(Press-News.org) Cancer poses significant challenges due to the development of resistance and the likelihood of relapse. Resistance may arise from permanent genetic changes in cancer cells or non-genetic alterations in cancer cell behavior induced by treatment. Standard of care in cancer treatments typically involves administering the maximum tolerated dose of a drug to eradicate drug-sensitive cells effectively. However, this approach often fails in the long term because drug-resistant cancer cells can grow more rapidly when all drug-sensitive cancer cells are killed off.
An evolution-based treatment approach, called adaptive therapy, personalizes treatment dose or breaks based on individual patient responses. The goal of adaptive therapy is to maintain a sufficient number of sensitive cells to control the growth of resistant cells. Recent studies and clinical trials have demonstrated that adaptive therapy could delay resistance more effectively compared to the standard of care.
Determining the dose and treatment breaks for each patient is challenging because cancer is a complex evolving system, and every patient is different. Mathematical models can be helpful in designing such patient-specific treatment strategies. Indeed, several mathematical models have been developed to explore the effects of various treatment strategies on patient outcomes. However, existing mathematical models often overlook the impact of acquired resistance and cancer cell plasticity. 'Acquired resistance' encompasses various types of resistance that emerge, often due to genetic changes. 'Cell plasticity' refers to cancer cells' ability to alter their phenotypes in response to changes in their microenvironment, such as fluctuations in treatment dosage or treatment cessation
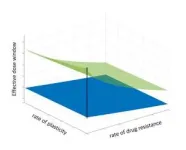
A research team led by Dr. Kim Eunjung at the Natural Products Informatics Research Center of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, Director Oh Sangrok) has established a theoretical foundation for cancer treatment strategies following tumor evolution. They have developed a mathematical model to predict tumor evolution, considering the acquisition of resistance by cancer cells and their ability to alter phenotypic behavior (plasticity) during treatment. The analysis of their model has identified the conditions for the existence of an effective dose window, a range of doses that could maintain tumor volume at an equilibrium point, where the tumor volume remains unchanged and stable. For some tumors with plasticity, taking breaks from treatment helps cancer cells become sensitive again, joining forces with other sensitive cells to suppress resistant cell growth. The research team has proposed evolutionary therapy dosing, which involves administering treatment in cycles comprising treatment holidays, minimum effective doses, and maximum tolerated doses. Pausing treatment allows plastic cancer cells to regain sensitivity, followed by the application of a minimum effective dose to control tumor volume. Subsequently, a maximum tolerated dose is administered to further reduce tumor size. This dosing cycle effectively contains tumor volume at a manageable level. Numerical simulations of the proposed strategies, applied to a melanoma patient, further illustrate these findings. The results show that evolutionary dosing can redirect tumor dynamics, maintaining tumor size below a tolerable burden.
The developed mathematical model can predict the effective dosage range of cancer treatment drug candidates prior to clinical trials. It can assist in determining the anticancer effects of new treatments and identifying the effective dosage range for each drug. Furthermore, the model contributes to personalized cancer treatment strategies by considering patient-specific tumor evolutionary dynamics during treatment.
Dr. Kim Eunjung stated, "In the current study, we emphasized the role of cancer cells’ phenotypic plasticity in enhancing the controllability of tumor burden with evolutionary treatment cycling doses." She also mentioned plans to utilize the mathematical model in designing animal experiments and clinical trials for potential natural product-derived anticancer drug candidates. This aims to establish dosage regimens that effectively control tumor burden.
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lee Jong-ho) through KIST's major projects and mid-career researcher programs (2019R1A2C1090219). The research findings were published in the February issue of the international journal "Chaos, Solitons & Fractals" (IF 7.8, JCR top 0.9% of the field).
END
Mathematical model driven evolutionary therapy dosing exploiting cancer cell plasticity
Develop a mathematical model of tumor dynamics considering acquired resistance and cancer cell plasticity
2024-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Biodiversity in the margins: Merging farmlands affects natural pest control
2024-05-28
A new study published in the Journal of Applied Ecology demonstrates how the diversity and abundance of arthropods decrease when hedgerows and field margins covered by wild grass and flowers are removed.
Researchers from the UK, Netherlands and China studied 20 rice fields in China for six years to see how the changing agricultural landscape affects the diversity and abundance of rice pests and their natural enemies, as well as the effect on rice yield.
Traditional Chinese smallholder fields are irregularly shaped and separated by areas of hedgerows, wild grass, and flowers. Using large-scale machinery in these farmlands is difficult, so there is low agricultural ...
1 in 8 pregnant people have a disability, but significant gaps exist in the provision of accessible care
2024-05-28
Toronto, ON, May 28, 2024 – People with disabilities account for 13% of all pregnancies in Ontario, but a new report shows that this population was more likely to experience pregnancy complications such as emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and preterm birth.
Researchers from ICES, the University of Toronto Scarborough, and the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) have released a landmark report detailing findings from one of the largest studies to date on disability and pregnancy.
Funded by the US National Institutes of Health, the Disability and Pregnancy Study used healthcare ...
Statins associated with decreased risk for CVD and death, even in very old adults
2024-05-27
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 27 May 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Statins associated with ...
Climate change is moving tree populations away from the soil fungi that sustain them
2024-05-27
As our planet warms, many species are shifting to different locations as their historical habitats become inhospitable. Trees are no exception – many species’ normal ranges are no longer conducive to their health, but their shift to new areas that could better sustain them has been lagging behind those of other plants and animals. Now, scientists show that the reason for this lag might be found belowground. A study published in PNAS on May X, shows that trees, especially those in the far ...
Secrets of sargassum: Scientists advance knowledge of seaweed causing chaos in the Caribbean and West Africa
2024-05-27
Researchers have been working to track and study floating sargassum, a prolific seaweed swamping Caribbean and West African shorelines, and causing environmental and economic harm.
The stranded seaweed blocks fishing boats; threatens tourism; disrupts turtle nesting sites, reefs and mangroves, and releases toxic gas, which impacts human health and damages electrical equipment.
First reported by Christopher Columbus in the 15th century, floating mats of sargassum have long been present in the North Atlantic. However, since 2011, a floating population has established ...
Bioinformatics approach could help optimize soldiers’ training for improved readiness and recovery
2024-05-27
Of the many perils facing members of the military, injuries incurred in training or on deployment repeatedly sideline elite operators.
“It’s a pervasive problem,” says Dhruv Seshadri, an assistant professor of bioengineering in Lehigh University’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science. “We’re looking at how we can integrate physiological data, biomechanical data, and subjective assessments to help reduce the risk of these injuries happening in the first place, and when they do happen, how we can use those data to accelerate the soldier’s return to operation.”
Seshadri ...
Earth scientists describe a new kind of volcanic eruption
2024-05-27
No two volcanic eruptions are exactly alike, but scientists think a series of explosive eruptions at Kīlauea volcano fit into a whole new category.
By analyzing the dynamics of 12 back-to-back explosions that happened in 2018, researchers describe a new type of volcanic eruption mechanism. The explosions were driven by sudden pressure increases as the ground collapsed, which blasted plumes of rock fragments and hot gas into the air, much like a classic stomp-rocket toy.
Researchers from the University of Oregon, United States Geological Survey and China’s Sichuan University report their findings in a paper published May 27 in Nature Geoscience.
The ...
Warmer wetter climate predicted to bring societal and ecological impact to the Tibetan Plateau
2024-05-27
While recent reports have stated that more than half the world’s largest lakes, including lakes in the Tibetan plateau, are drying up, a paper in Nature Geoscience today (27/5/24 DOI 10.1038/s41561-024-01446-w ) suggests that, by the end of this century, land-locked lakes on the Tibetan Plateau are set to increase exponentially, resulting in major land loss and related economic, environmental and climatic impacts.
Climate and weather predictions suggest that increased rainfall due to climate change will enlarge these lakes, and see water levels rise by up to 10 metres.
The volume of water caught in these land-locked lakes is estimated to ...
Feeding infants peanut products protects against allergy into adolescence
2024-05-27
Feeding children peanuts regularly from infancy to age five reduced the rate of peanut allergy in adolescence by 71%, even after many years when the children ate or avoided peanut as desired.
The new findings provide conclusive evidence that introducing peanuts into babies’ diets early will achieve long-term prevention of peanut allergy.
Lead investigator Professor Gideon Lack from King’s College London said: “Decades of advice to avoid peanuts has made parents fearful of introducing peanuts at an early age. The evidence is clear that early introduction of peanut in infancy ...
Who will like beetle skewers? What Europeans think about alternative protein food
2024-05-27
Why do people in Paris like seaweed and tofu salad? Will Italians be tempted to try a beetle skewer? How many young Polish consumers are "food innovators", eager to eat chickpea pâté? In an international project, researchers from SWPS University analysed European consumers' attitudes towards alternative protein food products.
In the face of the fight against climate change, more and more people are modifying their diets, giving up or limiting conventional sources of protein (e.g., beef, pork, poultry, and animal dairy) in favour of those with a lower environmental impact. These are the so-called alternative protein food (APF) products, which may be based on ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
When safety starts with a text message
CSIC develops an antibody that protects immune system cells in vitro from a dangerous hospital-acquired bacterium
New study challenges assumptions behind Africa’s Green Revolution efforts and calls for farmer-centered development models
Immune cells link lactation to long-lasting health
Evolution: Ancient mosquitoes developed a taste for early hominins
Pickleball players’ reported use of protective eyewear
Changes in organ donation after circulatory death in the US
Fertility preservation in people with cancer
A universal 'instruction manual' helps immune cells protect our organs
Fifteen-year results from SWOG S0016 trial suggest follicular lymphoma is curable
The breasts of a breastfeeding mother may protect a newborn from the cold – researchers offer a new perspective on breast evolution
More organ donations now come from people who die after their heart stops beating
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
[Press-News.org] Mathematical model driven evolutionary therapy dosing exploiting cancer cell plasticityDevelop a mathematical model of tumor dynamics considering acquired resistance and cancer cell plasticity