(Press-News.org) Many countries around the world are considering revising cannabis policies. A new study by a researcher at Carnegie Mellon University assessed cannabis use in the United States between 1979 and 2022, finding that a growing share of cannabis consumers report daily or near-daily use and that their numbers now exceed those of daily and near-daily alcohol drinkers. The study concludes that long-term trends in cannabis use parallel corresponding changes in policy over the same period. The study appears in Addiction.
“The data come from survey self-reports, but the enormous changes in rates of self-reported cannabis use, particularly of daily or near-daily use, suggest that changes in actual use have been considerable,” says Jonathan P. Caulkins, professor of operations research and public policy at Carnegie Mellon’s Heinz College, who conducted the study. “It is striking that high-frequency cannabis use is now more commonly reported than is high-frequency drinking.”
Although prior research has compared cannabis-related and alcohol-related outcomes before and after state-level policy changes to changes over the same period in states without policy change, this study examined long-term trends for the United States as a whole. Caulkins looked at days of use, not just prevalence, and drew comparisons with alcohol, but did not attempt to identify causal effects.
The study used data from the U.S. National Survey on Drug Use and Health (and its predecessor, the National Household Survey on Drug Abuse), examining more than 1.6 million respondents across 27 surveys from 1979 to 2022. Caulkins contrasted rates of use in four milestone years that reflected significant policy change points: 1979 (when the first data became available and the relatively liberal policies of the 1970s ended), 1992 (the end of 12 years of conservative Reagan-Bush-era policies), 2008 (the year before the U.S. Department of Justice signaled explicit federal non-interference with state-level legalizations), and 2022 (the year for the most recent data available). Among the study’s findings:
Reported cannabis use declined to a low in 1992, with partial increases through 2008 and substantial growth since then, particularly for measures of more intensive use.
Between 2008 and 2022, the per capita rate of reporting past-year use increased 120%, and days of use reported per capita increased 218% (in absolute terms, the rise was from 2.3 billion to 8.1 billion days per year).
From 1992 to 2022, the per capita rate of reporting daily or near-daily use rose 15-fold. While the 1992 survey recorded 10 times as many daily or near-daily alcohol users as cannabis users (8.9 million versus 0.9 million), the 2022 survey, for the first time, recorded more daily and near-daily users of cannabis than of alcohol (17.7 million versus 14.7 million).
While far more people drink than use cannabis, high-frequency drinking is less common. In 2022, the median drinker reported drinking on 4-5 days in the previous month versus using cannabis on 15-16 days in the previous month. In 2022, prior-month cannabis consumers were almost four times as likely to report daily or near-daily use (42% versus 11%) and 7.4 times more likely to report daily use (28% versus 3.8%).
“These trends mirror changes in policy, with declines during periods of greater restriction and growth during periods of policy liberalization,” explains Caulkins. He notes that this does not mean that policy drove changes in use; both could have been manifestations of changes in underlying culture and attitudes. “But whichever way causal arrows point, cannabis use now appears to be on a fundamentally different scale than it was before legalization.”
Among the study’s limitations, Caulkins says that because the study relied on general population surveys, the data are self-reported, lack validation from biological samples, and exclude certain subpopulations that may use at different rates than the rest of the population.
END
New study highlights significant increases in cannabis use in United States
Long-term trends parallel changes in policy over 43 years
2024-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bérénice Benayoun (USC) receives Rising Star Award in Aging Research
2024-05-22
New York, NY – The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR), a national non-profit organization whose mission is to support and advance healthy aging through biomedical research, is pleased to recognize the exemplary contributions of Bérénice Benayoun, PhD, to the field of aging research through the 2024 Vincent Cristofalo Rising Star Award in Aging Research.
This award is named in honor of the late Dr. Cristofalo, who dedicated his career to aging research and encouraged young scientists to investigate important issues in the biology of aging. Established in 2008, the award ...
Team fabricates tandem solar cell with power conversion efficiency greater than 20 percent
2024-05-22
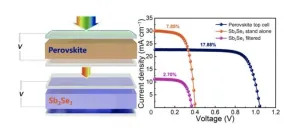
A research team has demonstrated for the first time a proof-of-concept tandem solar cell using antimony selenide as the bottom cell material and a wide-bandgap organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite material as the top cell material. The device achieved a power conversion efficiency of over 20 percent. This study shows that antimony selenide has great potential for bottom cell applications.
The research is published in the journal Energy Materials and Devices on March 4, 2024.
Photovoltaic technology, that harnesses sunlight and converts it into electricity, is popular because it provides a clean, renewable energy source. Scientists ...
Mitochondrial phosphate carrier plays an important role in virulence of Candida albicans
2024-05-22
This study is led by Professor Yan Wang (School of Pharmacy, Second Military Medical University (Naval Medical University), Shanghai, China). Her team found that the lack of MIR1 gene, which encodes mitochondrial phosphate carrier, can lead to severe virulence defects in Candida albicans.
In the Caenorhabditis elegans candidiasis model, the survival rate of the wild-type strain infected group dropped to about 20% at 120 h, while the survival rate of the mir1Δ/Δ-infected group remained about 90% at 120 h. Similar results were obtained in the murine model. None of the mice infected with mir1Δ/Δ mutant died during 21 days of ...
Enhanced plasticity of spontaneous coagulation cast oxide ceramic green bodies
2024-05-22
Spontaneous coagulation casting (SCC), a new type of colloidal forming process, has garnered significant attention since 2011 due to various advantages of a high bulk density and non-toxicity, as well as the ability to achieve dispersion and coagulation with very low additions (< 1 wt%) of copolymers of isobutylene and maleic anhydride (PIBM). Further research has revealed that the green bodies formed by this method are brittle, and the smaller the powder particle size used the more brittle the green bodies are. This paper reports ...
In vitro and circulation kinetic studies on π-π-stacked poly (ɛ-caprolactone)-based micelles loaded with olaparib
2024-05-22
Background and Aims
Olaparib is a selective poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor. However, its clinical application is hindered by low solubility and undesired pharmacokinetic profiles (e.g., relatively short circulation). Therefore, the present study aims to exploit polymeric micelles as a safe solubilizer and nanocarrier of olaparib, in order to improve its solubility and pharmacokinetics.
Methods
Poly (ε-caprolactone)-co-poly (benzyl 5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylate), i.e., benzyl-functionalized trimethylene carbonate)-b-poly (ethylene glycol) (P(CL-co-TMC-Bz)-PEG), was synthesized by ring-opening polymerization, ...
The effect of measurement depth and technical considerations in performing liver attenuation imaging
2024-05-22
Background and Aims
Clinical unmet need in managing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a common liver disorder affecting 25–30% of American adults is to develop noninvasive and robust biomarkers.
Methods
We re-measured liver AC by placing a region of interest (ROI, 3 cm tall and 3 cm wide) at 4.5 cm, 6 cm, and 7.5 cm from the skin and a large ROI (6.0 cm tall and 7.3 cm wide) on pre-recorded ATI images from 117 participants screened for NAFLD. The difference in AC value at variable ROI depths was tested using one-way ANOVA (analysis of variance). Diagnostic ...
New study: Cuddled cows who work as therapy animals showed a strong preference for women compared to men
2024-05-22
A new study – published in the Human-Animal Interactions journal – reveals that cows who are cuddled as therapy animals showed a strong preference for interactions with women when compared to men.
In turn, the research, which opens a new era on whether some therapies may be initially stronger based upon gender and not procedure, highlighted that the women also reported greater attachment behaviours towards the steers.
Dr Katherine Compitus, Clinical Assistant Professor at New York University, and Dr Sonya Bierbower, Associate Professor at United States Military Academy West Point, conducted the research using the ...
Flexible film senses nearby movements — featured in blink-tracking glasses
2024-05-22
I’m not touching you! When another person’s finger hovers over your skin, you may get the sense that they’re touching you, feeling not necessarily contact, but their proximity. Similarly, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have designed a soft, flexible film that senses the presence of nearby objects without physically touching them. The study features the new sensor technology to detect eyelash proximity in blink-tracking glasses.
Noncontact sensors can identify or measure an object without directly touching it. Examples of these devices include ...
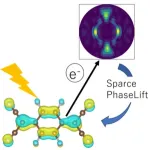
A simpler method for precise molecular orbital visualization
2024-05-22
Discoveries and progress in materials science often lay the foundation for technological breakthroughs that reshape many industrial and commercial fields, including medicine, consumer electronics, and energy generation, to name a few. Yet, the development of experimental techniques crucially underpins the exploration of new materials, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries. These techniques allow scientists to delve into a material’s chemical and physical properties, unlocking insights essential for realizing their potential applications.
In a recent study ...
New evidence suggests link between teen cannabis use and psychotic disorders may be stronger than previously thought
2024-05-22
Toronto, ON, May 22, 2024 – A new study published in the journal Psychological Medicine estimates that teens using cannabis are at 11 times higher risk of developing a psychotic disorder compared to teens not using cannabis.
This finding suggests that the association between cannabis and psychotic disorders may be stronger than indicated by previous research, which has relied largely on older data when cannabis was less potent than today. For context, the average THC potency of cannabis in Canada has increased from roughly 1% in 1980 to 20% in 2018.
Researchers from the University of Toronto, the Centre for Addiction and Mental ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] New study highlights significant increases in cannabis use in United StatesLong-term trends parallel changes in policy over 43 years