(Press-News.org) Researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School have found that a new class of light-sensitive proteins are capable of turning off brain cells with light, offering scientists an unprecedentedly effective tool to investigate brain function. The study, recently published in Nature Communications, opens exciting new opportunities to apply optogenetics to investigate the brain activity underlying neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and depression.
Optogenetics is a technique where specific cells are bioengineered to include light-sensitive proteins that act as switches, allowing researchers to precisely control the electrical activity of these cells. Neurons and nerve cells with optogenetic switches can be used to study how different cells participate in various brain circuits and behaviours.
The team showed that specific potassium channels, known as kalium channelrhodopsins, can serve as effective instruments for regulating brain-cell activity in three critical experimental animals: fish, worms, and flies.
Dr Stanislav Ott, Senior Research Fellow with Duke-NUS’ Neuroscience and Behavioural Disorders Programme and first author of the study, said:
“These potassium channels act like tiny gates on cell membranes. When exposed to light, these gates open and let potassium ions flow through, helping to quiet the activity in the brain cells. This offers us new insights into how brain activities are regulated.”
Potassium ions are essential to normal electrical function in all human cells. Potassium channels are specialised proteins present in cell membranes that allow the flow of potassium ions. They regulate the flow of potassium ions across the cell membrane to maintain various cellular processes, and are critical to nerve-impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and cellular-fluid balance maintenance.
Associate Professor Adam Claridge-Chang from Duke-NUS’ Neuroscience and Behavioural Disorders Programme and the senior author of this study, said:
“We’ve developed other remote-control switches previously, but we’ve found these potassium channels to be even more versatile, providing a very useful way to study how the brain works.”
When triggered by light, the new kalium channelrhodopsins let potassium ions leave a neuron, changing the electrical gradient across the membrane. This change, known as hyperpolarisation, makes it difficult for the neuron to generate the electrical signal known as an action potential. Without action potentials, a neuron’s communication with other cells is greatly suppressed or even silenced.
The ability to silence brain cells using light-triggered potassium channels opens exciting avenues for studying the intricate interactions between different brain regions. It also offers a promising approach for exploring the pathological mechanisms underlying neurodegenerative, neurodevelopmental, and psychiatric disorders. These tools will help scientists form a deeper understanding of the brain and build paths to more effective treatments for brain disorders.
Professor Patrick Tan, Senior Vice-Dean for Research at Duke-NUS, said:
“Unlocking the mysteries of the brain remains one of science’s greatest challenges. Research like this by Adam Claridge-Chang and team equips scientists with better tools to study the intricate communication that goes on in the human brain and is essential to advancing our understanding of both healthy brains and neurological disorders, understanding that will enable us to develop effective new treatments for these conditions.”
Duke-NUS is a leader in medical research and innovation, with a commitment to improving patient care through scientific discovery. This study is part of its ongoing efforts to advance understanding of neurological and psychiatric conditions.
END
Duke-NUS researchers develop new light-controlled ‘off switch’ for brain cells
2024-05-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
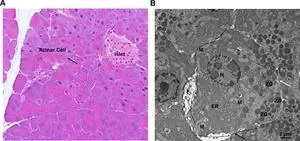
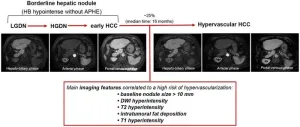
Liver lesions at risk of transformation into hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients
2024-05-24
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents a significant global health burden as one of the most common malignancies in individuals with chronic liver disease or cirrhosis. This malignancy evolves through a multistep process, beginning with dysplastic nodules (DNs) and early HCC, progressing to overt HCC. Recent advancements in liver imaging, particularly the use of hepatocyte-specific contrast agents, have enhanced the detection of these precursor lesions, known as borderline hepatic nodules. These nodules, especially those hypointense in the hepatobiliary phase (HBP) without arterial phase hyperenhancement (APHE), present ...
Update on the STING signaling pathway in developing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
2024-05-24
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most prevalent chronic liver condition worldwide, affecting about 25% of the global population due to the increasing rates of obesity and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of liver conditions ranging from simple hepatic steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Despite its prevalence, there are limited effective treatment options available. Inflammation driven by metabolic disturbances is a key factor in the development and progression of ...
Autonomous medical intervention extends ‘golden hour’ for traumatic injuries with emergency air transport
2024-05-24
For the first time, a closed loop, autonomous intervention nearly quadrupled the “golden hour” during which surgeons could save the life of a large animal with internal traumatic bleeding while in emergency ground and air transport.
This breakthrough in trauma care, announced today in Intensive Care Medicine Experimental by physician-scientists at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, has enormous potential for saving the lives of traumatically injured ...
More than spins: Exploring uncharted territory in quantum devices
2024-05-24
Many of today’s quantum devices rely on collections of qubits, also called spins. These quantum bits have only two energy levels, the ‘0’ and the ‘1’. However, spins in real devices also interact with light and vibrations known as bosons, greatly complicating calculations. In a new publication in Physical Review Letters, researchers in Amsterdam demonstrate a way to describe spin-boson systems and use this to efficiently configure quantum devices in a desired state.
Quantum devices use the quirky behaviour of quantum ...
SG ramps up cancer fight with S$50 million in national grant funding for precision oncology
2024-05-24
Singapore, 24 May 2024 – Two multi-institution and multidisciplinary Singapore teams of clinician-scientists and researchers have been awarded grants of S$25 million each, by the Singapore Ministry of Health through the NMRC Office, MOH Holdings Pte Ltd, under the NMRC Open Fund-Large Collaborative Grant (OF-LCG) programme. The S$50 million support for cancer research establishes the SYMPHONY 2.0 and Colo-SCRIPT research programmes to drive precision oncology research in Singapore aimed at improving the understanding, diagnosis and treatment of lymphoma and colorectal cancer.
Led by the ...
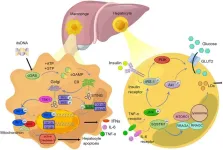
Autophagy in pancreatitis
2024-05-24
Researchers are exploring a new potential avenue for pancreatitis treatment: autophagy, a cellular recycling process. Autophagy helps maintain healthy pancreatic acinar cells by removing damaged organelles like mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
A new review published in eGastroenterology highlights the link between defective autophagy and pancreatitis. Impaired autophagy contributes to pancreatitis by allowing damaged organelles to accumulate within acinar cells. This accumulation disrupts cellular function and can ultimately lead to cell death.
"Autophagy plays a vital role in keeping pancreatic acinar cells healthy," ...
To 6G and beyond: Penn engineers unlock the next generation of wireless communications
2024-05-24
In the early 2010s, LightSquared, a multibillion-dollar startup promising to revolutionize cellular communications, declared bankruptcy. The company couldn’t figure out how to prevent its signals from interfering with those of GPS systems.
Now, Penn Engineers have developed a new tool that could prevent such problems from ever happening again: an adjustable filter that can successfully prevent interference, even in higher-frequency bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
“I ...
USF researcher using VR to map the brain, understand and treat disorders such as autism
2024-05-24
TAMPA, Fla. (May 24, 2024) – Through high-tech imaging and virtual reality, a University of South Florida medical engineering professor is creating a detailed map of the brain that can be used to better understand developmental disorders, such as autism, and provide earlier, more effective treatments for brain injuries and diseases.
Funded by a $3.3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health, George Spirou is expanding on his four decades of brain research to focus on the part of the brain that ...
Semaglutide significantly reduces risk of major kidney disease events, cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease, groundbreaking study reveals
2024-05-24
Semaglutide significantly reduces risk of major kidney disease events, cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease, groundbreaking study reveals
A pioneering study has demonstrated that semaglutide significantly reduces the risk of major kidney disease events, cardiovascular outcomes, and all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.1 The landmark trial, presented today at the 61st ERA Congress, will pave the way for new treatment strategies and ...
Unveiling a novel AAK1 inhibitor: How chemical proteomics unlocked therapeutic potential
2024-05-24
Enhancing drug development for life-threatening diseases like cancer hinges on a deep understanding of protein kinases, making it a focal point for researchers. These enzymes, encoded by more than 500 human genes, serve as critical players in cellular signaling pathways. However, if these signals are dysregulated, they can disrupt the normal cellular mechanisms, leading to diseases such as cancer. Protein kinase inhibitors have therefore provided a promising avenue in therapeutic intervention to disrupt the aberrant signaling ...