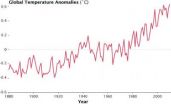
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON -- Global surface temperatures in 2010 tied 2005 as the warmest on record, according to an analysis released Wednesday by researchers at NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York.
The two years differed by less than 0.018 degrees Fahrenheit. The difference is smaller than the uncertainty in comparing the temperatures of recent years, putting them into a statistical tie. In the new analysis, the next warmest years are 1998, 2002, 2003, 2006 and 2007, which are statistically tied for third warmest year. The GISS records begin in 1880.
The analysis found 2010 approximately 1.34 F warmer than the average global surface temperature from 1951 to 1980. To measure climate change, scientists look at long-term trends. The temperature trend, including data from 2010, shows the climate has warmed by approximately 0.36 F per decade since the late 1970s.
"If the warming trend continues, as is expected, if greenhouse gases continue to increase, the 2010 record will not stand for long," said James Hansen, the director of GISS.
The analysis produced at GISS is compiled from weather data from more than 1000 meteorological stations around the world, satellite observations of sea surface temperature and Antarctic research station measurements. A computer program uses the data to calculate temperature anomalies -- the difference between surface temperature in a given month and the average temperature for the same period during 1951 to 1980. This three-decade period acts as a baseline for the analysis.
The resulting temperature record closely matches others independently produced by the Met Office Hadley Centre in the United Kingdom and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Climatic Data Center.
The record temperature in 2010 is particularly noteworthy, because the last half of the year was marked by a transition to strong La Niña conditions, which bring cool sea surface temperatures to the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
"Global temperature is rising as fast in the past decade as in the prior two decades, despite year-to-year fluctuations associated with the El Niño-La Niña cycle of tropical ocean temperature," Hansen and colleagues reported in the Dec. 14, 2010, issue of Reviews of Geophysics.
A chilly spell also struck this winter across northern Europe. The event may have been influenced by the decline of Arctic sea ice and could be linked to warming temperatures at more northern latitudes.
Arctic sea ice acts like a blanket, insulating the atmosphere from the ocean's heat. Take away that blanket, and the heat can escape into the atmosphere, increasing local surface temperatures. Regions in northeast Canada were more than 18 degrees warmer than normal in December.
The loss of sea ice may also be driving Arctic air into the middle latitudes. Winter weather patterns are notoriously chaotic, and the GISS analysis finds seven of the last 10 European winters warmer than the average from 1951 to 1980. The unusual cold in the past two winters has caused scientists to begin to speculate about a potential connection to sea ice changes.
"One possibility is that the heat source due to open water in Hudson Bay affected Arctic wind patterns, with a seesaw pattern that has Arctic air downstream pouring into Europe," Hansen said.
INFORMATION:
For more information about GISS's surface temperature record, visit:
http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/
A Warming World
http://climate.nasa.gov/warmingworld/
Global Temperatures Animation
http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a000000/a003600/a003674/index.html
NASA research finds 2010 tied for warmest year on record
2011-01-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New telescope is exploring solar system 'outback'
2011-01-14
In the outer reaches of our solar system lies a mysterious region far more remote and difficult to explore than the Australian outback. It remains the only part of our solar system not visited by spacecraft. Called the Kuiper Belt, this area beyond Neptune is home to the dwarf planets Pluto, Eris, Makemake, and Haumea. It also harbors thousands of smaller objects that form a second, icy asteroid belt (or more appropriately, comet belt). In this realm of perpetual twilight, the distant sun looks like just another bright star.
A new telescope has begun to virtually explore ...
Deep genomics
2011-01-14
In 2003, the year a complete draft of the human genome was released, the U.S. National Human Genome Research Institute launched the ENCODE project (ENCyclopedia of DNA Elements), to develop an encyclopedia of the epigenome, that is, of all of the many factors that can change the expression of the genes without changing the genes.
Four years later, the National Institutes of Health funded modENCODE (the Model Organism ENCylopedia of DNA Elements) to work out the epigenomes of two model organisms: the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, lurker among rotten bananas, and the ...
Why coffee protects against diabetes
2011-01-14
Coffee, that morning elixir, may give us an early jump-start to the day, but numerous studies have shown that it also may be protective against type 2 diabetes. Yet no one has really understood why.
Now, researchers at UCLA have discovered a possible molecular mechanism behind coffee's protective effect. A protein called sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) regulates the biological activity of the body's sex hormones, testosterone and estrogen, which have long been thought to play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes. And coffee consumption, it turns out, increases ...
Skin provides Australia's first adult stem cells for rare genetic disease
2011-01-14
Scientists have developed Australia's first adult induced pluripotent stem cell lines using skin biopsies from patients with the rare genetic disease Friedreich Ataxia (FA).
The study was conducted by the University of Melbourne and Monash Institute of Medical Research and is published in the current online edition of the international journal Stem Cell Reviews and Reports. It is the first time adult pluripotent stem cells, known as iPS cells have been developed for a specific disease in Australia, allowing for the development of new treatments for FA and related conditions ...
Fruit fly nervous system provides new solution to fundamental computer network problem
2011-01-14
PITTSBURGH—The fruit fly has evolved a method for arranging the tiny, hair-like structures it uses to feel and hear the world that's so efficient a team of scientists in Israel and at Carnegie Mellon University says it could be used to more effectively deploy wireless sensor networks and other distributed computing applications.
With a minimum of communication and without advance knowledge of how they are connected with each other, the cells in the fly's developing nervous system manage to organize themselves so that a small number of cells serve as leaders that provide ...
GM chickens that don't transmit bird flu developed
2011-01-14
Chickens genetically modified to prevent them spreading bird flu have been produced by researchers at the Universities of Cambridge and Edinburgh.
The scientists have successfully developed genetically modified (transgenic) chickens that do not transmit avian influenza virus to other chickens with which they are in contact. This genetic modification has the potential to stop bird flu outbreaks spreading within poultry flocks. This would not only protect the health of domestic poultry but could also reduce the risk of bird flu epidemics leading to new flu virus epidemics ...
Overexpression of repetitive DNA sequences discovered in common tumor cells
2011-01-14
Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Cancer Center researchers have discovered a previously unknown feature of common tumor cells – massive overexpression of certain DNA sequences that do not code for proteins. These DNA sequences – called satellite repeats – have been studied for their role in chromosomal structure but previously were not suspected of having a role in cancer. The report will appear in the journal Science and is receiving early online release.
"Satellite repeats make up a large part of our genome but had been thought to be inactive," explains David ...
When a kidney transplant fails, home-based dialysis is an option
2011-01-14
Patients returning to dialysis after kidney transplant failure present unique challenges compared with other dialysis patients: they have been exposed to very powerful immunosuppressive medications and have been on dialysis for a longer period of time than other dialysis patients. This puts them at particularly high risk for various complications and death. According to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Clinical Journal of the American Society Nephrology (CJASN), despite complications, these patients can choose to undergo dialysis in the comfort of their own ...
Forget Planet X! New technique could pinpoint Galaxy X
2011-01-14
Planet X, an often-sought 10th planet, is so far a no-show, but Sukanya Chakrabarti has high hopes for finding what might be called Galaxy X – a dwarf galaxy that she predicts orbits our Milky Way Galaxy.
Many large galaxies, such as the Milky Way, are thought to have lots of satellite galaxies too dim to see. They are dominated by "dark matter," which astronomers say makes up 85 percent of all matter in the universe but so far remains undetected.
Chakrabarti, a post-doctoral fellow and theoretical astronomer at the University of California, Berkeley, has developed ...
Writing about worries eases anxiety and improves test performance
2011-01-14
Students can combat test anxiety and improve performance by writing about their worries immediately before the exam begins, according to a University of Chicago study published Friday in the journal Science.
Researchers found that students who were prone to test anxiety improved their high-stakes test scores by nearly one grade point after they were given 10 minutes to write about what was causing them fear, according to the article, "Writing about Testing Boosts Exam Performance in the Classroom." The article appears in the Jan. 14 issue of Science and is based on research ...