Better disciplinary structures in schools can help reduce hate speech directed against Asian American students
UC Davis research suggests hate speech experiences drop when schools offer structure and adult support
2024-05-28
(Press-News.org) Asian Americans have been the targets of hate speech for generations, particularly during the COVID pandemic. But new research by the University of California, Davis, suggests that Asian American adolescents experience fewer incidents of hate speech in schools with stronger disciplinary structures and adult support.
A new study looks at hate speech experiences even before COVID, during the period between 2015 and 2019. The article, “Hate Speech Against Asian American Youth: Pre-Pandemic Trends and The Role of School Factors,” was published May 4 in the Journal of Youth and Adolescents.
“Although hate against Asian American and Pacific Islander communities is longstanding and systemic, a strong confluence of recent events — the pandemic, coupled with social and political rifts — has intensified this hate,” said lead author Kevin Gee, a professor in the UC Davis School of Education who specializes in school organization and educational policy.
Gee and his co-authors sought to look at how school environments might perpetuate, or in the alternative, offer protection from hate speech.
“This study found that stronger authoritative climates alongside supportive adults in schools are linked to lower probability that Asian American adolescents experience hate speech at school,” Gee said. He said the research also showed that adolescents who report engaging in fights were more likely to experience hate speech and social victimization in general.
Gee said that schools can help reduce hate speech though more positive school climates, in particular. “Authoritative school climate and exposure to fights are malleable and can be shaped directly by broader school climate-related policies, programs and interventions,” he said. “School climate has potential to protect Asian American youth from hate speech at school.”
Researchers analyzed data collected from 938 Asian American adolescents from 2015, 2017 and 2019 School Crime Supplement to the National Crime Victimization Survey. On average, about 7% of Asian Americans were targets of hate speech at school between 2015 and 2019. Rates went down for students who experienced “strict, yet fair” disciplinary rules when coupled with strong adult support.
Delving deeper into the numbers, about 1 in 15 Asian American adolescents reported being victims of hate speech during the study period, with 1 in 5 reporting hate speech in school environments with the least disciplinary structure. Those schooled in the most disciplinary structured environments experienced hate speech at a level of 1 in 20, according to the research.
For students who engaged in fights, their predicted probability of encountering hate speech is roughly 30%, compared to 12% for counterparts who did not engage in fights.
Co-authors of the study include North Cooc, associate professor at University of Texas, Austin; and Peter Yu, an undergraduate researcher at UC Davis.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-28
Using ancient DNA extracted from the toe bone of a museum specimen, Harvard biologists have sequenced the genome of an extinct, flightless bird called the little bush moa, shedding light into an unknown corner of avian genetic history.
Published in Science Advances, the work is the first complete genetic map of the turkey-sized bird whose distant living cousins include the ostrich, emu, and kiwi. It is one of nine known species of moa, all extinct for the last 700 years, that inhabited New Zealand before the late 1200s and the arrival of Polynesian human settlers.
“We’re pulling ...
2024-05-28
PHILADELPHIA — (May 28, 2024) — The Wistar Institute’s Paul M. Lieberman, Ph.D., and lab team led by senior staff scientist and first author, Samantha Soldan, Ph.D., have demonstrated how B cells infected with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) can contribute to a pathogenic, inflammatory phenotype that contributes to multiple sclerosis (MS); the group has also shown how these problematic B cells can be selectively targeted in a way that reduces the damaging autoimmune response of multiple sclerosis. The lab’s findings were published in Nature Microbiology in the paper, “Multiple sclerosis patient derived spontaneous B cells have distinct EBV and ...
2024-05-28
Among fathers, heart health was worse for men who became fathers under the age 25
First U.S. multiethnic longitudinal study to analyze cardiovascular health outcomes of fathers
Results differed by race and ethnicity subgroups
Age-adjusted rate of death for Black fathers was lower than for nonfathers
‘Fatherhood may be protective for Black men’
CHICAGO --- Heart disease is the leading cause of death among men, and being a father may put men at an even greater risk of poor heart health later in life, reports a new study from scientists at Northwestern University and Ann & ...
2024-05-28
“This consideration could be the starting point to study whether Silibinin could contrast tumor progression, aging and inflammaging through molecular and cellular mechanisms [...].”
BUFFALO, NY- May 28, 2024 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on May 23, 2024, entitled, “The importance of integrated therapies on cancer: Silibinin, an old and new molecule.”
In this new review, researchers Elisa Roca, Giuseppe Colloca, Fiorella Lombardo, Andrea Bellieni, Alessandra Cucinella, Giorgio Madonia, Licia Martinelli, Maria Elisa Damiani, Ilaria Zampieri, and ...
2024-05-28
A pioneering study has used extensive global datasets and machine learning to map the activities of seafloor invertebrate animals, including worms, clams and shrimps, across the entire ocean, revealing for the first time critical factors that support and maintain the health of marine ecosystems.
The international team, led by Texas A&M University and including investigators from Yale University and the University of Southampton, specifically focused on the unsung yet vital role burrowing animals play as "ecosystem engineers" in shaping nutrient ...
2024-05-28
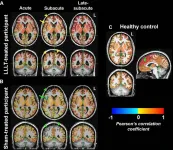
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Low-level light therapy appears to affect healing in the brains of people who suffered significant brain injuries, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Lights of different wavelengths have been studied for years for their wound-healing properties. Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) conducted low-level light therapy on 38 patients who had suffered moderate traumatic brain injury, an injury to the head serious enough to alter cognition and/or be visible on a brain scan. Patients received ...
2024-05-28
Background and Goal: Team-based care is considered the gold standard in delivery models. It uses integrated clinical teams with diverse skills and perspectives to provide efficient, high-quality health care services. Within these teams, individuals from minoritized racial-ethnic groups, often referred to as persons of color (POC), typically occupy roles with less authority (e.g., medical assistants), while white individuals more frequently hold positions of greater power (e.g., physicians). Few studies have explored the viewpoints of staff members in lower-power roles, who are disproportionately POC and constitute the majority of a health care team. This study aims to ...
2024-05-28
NRG Oncology (NRG), a National Cancer Institute (NCI) National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) group focused on improving outcomes for adults with cancer through multi-center clinical research, recently announced two new Vice-Chairs to co-lead the NRG Patient Advocate Committee (PAC) alongside the current PAC Committee Chair, Dorothy Erlanger.
Marlyn Molero, was appointed as Vice-Chair of the NRG PAC. Marlyn is a clinical researcher in the oncology area with Commonspirit Research Institute as well as a Spanish interpreter at Vituity. Marlyn brings a unique perspective to the NRG PAC leadership ...
2024-05-28
The toe tapping behavior of various amphibians has long attracted attention from researchers and pet owners. Despite being widely documented, the underlying functional role is poorly understood. In a new paper, researchers demonstrate that Dyeing poison frogs modulate their taps based on specific stimuli.
Dyeing poison frogs, Dendrobates tinctorius, have been shown to tap their posterior toes in response to a range of prey sizes, from small fruit flies to large crickets. In the present study, ...
2024-05-28
Irvine, Calif., May 28, 2024 — A multidisciplinary research team at the University of California, Irvine has revealed that the circadian clock – the biological pacemaker that governs daily rhythms in physiological processes, including immune functions – can be leveraged to enhance the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitor cancer therapy. Checkpoint inhibitors block different proteins from binding to tumor cells, allowing the immune system’s T cells to kill the tumor.
The study, published online ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Better disciplinary structures in schools can help reduce hate speech directed against Asian American students
UC Davis research suggests hate speech experiences drop when schools offer structure and adult support