(Press-News.org) It’s important to ensure that care provided at US hospitals that predominantly serve Black and Hispanic populations is as high-quality as the care provided at other US hospitals. New research reveals significant disparities in the delivery of cancer-related care at minority serving hospitals (MSHs) compared with non-MSHs, however. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, investigators analyzed information from the National Cancer Database (which accrues approximately 70% of US cancer diagnoses) to identify patients eligible for definitive treatment for breast, prostate, non-small cell lung, and colon cancers between 2010 and 2019. Definitive treatment was defined as surgery for breast and colon cancer; surgery, radiation, or ablation for prostate cancer; and surgery or radiation for non-small cell lung cancer.
Of approximately 2.9 million patients who received care at 1,330 hospitals between 2010 and 2019, 9.3% were treated at MSHs. Among patients with breast cancer, those treated at MSHs were 17% less likely to receive definitive cancer treatment. For prostate, lung, and colon cancer, those treated at MSHs were 31%, 27%, and 19% less likely to receive definitive treatment respectively. These disparities persisted even after accounting for various sociodemographic and clinical factors.
The study’s authors calculated that if efforts successfully improved treatment rates at MSHs to match those at non-MSHs, 5,719 additional patients would receive definitive cancer treatment over 10 years. Providing additional funding and targeted improvements to hospitals without adequate resources may be important steps towards reaching this goal and could help to reduce racial and ethnic disparities in cancer outcomes.
“Access to care is a significant factor contributing to racial differences in cancer mortality, alongside biological differences. Therefore, improving services at hospitals that primarily serve minority populations could be a crucial part of a wider effort to achieve healthcare equity,” said lead author Quoc-Dien Trinh, MD, MBA, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Additional information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. A free abstract of this article will be available via the CANCER Newsroom upon online publication. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com
Full Citation:
“Estimating the Impact of Enhanced Care at Minority-Serving Hospitals on Disparities in the Treatment of Breast, Prostate, Lung, and Colon Cancers.” Edoardo Beatrici, Marco Paciotti, David-Dan Nguyen, Dejan K. Filipas, Zhiyu Qian, Giovanni Lughezzani, Danesha Daniels, Stuart R. Lipsitz, Adam S. Kibel, Alexander P. Cole, and Quoc-Dien Trinh. CANCER; Published Online: May 27, 2024 (DOI: 10.1002/cncr.35328).
URL Upon Publication: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/cncr.35328
Author Contact: Brigham and Women’s Hospital’s External Communications & Media Relations office, at mediarelations@bwh.harvard.edu
About the Journal
CANCER is a peer-reviewed publication of the American Cancer Society integrating scientific information from worldwide sources for all oncologic specialties. The objective of CANCER is to provide an interdisciplinary forum for the exchange of information among oncologic disciplines concerned with the etiology, course, and treatment of human cancer. CANCER is published on behalf of the American Cancer Society by Wiley and can be accessed online. Follow CANCER on Twitter @JournalCancer and Instagram @ACSJournalCancer, and stay up to date with the American Cancer Society Journals on LinkedIn.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Study assesses cancer-related care at US hospitals predominantly serving minority populations compared with non-minority serving hospitals
Analysis reveals systemic disparities in the delivery of definitive cancer treatment.
2024-05-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
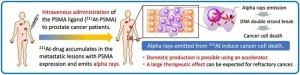
First in-human investigator-initiated clinical trial to launch for refractory prostate cancer patients: Novel alpha therapy targets prostate-specific membrane antigen
2024-05-27
Osaka, Japan - A research team at Osaka University will start an investigator-initiated clinical trial for refractory prostate cancer patients after successful development of a new alpha-ray therapeutic agent ([At-211] PSMA-5) and confirmation of its efficacy in animal models. This will be a world-first in-human clinical trial with [At-211] PSMA-5.
Prostate cancer is on the rise worldwide and is the most commonly diagnosed new cancer in men in Japan. Various treatments are offered for prostate cancer, but the prognosis is very poor when the disease is resistant to standard treatment and associated with multiple metastases.
In ...
Will generative AI change the way universities communicate?
2024-05-27
Since the launch of ChatGPT 3 in November 2022, we've been abuzz with talk of artificial intelligence: is it an unprecedented opportunity, or will it rob everyone of jobs and creativity? As we debate on social media (and perhaps use ChatGPT almost daily), generative AIs have also entered the arena of university communication. These tools—based on “Large Language Models” that were optimized for interactive communication—can indeed support, expand, and innovate university communication ...
Artificial Intelligence could help cure loneliness, says expert
2024-05-27
Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology could offer companionship to lonely people amid an international epidemic of loneliness, says a robotics expert.
Tony Prescott, a professor of cognitive robotics at the University of Sheffield, argues in his new book The Psychology of Artificial Intelligence that ‘relationships with AIs could support people’ with forms of social interaction..
Loneliness has been found to seriously impair human health, and Professor Prescott makes a case that advances in AI technology could ...
Echidnapus identified from an ‘Age of Monotremes’
2024-05-26
Published today in the Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology, evidence of an ‘Age of Monotremes’ has been unearthed by a team of Australian scientists at the Australian Museum (AM), Museums Victoria and Australian Opal Centre.
The findings were led by two renowned mammalogists, Honorary Associate of the Australian Museum, Professor Tim Flannery; and Professor Kris Helgen, Chief Scientist and Director of the Australian Museum Research Institute (AMRI).
Found in the Lightning Ridge opal fields, NSW, the opalised jaws ...
Semaglutide may protect kidney function in individuals with overweight or obesity and cardiovascular disease
2024-05-25
The SELECT Trial has revealed the potential of semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, in combating kidney function decline among individuals with overweight or obesity and established cardiovascular disease but without diabetes.1
Unveiling the results today at the 61st ERA Congress, researchers presented the impressive secondary analysis from the SELECT (Semaglutide Effects on Heart Disease and Stroke in Patients with Overweight or Obesity) trial, a randomised trial comprising a participant pool of 17,604 individuals.
Experts believe the study’s results offer hope for those affected by obesity, a condition known ...
New technique detects novel biomarkers for kidney diseases with nephrotic syndrome
2024-05-25
A groundbreaking study, presented today at the 61st ERA Congress, has uncovered a significant breakthrough in the diagnosis and monitoring of kidney diseases associated with nephrotic syndrome.1
Using a hybrid technique, researchers identified anti-nephrin autoantibodies as a reliable biomarker for tracking disease progression, opening new avenues for personalised treatment approaches.
Nephrotic syndrome, characterised by elevated protein levels in the urine, is linked to kidney diseases such as minimal change disease (MCD), primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), and membranous nephropathy (MN). The primary cause behind nephrotic syndrome is damage to podocytes, the ...
Political elites take advantage of anti-partisan protests to disrupt politics
2024-05-24
Protest movements that reject political parties have an unintended consequence, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame: They empower savvy politicians who channel them to shake up the status quo.
The findings provide a framework for understanding recent global political realignments and offer lessons for activists who want to make a meaningful impact. They are particularly relevant in an era when mass protests have become an increasingly common tool to voice dissent with powerful institutions and draw attention to overlooked issues ranging from climate and conflict ...
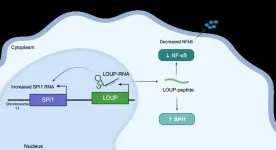
Tiny target discovered on RNA to short-circuit inflammation, UC Santa Cruz researchers find
2024-05-24
UC Santa Cruz researchers have discovered a peptide in human RNA that regulates inflammation and may provide a new path for treating diseases such as arthritis and lupus. The team used a screening process based on the powerful gene-editing tool CRISPR to shed light on one of the biggest mysteries about our RNA–the molecule responsible for carrying out genetic information contained in our DNA.
This peptide originates from within a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) called LOUP. According to the researchers, ...
Charge your laptop in a minute? Supercapacitors can help; new research offers clues
2024-05-24
Imagine if your dead laptop or phone could charge in a minute or if an electric car could be fully powered in 10 minutes.
While not possible yet, new research by a team of CU Boulder scientists could potentially lead to such advances.
Published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers in Ankur Gupta’s lab discovered how tiny charged particles, called ions, move within a complex network of minuscule pores. The breakthrough could lead to the development of more efficient energy storage devices, such as supercapacitors, said Gupta, an assistant professor of chemical and biological engineering.
“Given the critical role ...
Scientists discover CO2 and CO ices in outskirts of solar system
2024-05-24
ORLANDO, May 24, 2024 – For the first time, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide ices have been observed in the far reaches of our solar system on trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs).
A research team, led by planetary scientists Mário Nascimento De Prá and Noemí Pinilla-Alonso from the University of Central Florida’s Florida Space Institute (FSI), made the findings by using the infrared spectral capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to analyze the chemical composition of 59 trans-Neptunian objects and Centaurs.
The pioneering study, published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Study assesses cancer-related care at US hospitals predominantly serving minority populations compared with non-minority serving hospitalsAnalysis reveals systemic disparities in the delivery of definitive cancer treatment.