(Press-News.org) May 28, 2024
For more information, contact:
Nicole Fawcett, nfawcett@umich.edu
EMBARGOED for release at 6:30 p.m. ET May 28, 2024
Altering cancer treatment dosing could reduce climate impact, study finds
Model estimates potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by delivering treatment every 6 weeks
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — Changing how often a popular cancer therapy is delivered would reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve environmental impact without decreasing cancer survival, according to a new analysis from researchers at the University of Michigan Health Rogel Cancer Center.
The team looked at 7,813 veterans receiving the immunotherapy treatment pembrolizumab through the Veterans Health Administration. Pembrolizumab is an intravenous treatment that is often given every three weeks at a standard, one-size-fits-all dose of 200 milligrams. Researchers estimated the environmental impact of patients coming in for this care every three weeks: carbon dioxide emissions from patients’ transportation to and from the clinic, manufacturing of the drug, and medical waste like needles, tubing and bags used during the compounding and infusing process.
Then they considered alternative scenarios. What if patients received 400 milligrams of pembrolizumab every six weeks, a dose approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration? What if they received a dose proportionate to their weight instead of the standard dose, as pembrolizumab was originally approved by FDA? Data suggests these approaches achieve cancer outcomes equivalent to the standard three-week flat dosing and likely reduce the burdens of cancer treatment that patients face.
They found that for this cohort of patients, extending treatments to every six weeks instead of every three weeks would have required 15,000 fewer infusions. That means 15,000 fewer trips to the clinic and 15,000 fewer incidences of compounding and infusing treatments. In total, this change would reduce greenhouse gas emissions in just the VHA by 200 tons per year. Results are published in The Lancet Oncology.
“As providers, every time we’re with a patient we’re faced with this litany of decisions that both we and the patient have to make. Those decisions – every three week dosing or every six week dosing – seem small but they really add up,” said study author Garth W. Strohbehn, M.D., M.Phil., assistant professor of internal medicine at Michigan Medicine.
Next, researchers looked at the impact that the reduced carbon emissions could have on climate change and human health – not just for the person with cancer, but for all of us, due to rising global temperatures. The model indicates that by continuing the current trends in pembrolizumab dosing instead of changing to less-frequent dosing, about three more people will die per year between now and 2100 because of the extra greenhouse gas emissions.
“There will more than likely be folks completely uninvolved in cancer care who are harmed by choosing to dose this medicine the way that we do. It doesn’t need to happen,” said Strohbehn, who is also a member of the U-M Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation and early career research scientist at the VA Ann Arbor Center for Clinical Management Research.
“That’s the point we’re trying to make here: There are likely to be health costs that non-patients in a society can expect to bear when we choose to practice cancer care the way we do. Do we have a moral obligation to change the way we’re doing things if the patient in front of us is not harmed by it?”
Patient transportation to and from appointments was the biggest driver of carbon emissions, researchers found, which suggests that less-frequent infusion treatments would not only help the environment but also potentially improve patient quality of life due to fewer trips to the hospital. Researchers also estimated significant cost savings for VHA from the alternative dosing regimens since the total amount of drug used with the weight-based doses is lower than the one-size-fits-all approach, echoing earlier findings from Strohbehn’s team.
The study authors suggest that multiple policy actions would need to be aligned to facility this change. They suggest payers could develop targeted incentives around environmentally conscious care. Professional societies could alter guidelines with environmental sustainability in mind, where patient outcomes are not expected to be impacted by the adoption of more sustainable care. Requiring environmental report cards for individual drugs at the time of approval could also increase awareness.
“I think there’s value in holding a mirror up to the conventional system and encouraging self-reflection,” Strohbehn said.
Additional authors: Alex K. Bryant, Jacqueline R. Lewy, R. Daniel Bressler, Zoey Chopra, Derek J. Gyori, Brian G. Bazzell, Julie A. Moeller, Sofia I. Jacobson, A. Mark Fendrick, Eve A. Kerr, Nithya Ramnath, Michael D. Green, Timothy P. Hofer, Parth Vaishnav
Bryant, Ramnath, Green, Hofer and Strohbehn are supported by the National Cancer Institute grant P30 CA046592.
Disclosure: None
Paper cited: “Projected environmental and public health benefits of extended-interval dosing: An analysis of pembrolizumab use in a U.S. national health system,” The Lancet Oncology. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(24)00200-6
Resources:
University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center, www.rogelcancercenter.org
Michigan Medicine Cancer AnswerLine, 800-865-1125
# # #
END
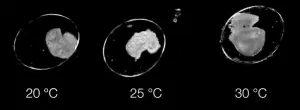
Corals play an essential role in ocean ecosystems, and like many organisms, they are under threat from climate change and other human activities. To better protect coral, it’s first necessary to understand them, in particular their reproductive life cycle, which only happens once a year. For the first time, researchers have produced a model for coral spawning, based on various environmental factors. They achieved this by tapping an often overlooked source of aquatic knowledge, an aquarium.
Given their branching shapes or waving tendrils, you would be ...
Research led by the University of Plymouth has shown that a new deep learning AI model can identify what happens and when during embryonic development, from video.
Published today (Wednesday 29 May) in the Journal of Experimental Biology, the study highlights how the model, known as Dev-ResNet, can identify the occurrence of key functional developmental events in pond snails, including heart function, crawling, hatching and even death.
A key innovation in this study is the use of a 3D model that uses changes occurring between frames of the video, and enables the AI to learn from these features, as opposed to the more traditional use of still images.
The ...
Primates, including humans, have larger brains than most other mammals, but why? Scientists searching for the answer have long followed a trail pointing to diet—specifically fruit—as the reason for why primates evolved larger brains. A team from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior and the Smithsonian Institute of Tropical Research tested this idea for the first time—finding that the fruit-diet theory might be out of juice. The researchers used drone imaging, GPS tracking, and fine-scale behavioral analyses to test how four species of fruit-eating mammals solved the same natural foraging puzzle in a Panamanian rainforest. They ...
A new paper published in The Quarterly Review of Biology examines the question of what Darwinism is and how its nonscientific uses relate to the scientific theory of evolution.
Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species in 1859 as a work in biology. However, in the past century and a half, Darwin’s ideas have impacted a broad range of domains and stimulated scientists and scholars to advance "evolutionary approaches" in domains as diverse as economics, engineering, psychology, and history. The ideas have been used (and abused) to undermine religiously inspired ideas about the origin of humans and their status concerning other species, ...
AUSTIN, Texas — Wifi-enabled washing machines. Voice-controlled microwaves. App-enabled TVs, vacuum cleaners, and even window blinds you can control from the comfort of your couch.
Many of the technological features now included in everyday products are useful and accessible. But research has shown that having too many can overwhelm potential buyers, making them less likely to make a purchase.
In new research, Wayne Hoyer, marketing professor and James L. Bayless/William S. Farrish Fund Chair for Free Enterprise at Texas McCombs, digs into the phenomenon of “feature creep” and its impact on consumer sentiment. ...
A new study by researchers from Arizona State University and their colleagues highlights a dietary strategy for significant health improvement and weight management.
Participants following an intermittent fasting and protein-pacing regimen, which involves evenly spaced protein intake throughout the day, saw better gut health, weight loss and metabolic responses. These benefits were notably greater than those seen with simple calorie restriction.
The findings, reported today in the journal Nature ...
AMES, Iowa – A widely found gene in plants has been newly identified as a key transporter of a hormone that influences the size of corn. The discovery offers plant breeders a new tool to develop desirable dwarf varieties that could enhance the crop’s resilience and profitability.
A team of scientists led by Iowa State University spent years working to pinpoint the functions of the gene ZmPILS6. Now, they have been able to characterize it as an important driver of plant size and architecture, a carrier for an auxin hormone that helps govern growth in roots below ground and shoots, or stalks, above ground. Their findings were published in the Proceedings ...
Many primary care clinicians directly receive messages from patients via electronic health records’ portal inboxes. The COVID-19 pandemic saw a rapid uptick in this trend. Data suggests that this additional work is linked to clinician burnout. Penn Family Care, a primary care group at Penn Medicine, instead routed incoming messages to certified medical assistants who had been taught how to distribute each message to the most appropriate physician. There was a 40% decrease in the number of messages going directly to primary care physicians, and both practice and clinician efficiency showed improvement after adopting this team-based care model.
Utilizing Medical Assistants ...
Background and Goal: Relational continuity, the ongoing relationship between a patient and a family physician, is linked to better patient care, fewer unnecessary procedures, hospitalizations, emergency department visits, and lower costs, along with higher patient satisfaction. With the rise of part-time practices, patients often see multiple family physicians within the same clinic. This study aimed to explore how continuity in a primary care clinic—separate from individual physician continuity—affects patient ...
Background: Currently, people of Latiné/e/x/o/a, Hispanic, and/or Spanish (LHS) origin make up 19.1% of the population of the U.S. There is great variation in the personal experiences and family backgrounds of LHS individuals, including differences in country of origin, time in the U.S., colonization histories and immigration experiences.
Key Argument: This essay considers the importance of recognizing the heterogeneity of lived experiences among LHS populations in the U.S. in a health care context.
Why ...