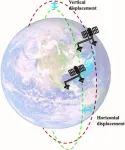
(Press-News.org) The new Tandem Dual-Antenna Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Interferometry (TDA-InSAR) system, addresses the limitations of current spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems by providing a more reliable and efficient method for 3D surface mapping. The system's innovative design allows for single-pass acquisitions, significantly reducing the time required for data collection and enhancing the precision of 3D reconstructions in various terrains, including built-up areas and vegetation canopies.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) interferometry (InSAR) is a powerful tool for producing high-resolution topographic maps. However, traditional InSAR techniques face challenges such as the ill-posed 2D phase unwrapping problem and the need for multiple acquisitions over time, which can introduce errors due to atmospheric and orbital changes. The TDA-InSAR system overcomes these challenges by utilizing dual-antenna and dual-satellite configurations to acquire optimal interferograms for an asymptotic 3D phase unwrapping algorithm.
Researchers from Fudan University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a novel Tandem Dual-Antenna Spaceborne SAR Interferometry (TDA-InSAR) system, designed to achieve optimal multi-baseline interferograms for fast 3D reconstruction. The study (DOI: 10.34133/remotesensing.0137), published on 6 May 2024, in the journal Journal of Remote Sensing, presents a systematic investigation into the performance of various baseline configurations and the impact of different error sources on the system's accuracy.
The TDA-InSAR system employs a dual-antenna and dual-satellite approach to capture optimal interferograms, which are then processed through an asymptotic 3D phase unwrapping algorithm. This method allows for rapid and accurate 3D reconstruction with minimal acquisitions, overcoming the limitations of previous technologies. The study's simulations demonstrated that the TDA-InSAR system could achieve a remarkable relative height precision of 0.3 meters in urban areas and 1.7 meters in dense vegetation, outperforming existing SAR interferometry methods. The research also explored various baseline configurations, finding that a bi-static mode with a flexible satellite baseline provided the best results.
"The TDA-InSAR system represents a significant advancement in SAR interferometry," said Fengming Hu, the lead researcher of the study. "By tailoring the system to work with an asymptotic 3D phase unwrapping algorithm, we've been able to achieve a relative height precision of 0.3 meters in built-up areas and 1.7 meters in vegetation canopies, which is a substantial improvement over existing technologies."
The TDA-InSAR system has significant implications for various applications, including terrain mapping, target recognition, and forest height inversion. Its ability to perform rapid 3D reconstruction in a single flight makes it a valuable tool for both scientific research and practical applications such as disaster response and environmental monitoring.
###
References
DOI
10.34133/remotesensing.0137
Original Source URL
https://spj.science.org/doi/10.34133/remotesensing.0137
Funding information
This work was supported in part by the National Nature Science Foundation of China under grants 61991422 and 62201158.
About Journal of Remote Sensing
The Journal of Remote Sensing, an online-only Open Access journal published in association with AIR-CAS, promotes the theory, science, and technology of remote sensing, as well as interdisciplinary research within earth and information science.
END
Advancing 3D mapping with tandem dual-antenna SAR interferometry
2024-05-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mount Sinai launches Center for Healthcare Readiness to strengthen practice and partnerships in public health emergency response
2024-05-20
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai announced the launch of its new Center for Healthcare Readiness, bringing together a diverse team of academic and operational experts to strengthen the Mount Sinai Health System’s strategies and the U.S. health care sector’s capacity to prepare for and respond to any large-scale public health emergency.
The Center will work with both Mount Sinai’s own resources, and public and private partners at the local, regional, and federal levels, to pursue strategies in research, advocacy, innovation, and collaboration to plan ...
Study sheds light on bacteria associated with pre-term birth
2024-05-20
Researchers from North Carolina State University have found that multiple species of Gardnerella, bacteria sometimes associated with bacterial vaginosis (BV) and pre-term birth, can coexist in the same vaginal microbiome. The findings add to the emerging picture of Gardnerella’s effects on human health.
Gardnerella is a group of anaerobic bacteria that are commonly found in the vaginal microbiome. Higher levels of the bacteria are a signature of BV and associated with higher risk of pre-term birth, ...
Evolving market dynamics foster consumer inattention that can lead to risky purchases
2024-05-20
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers have developed a new theory of how changing market conditions can lead large numbers of otherwise cautious consumers to buy risky products such as subprime mortgages, cryptocurrency or even cosmetic surgery procedures.
These changes can occur in categories of products that are generally low risk when they enter the market. As demand increases, more companies may enter the market and try to attract consumers with lower priced versions of the product that carry more risk. If the negative effects of that risk are not immediately noticeable, the market can evolve to keep consumers ignorant of the risks, said Michelle Barnhart, an associate professor ...
Ex-cigarette smokers who vape may be at higher risk for lung cancer
2024-05-20
EMBARGOED UNTIL: 9:15 a.m. PT, May 20, 2024
Session: B20 – Lung Screening: One Size Does Not Fit All
Association of Electronic Cigarette Use After Conventional Smoking Cessation with Lung Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Date and Time: Monday, May 20, 2024, 9:15 a.m. PT
Location: San Diego Convention Center, Room 30A-B (Upper Level)
ATS 2024, San Diego – Former cigarette smokers who use e-cigarettes or vaping devices may be at higher risk for lung cancer than those who don’t ...
The impacts of climate change on food production
2024-05-20
A new peer-reviewed study from researchers at The University of Texas at Arlington; the University of Nevada, Reno; and Virginia Tech shows that climate change has led to decreased pollen production from plants and less pollen more diversity than previously thought, which could have a significant impact on food production.
“This research is crucial as it examines the long-term impacts of climate change on plant-pollinator interactions,” said Behnaz Balmaki, lead author of the study and an assistant professor of research in biology at UTA. “This study investigates how shifts in flowering times and extreme weather events affect the availability of critical food ...
Mothers live longer as child mortality declines
2024-05-20
ITHACA, N.Y. – The dramatic decline in childhood mortality during the 20th century has added a full year to women’s lives, according to a new study.
“The picture I was building in my mind was to think about what the population of mothers in the U.S. looked like in 1900,” said Matthew Zipple, a Klarman Postdoctoral Fellow in neurobiology and behavior at Cornell University and author of “Reducing Childhood Mortality Extends Mothers’ Lives,” which published May 9 in Scientific Reports.
“It was a population made up of two approximately equal-sized ...
Study reveals promising development in cancer-fighting nanotechnologies
2024-05-20
A new study conducted by the Wilhelm Lab at the University of Oklahoma examines a promising development in biomedical nanoengineering. Published in Advanced Materials, the study explores new findings on the transportation of cancer nanomedicines into solid tumors.
A frequent misconception about many malignant solid tumors is that they are comprised only of cancerous cells. However, solid tumors also include healthy cells, such as immune cells and blood vessels. These blood vessels are nutrient transportation ...
Fat cells influence heart health in Chagas disease
2024-05-20
Jyothi Nagajyothi, Ph.D. and her laboratory at the Hackensack Meridian Center for Discovery and Innovation (CDI) have identified what may be the main mechanism for how chronic Chagas Disease, a parasitic infection affecting millions of people worldwide, can cause irreversible and potentially fatal heart damage.
The culprit is in the adipose (fat tissue) which the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi destroys in the course of infection, releasing smaller particles which induce the dysfunction of heart tissue, conclude the scientists in the journal iScience, a Cell Press open-access journal.
“We are attempting to understand this ...
C-Path’s TRxA announces its first biologics-focused RFP for academic investigators
2024-05-20
TUCSON, Ariz, May 20, 2024 – Critical Path Institute’s (C-Path) Translational Therapeutics Accelerator (TRxA) today announced its inaugural biologics-focused Request for Proposals (RFP) in its Bridging Research and Innovation in Drug Development Grants program (BioBRIDGe). BioBRIDGe awards are designed to help academic researchers traverse the drug development valley of death by providing funding and defining optimal strategies for advancing new, cutting-edge protein-based therapeutics (PBT) from the lab to patients.
For this funding cycle, ...
Enhancing superconductivity of graphene-calcium superconductors
2024-05-20
Superconductors are materials that can conduct electricity with zero resistance when they are cooled below a certain critical temperature. They have applications in several fields, including magnetic resonance imaging, particle accelerators, electric power, and quantum computing. However, their widespread use is limited by the need for extremely low temperatures. Graphene-based materials are promising for superconductors due to their unique properties such as optical transparency, mechanical strength, and flexibility. Graphene is a single layer of carbon (C) atoms arranged in a two-dimensional honeycomb structure. Among these materials, ...