(Press-News.org) New Haven, Conn. – As the planet’s most expansive ecosystem, the deep sea can be a tough place to find a mate. Though, scientists say, some deep-sea anglerfishes evolved a unique method of reproduction that ensures that once they land a partner in the vast open waters, they remain latched for life.
These anglerfishes, called ceratioids, reproduce through sexual parasitism, in which the tiny males attach to their much larger female counterparts to mate. In some species, the males bite the females and then release once the mating process is complete. In others, the male permanently fuses to the female. In a process called obligate parasitism, the male’s head dissolves into the female and their circulatory systems merge. He transforms into a permanent sperm-producing sexual organ.
In a new study published May 23 in the journal Current Biology, Yale researchers examined how sexual parasitism works in synergy with other traits associated with the fish to influence the diversification of anglerfishes, an animal that is found throughout the oceans and whose name is inspired by the fishing rod-like appendage females use to lure prey.
Understanding the evolution of sexual parasitism has implications that could one day inform advances in medicine, according to the researchers.
Using genetic data from the genomes of anglerfishes, the researchers showed how complex features — such as sexual parasitism — assisted some anglerfish groups in transitioning from roaming shallow habitats, such as coral reefs, to swimming in the dark, open waters of the “midnight zone,” the deep-sea ecosystem where sunlight cannot penetrate.
“People tend to have single-trait explanations for why a group of animals can thrive in a given ecosystem, but in most living things, it seems that several distinctive innovations work synergistically to exploit new habitats,” said Chase D. Brownstein, a graduate student in Yale’s Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and the study’s co-lead author. “We found that a cascade of traits, including those required for sexual parasitism, allowed anglerfishes to invade the deep sea during a period of extreme global warming when the planet’s oceans where in ecological upheaval.”
For the study, the researchers reconstructed the evolutionary history of the deep-sea species. They demonstrated that the rapid transition of ceratioid anglerfishes from benthic walkers, which use modified fins to “walk” the ocean floor in the shallows, to deep-sea swimmers occurred 50 to 35 million years ago during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum, a period of high global temperatures that induced extinction throughout the oceans.
Ultimately, the researchers were unable to infer a clear evolutionary tree for deep-sea anglerfishes because the various lineages diverged from each other so rapidly, leaving relationships among lineages unresolvable, Brownstein said. But they found that the origins of sexual parasitism coincided with anglerfishes’ transition to the deep sea, although they could not determine which of the two forms of parasitism — temporary attachment or obligate parasitism — first occurred, Brownstein said.
Multiple traits evolved simultaneously to enable sexual parasitism. For example, ceratioids needed to evolve extreme sexual dimorphism with large females and miniature males. They also needed to shed their adaptive immunity — the system of specialized immune cells and antibodies that attack and eliminate pathogens — so that the female hosts’ bodies do not reject the parasitic male.
By reconstructing the evolutionary history of key genes involved in adaptive immunity, the researchers learned that multiple groups of deep-sea anglerfishes convergently degenerated their adaptive immunity, enabling sexual parasitism. And although sexual parasitism was evolving as deep-sea anglerfishes moved into the deep sea, they concluded that it is not necessarily the key trait driving species diversification among ceratioids. However, it did enable anglerfish to succeed in the midnight zone, Brownstein said.
“Sexual parasitism is thought to be advantageous to inhabiting the deep sea, which is Earth’s largest and most homogonous habitat,” he said. “Once individuals find a mate in that vast expanse, obligate sexual parasitism allows them to permanently latch, which seems to be a critical aid to the evolution of deep-sea anglerfish.”
The research has potential implications on human health, said senior author Thomas Near, professor of ecology and evolutionary biology in Yale’s Faculty of Arts and Sciences and Bingham Oceanographic Curator of Vertebrates at the Yale Peabody Museum.
“Better understanding how deep-sea anglerfishes lost adaptive immunity could one day contribute to advances in medical procedures, such as organ transplants and skin grafting, where suppressing immunity is crucially important,” he said. “It’s an interesting area for future medical research.”
The study was co-authored by Katerina L. Zapfe and Alex Dornburg of the University of North Carolina at Charlotte; Spencer Lott of Yale; Richard Harrington of the U.S. Department of Natural Resources, Marine Resources Division; and Ava Ghezelayagh of the University of Chicago.
END
Sea of love: Behind the unusual sexual parasitism of deep-water anglerfishes
2024-05-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
USTC proposes therapeutic approach for inflammatory bowel disease
2024-05-23
In a study published in Cell Host & Microbe, a research team led by Prof. PAN Wen from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with research teams led by Prof. ZHU Shu and Prof. SONG Xinyang, demonstrated the causal link between microbial factors and dysfunction of intestinal stem cells (ISCs) in colitis. On the basis of this mechanism, they proposed a possible approach to restore ISC function in colitis.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic disease characterized by the microbial ...
International planet hunters unveil massive catalog of strange worlds
2024-05-23
While thousands of planets have been discovered around other stars, relatively little is known about them. A NASA catalog featuring 126 exotic, newly discovered worlds includes detailed measurements that allow for comparisons with our own solar system.
The catalog details a fascinating mix of planet types beyond our solar system, from rare worlds with extreme environments to ones that could possibly support life.
The planets were analyzed by a large, international team of scientists using NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) in collaboration with the W.M. Keck Observatory on Maunakea, Hawai’i. They are described in today’s edition of The Astrophysical ...
Innovative techniques open new avenues in drug discovery for brain diseases
2024-05-23
Oak Brook, IL – Volume 29, Issue 2 of SLAS Discovery features two review articles, six original research articles covering phenotypic screening perspectives, medulloblastoma therapies and interventions for neurodegenerative diseases.
Reviews
Perspectives on phenotypic screening−Screen Design and Assay Technology Special Interest Group
The SLAS Screen Design and Assay Special Interest Group articulate the group’s discussion held at the SLAS2023 International Conference. Collectively, the group members’ perspectives highlight various challenges, progress and proposed solutions to ...
SLAS Technology presents: Advances in Synthetic Biology
2024-05-23
Oak Brook, IL – Volume 29, Issue 2 of SLAS Technology, includes three original research articles covering skin cutaneous melanoma, glycan-bead coupling and acoustic ejection mass spectrometry, and eight articles from the Advances in Synthetic Biology Special Issue.
Original Research
Validating core therapeutic targets for osteoporosis treatment based on integrating network pharmacology and informatics
This study recognizes metabolism-related lncRNAs associated with osteoporosis (OP) and constructed a prediction model for OP progression using these lncRNAs. The authors identify central therapeutic targets including CBFB, GLO1, NFKB2 ...
YouTubers cheer people up more than casual friends
2024-05-23
One-sided relationships with YouTubers are more emotionally fulfilling than talking to casual friends, a new study suggests.
The University of Essex research discovered people feel watching online stars like Zoella, KSI and PewDiePie can cheer them up more than weak-tie acquaintances – like neighbours or co-workers.
Dr Veronica Lamarche, from the Department of Psychology, also found people feel liked, respected and understood by fictional characters.
The study suggests watching online celebrities offer positive reinforcement - despite them not being able to respond.
Dr ...
Researchers advocate for structured framework to study the benefits of exercise training in multiple sclerosis rehabilitation
2024-05-23
East Hanover, NJ – May 22, 2024 – A team of experts in multiple sclerosis (MS) research recommends a structured approach to the study of mechanisms of exercise training for improving outcomes for multiple sclerosis (MS). In a review article, “Focusing on neural mechanisms of exercise training benefits in multiple sclerosis,” (doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2024.105633) published in Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders on April 16, 2024, they emphasize the value of adopting an experimental medicine framework to optimize ...
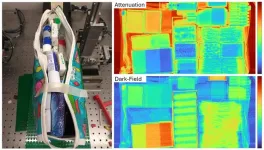
Researchers detect hidden threats with advanced x-ray imaging
2024-05-23
WASHINGTON — Researchers have combined various x-ray imaging technologies to create multi-contrast images that can be used to detect threatening materials such as explosives in thousands of complicated scenarios. The new approach, which also leverages readily available machine learning procedures for materials classification, could be useful for security screening as well as applications in the life and physical sciences.
“This method is particularly well suited to discriminating objects with very ...
Hypertension and kidney function after living kidney donation
2024-05-23
About The Study: In this cohort study of living kidney donors and nondonors with the same follow-up schedule, the risks of hypertension and albuminuria were not significantly different. After the initial drop in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) from nephrectomy, donors had a slower mean rate of eGFR decline than nondonors but were more likely to have an eGFR between 30 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 at least once in follow-up.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Amit X. Garg, M.D., Ph.D., email amit.garg@lhsc.on.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Kidney transplant outcomes from deceased donors who received dialysis
2024-05-23
About The Study: Compared with receiving a kidney from a deceased donor who did not undergo dialysis, receiving a kidney from a deceased donor who underwent dialysis prior to kidney donation was associated with a significantly higher incidence of delayed graft function, but no significant difference in graft failure or death at follow-up.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Chirag R. Parikh, M.D., Ph.D., email chirag.parikh@jhmi.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.8469)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
Potentially habitable 'exo-Venus' with Earth-like temperature discovered
2024-05-23
Potentially habitable 'exo-Venus' with Earth-like temperature discovered
Royal Astronomical Society press release
RAS PR 24/12
Embargoed until 15:00 BST on Thursday 23 May 2024
Astronomers have made the rare and tantalising discovery of an Earth-like exoplanet 40 light-years away that may be just a little warmer than our own world.
The potentially-habitable planet, named Gliese 12 b, orbits its host star every 12.8 days, is comparable in size to Venus - so slightly smaller than ...