducted by the Wilhelm Lab at the University of Oklahoma examines a promising development in biomedical nanoengineering. Published in Advanced Materials, the study explores new findings on the transportation of cancer nanomedicines into solid tumors.
A frequent misconception about many malignant solid tumors is that they are comprised only of cancerous cells. However, solid tumors also include healthy cells, such as immune cells and blood vessels. These blood vessels are nutrient transportation ...
Fat cells influence heart health in Chagas disease
2024-05-20
Jyothi Nagajyothi, Ph.D. and her laboratory at the Hackensack Meridian Center for Discovery and Innovation (CDI) have identified what may be the main mechanism for how chronic Chagas Disease, a parasitic infection affecting millions of people worldwide, can cause irreversible and potentially fatal heart damage.
The culprit is in the adipose (fat tissue) which the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi destroys in the course of infection, releasing smaller particles which induce the dysfunction of heart tissue, conclude the scientists in the journal iScience, a Cell Press open-access journal.
“We are attempting to understand this ...
C-Path’s TRxA announces its first biologics-focused RFP for academic investigators
2024-05-20
TUCSON, Ariz, May 20, 2024 – Critical Path Institute’s (C-Path) Translational Therapeutics Accelerator (TRxA) today announced its inaugural biologics-focused Request for Proposals (RFP) in its Bridging Research and Innovation in Drug Development Grants program (BioBRIDGe). BioBRIDGe awards are designed to help academic researchers traverse the drug development valley of death by providing funding and defining optimal strategies for advancing new, cutting-edge protein-based therapeutics (PBT) from the lab to patients.
For this funding cycle, ...
Enhancing superconductivity of graphene-calcium superconductors
2024-05-20
Superconductors are materials that can conduct electricity with zero resistance when they are cooled below a certain critical temperature. They have applications in several fields, including magnetic resonance imaging, particle accelerators, electric power, and quantum computing. However, their widespread use is limited by the need for extremely low temperatures. Graphene-based materials are promising for superconductors due to their unique properties such as optical transparency, mechanical strength, and flexibility. Graphene is a single layer of carbon (C) atoms arranged in a two-dimensional honeycomb structure. Among these materials, ...
Federal Trade Commission actions on prescription drugs, 2000-2022
2024-05-20
About The Study: The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) brought about one enforcement action and three merger actions per year against pharmaceutical manufacturers from 2000-2022, pursuing a small fraction of the estimated misconduct and consolidation in the pharmaceutical marketplace. Although the FTC faces substantial legal and practical limitations, important tools remain untested, including a rule defining “unfair methods of competition,” that may allow it to more effectively prevent repetitive patterns of anticompetitive behavior.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Aaron S. Kesselheim, ...
Fluoride exposure during pregnancy linked to increased risk of childhood neurobehavioral problems, study finds
2024-05-20
Nearly three-quarters of the United States population receives drinking water that contains fluoride, a practice that began in 1945 to help prevent tooth decay. But recent studies suggest that fluoride exposure can cause harm to a fetus if consumed during pregnancy, a critical period for brain development.
A new study, led by researchers at the Keck School of Medicine of USC and funded in part by the National Institutes of Health, analyzed more than 220 mother-child pairs, collecting data on fluoride levels during pregnancy and child behavior at age three. The researchers found that a 0.68 milligram per ...
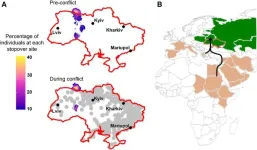
The Ukraine war caused migrating eagles to deviate from their usual flight plan
2024-05-20
When migrating through Ukraine in 2022, Greater Spotted Eagles were exposed to multiple conflict events that altered their migratory course, according to a study reported on May 20 in the journal Current Biology. Greater Spotted Eagles are large raptors that are classified as a vulnerable species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
“Armed conflicts can have wide-ranging impacts on the environment, including changes in animal behavior,” says Charlie Russell (@CJG_Russell) of the University of East Anglia, UK. “Our ...
Endangered migrating eagles impacted by Ukraine war
2024-05-20
A new study reveals for the first time the impact of ongoing conflicts on the migration of an endangered bird species.
Researchers from the University of East Anglia (UEA), the British Trust for Ornithology (BTO) and the Estonian University of Life Sciences compared the movement and migration of the Greater Spotted Eagle through Ukraine, before and shortly after it was invaded by Russia in February 2022.
They were already studying the species when the war started, with the dangers faced by migratory birds usually related to disruptive weather or drought, changes in land use affecting traditional stopping-off ...